abdomen
advertisement
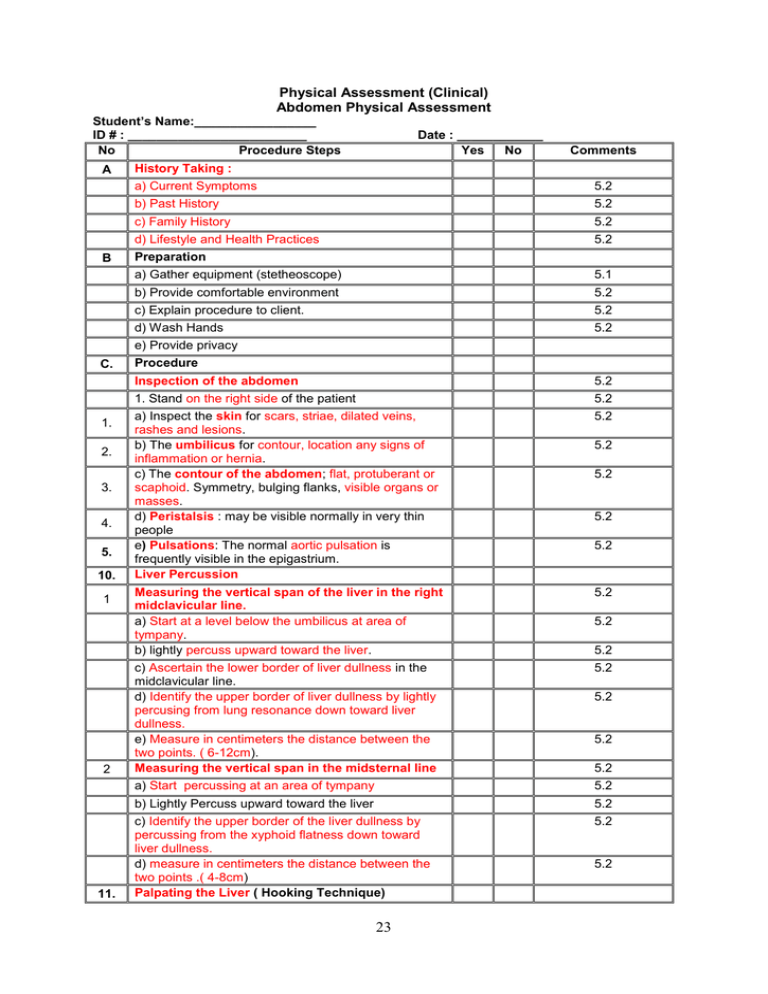
Physical Assessment (Clinical) Abdomen Physical Assessment Student’s Name:_________________ ID # : _________________________ No Procedure Steps A B C. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 10. 1 2 11. Date : ____________ Yes No Comments History Taking : a) Current Symptoms 5.2 b) Past History 5.2 c) Family History 5.2 d) Lifestyle and Health Practices Preparation 5.2 a) Gather equipment (stetheoscope) 5.1 b) Provide comfortable environment 5.2 c) Explain procedure to client. 5.2 d) Wash Hands 5.2 e) Provide privacy Procedure Inspection of the abdomen 5.2 1. Stand on the right side of the patient a) Inspect the skin for scars, striae, dilated veins, rashes and lesions. b) The umbilicus for contour, location any signs of inflammation or hernia. c) The contour of the abdomen; flat, protuberant or scaphoid. Symmetry, bulging flanks, visible organs or masses. d) Peristalsis : may be visible normally in very thin people e) Pulsations: The normal aortic pulsation is frequently visible in the epigastrium. Liver Percussion 5.2 Measuring the vertical span of the liver in the right midclavicular line. a) Start at a level below the umbilicus at area of tympany. b) lightly percuss upward toward the liver. 5.2 c) Ascertain the lower border of liver dullness in the midclavicular line. d) Identify the upper border of liver dullness by lightly percusing from lung resonance down toward liver dullness. e) Measure in centimeters the distance between the two points. ( 6-12cm). Measuring the vertical span in the midsternal line 5.2 a) Start percussing at an area of tympany 5.2 b) Lightly Percuss upward toward the liver 5.2 c) Identify the upper border of the liver dullness by percussing from the xyphoid flatness down toward liver dullness. d) measure in centimeters the distance between the two points .( 4-8cm) Palpating the Liver ( Hooking Technique) 5.2 23 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 a) Stand to the right of the patient’s chest. 5.2 b) Place both hands side by side on the right abdomen below the border of the liver dullness. c) Press in with fingers and up toward the costal margin. d) Ask the patient to take a deep breath. To assess possible acute cholecystitis ( Murphy’s Sign ) a) Hook the left thumb or the fingers of the right hand under the costal margin at the point where the lateral border of the rectus muscle intersects with the costal margin. b) Ask the patient to take a deep breath 5.2 5.2 12. c) Watch the patient’s breathing and note the degree of tenderness. Assessing Kidney Tenderness 5.2 13. a) Palpate by the fingertips in each costovertebral angel. b) If no tenderness in (a), place the ball of one hand in the costovertebral angle and strike it with the ulnar surface of the fist. Ascites 13.1 Mapping for ascites 12. 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 a) With the patient supine 5.2 b) Percuss outward in several directions from the central area of tympany c) map the border between tympany and dullness Test for shifting dullness (after mapping) 5.2 a) ask the patient to turn onto one side 5.2 5.2 13.3 b) Percuss and mark the borders of tympany and dullness again Test for a fluid wave 5.2 14. a) Ask the patient or an assistant to press the edges of both hands firmly down the midline of the abdomen b) Tap sharply on the flank with the fingertips, feel on the opposite flank for an impulse transmitted through the fluid. Assess for Possible Appendicitis Rebound tenderness 5.2 a) Press deeply and evenly in the right lower quadrant 5.2 b) Quickly withdraw the fingers 5.2 c) Ask the patient when pain is felt more. Rovsing’s sign and referred rebound tenderness 5.2 a) Press deeply and evenly in the left lower quadrant 5.2 b) quickly withdraw the fingers Psoas Sign 5.2 13.2 14.1 14.2 14.3 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 5.2 a) Place hand just above the patient’s right knee 14.4 b) Ask the patient to raise that thigh against hand 5.2 c) Ask the patient to turn onto the left side 5.2 d) extend the patient’s right leg at the hip Obturator Sign 5.2 24 5.2 14.5 a) Flex the patient’s right thigh at the hip, with the knee bent. b) Rotate the leg internally at the hip by stabilizing the thigh with one hand and grasping the ankle with the other and swing the lower leg laterally. Cutaneous hyperesthesia 5.2 D At a series of points down the abdominal wall, gently pick up a fold of skin between thumb and index finger, without pinching it. Procedure Termination 5.2 16. a) Put client in comfortable position according to health status b) Provide patient with reassurance 17. c) Return back equipments 5.2 18. d) Wash hands 5.2 15. 25 5.2 5.2







