Experiment meter bridge
advertisement

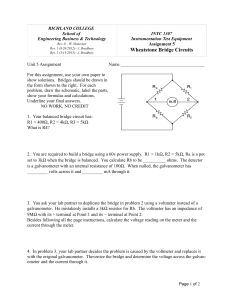
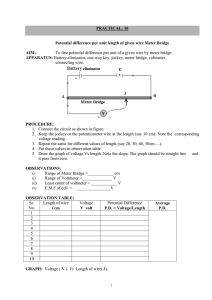
Student name: General Physics (Phy 103) Student ID: Date: Experiment ( ) Meter Bridge Aim : To verify series and parallel combination of resistances. To determine the specific resistance of the wire. Apparatus : Meter bridge, connecting wires, cell, plug key, resistance box, high resistance, galvanometer and a jockey. Theory: A meter bridge is the practical application of Wheatstone bridge arrangement as shown in figure below. The four resistances are connected to each other as shown and if the bridge is in balanced state, i.e., there is no deflection in the galvanometer (G), We can use this relation to find the unknown resistance. RX R A RS RB The unknown resistance Rx can be found by Meter bridge which uses the principle of Wheatstone bridge. The unknown resistance Rx of the given wire is obtained by relation : Rx B A C Procedure : 1. Take out some suitable resistance R form the resistance box (R. B.). 2. Touch the jockey at point A; see that there is a deflection in the galvanometer on one side, then touch the jockey on the point C of the wire, the deflection in the galvanometer should be on the other side. If it is so, your connections are correct.' 3. Now find the position of null point where deflection in galvanometer becomes zero. 4. Note length AB (L) BC will be (100 - L). 5. Repeat the above procedure for different values of R. The value of this resistance R taken out from R. B. should be such that the null point is in between 30 cm and 70 cm in the meter bridge wire. Note the point where the galvanometer shows 0 deflections, this is called the balance point. OBSERVATIONS: Unknown resistance Rx (Ω) Reading of resistance Box R (Ω) Balancing length L (cm) 50 100 200 The unknown resistance Rx = ……………………… Ω