Power point version
advertisement

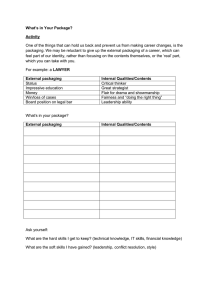
The Value of Information Technology Anheuser-Busch Companies, Inc. September 29, 2003 AGENDA • Anheuser-Busch Overview • Why is there I.T.? • Value of I.T. • Examples • Questions QUALITY A COMPANY OF FIRSTS Pasteurization Refrigerated Railcars Extensive Bottling INDUSTRY LEADER SINCE 1957 Nearly 5 out of every 10 beers sold today ANHEUSER-BUSCH • 100+ million barrels in 2001 • 12 domestic breweries • 2 international breweries More Than 30 Brands +3 Billion Gallon Capacity Corporate Overview Anheuser-Busch, Inc. Metal Container Corporation Anheuser-Busch International, Inc. Busch Agricultural Resources, Inc. St. Louis Refrigerator Anheuser-Busch Car Company Recycling Corporation Corporate Overview (continued) Precision Printing Longhorn Glass Busch Media Group, Inc. Busch Entertainment Corporation Manufacturer’s Railway Company Busch Properties, Inc. Invested More Than $375 Million I.T. is Part of the Business • A-B Companies is a $16B Business • A-B spends approximately $200MM on Information Technology • There are approximately 1,300 employees and contractors working on Information Technology Management Systems Group Mission for MSG A-B Business Growth • Through the systems we build, run, and maintain for our customers • Through the business strategies we support Cost Reduction • Business initiatives enabled by Information Technology • Internal MSG cost reduction initiatives Standardization and Service Excellence • In maintenance and replacement of infrastructure hardware and software • Service delivery to both internal and external customers MSG Message to Our Employees, Customers, and Vendors • We are not an Information Technology company. • There will be no Information Technology driven initiatives. Overview of MSG Design, Develop, & Install Systems Development • • • • Supply Chain Sales and Marketing Finance & HR Systems Purchasing Systems Operate & Maintain Applications Support/Maintenance Data Center • Centralized Information Processing Network • Communication • E-mail • Internet Desktop • Personal Computers • Help Desks MSG designs, develops, installs, and runs the systems that are key to A-B Business Operations. Evolution of Information Technology Automation of Work Management of Information IT Business IT Business IT Transformation of Business Business Investments are increasing and... ... complexity is increasing! Why is there IT? • Support the business – Increase sales – Decrease cost – Defensive posture • Strategic in nature for most organizations – CRM, PLM, Order Mgmt, Account Mgmt, Internet, Accounting – IT is all along the value chain Example • We work for a company that sells computer products to the general public using the Internet • The sales department has requested to add a set of “My” features to the website (I.e. my.yahoo) • As the IT department what are the next steps on this project? IT is the Business • IT doesn’t exist without the business • IT exists only to enhance the business • IT Supports the business – Increase sales – Decrease cost – Defensive posture There will be no Information Technology driven initiatives. Increase Sales • • • • • • • Reduce order fulfillment cycle time Increase order quality (reduce stockouts) Determine and set pricing Rationalize discount pricing E-commerce to acquire new markets Improve product quality Improve customer service Decrease Cost • • • • • • • Leverage buy capability Warehouse fork truck continuous moves Automated guided vehicles Transportation backhaul opportunities On-line bid purchase or sale Supplier collaboration efforts Increase product quality (reduce defects) Defensive Posture • • • • Follow the leader Y2K Replacement systems (old, lost support) New e-commerce companies – Order consolidators – Buy consolidators • Infrastructure Other • Product awareness • Environmental • Community awareness Link to the Business IT Projects Business Objectives Business Strategy Example 1 Supply Chain Initiative Business Driven Project Supply Chain Vision Business Strategy: Reduce the total supply chain costs while improving product freshness and customer service. Targeted Business Objectives: • Support purchasing in reducing packaging material price by improving supplier costs • Support operations in reducing brewery conversion costs • Reduce cost of transportation of full goods, trade returns, and packaging materials • Avoid capital spending through asset utilization 2:52:56 AM View, Header and and Footer... to • 7/1/2016 Improve product Click freshness customer service 27 add file name here Supply Chain Scope The integration of all activities that are part of the process of going from raw materials to delivering finished products Its success requires a balanced scorecard that measures the success of the whole, versus the parts Planning, Scheduling & Execution Processes Suppliers Brewing Packaging Wrhse/Shipping Wholesalers Management / Infrastructure Requirements Retail Supply Chain Initiative Stability Lowers Costs The Leadership Team believes increasing stability will lower Supply Chains costs. We will measure key Performance Indicators (KPI’s) of stability. We will track Total Supply Chain cost per barrel. 29 The Supply Chain Program Four Major Initiatives for 2001 / 2002 Strategic Network Models • Create a facility location model to analyze optimal locations for production and distribution facilities, responding to shifts in demand and minimizing all relevant costs • Create a weekly planning model that fully integrates brewing and packaging decisions and minimizes all relevant costs Transportation Advantage • Increase inbound packaging material backhaul • Integrate Transportation Advantage objectives into shipment and production scheduling Shipment & Production Scheduling • New material requirements planning for packaging and support materials • Postpone order content decision by utilizing the most up-to-date information • Reduce the freight costs of trade return movements (cooperage and pallets) • Rollout web based schedule exchange to all plants and selected suppliers BudExchange.com Supply Chain Scorecard • Provide a tool to ensure all Supply Chain costs are measured (current prototype is bottle only) Summary • This project will deliver improvements in: – Management and purchasing of direct materials and supplies – Order Filling decision through automation – Facility location decisions – Trade return management – Inbound packaging material backhaul DCFROI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17.4% Total Spending . . . . . . . . . . . . . $ 20 MM Average Yearly Savings . . . . . $ 6 MM NPV at 9% . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .$ 2.4 MM Years to attain Hurdle Rate . . . . . . . . . .4.5 7/1/2016 2:52:56 AM Click View, Header and Footer... to add file name here 31 Example 2 IT Process Improvement Project Manufacturing Process Materials Finished Goods Manufacturing Standard Operating Procedures Machinery Skilled Labor Improve Measure Our plants are very efficient, due to stringent operating procedures, efficient equipment, and skilled labor Software Manufacturing Business Requirements Software Development Systems Methodology Tools Skilled Labor Improve Measure With a stringent approach to Software Development, cost and time to deliver can be significantly reduced while improving quality Standardization Benefits Industry estimates 5 – 40%* savings of development and operational costs at maturity (4-5 years) Reduced Cost Standard Process, Tools and Metrics Productivity Reduced Cycle Time Reuse Increased Quality * - compilation of sources – META, Gartner, AG Edwards, SBC, Transcentric, VISA Business Benefits Increased Quality Reduced Cycle Time Decreased Cost More Benefits Realized Sooner + = Higher ROI IT standardization will result in compounded benefits for subsequent IT projects with an ROI ABPG IT Objectives • Implement standard process, tools, training and the supporting measurements to enable on-going productivity improvement: – Implement metrics collection around productivity, quality, cost, and continue customer satisfaction – Increase IT productivity 20% by 2007 – Decrease IT defects 20% by 2007 – Reduce IT cycle time 20% by 2007 – Establish a foundation for continuous IT will contribute on-going cost savings to our Business Units improvement within the IT department PI and Reuse Savings ($M) Deferred Dev. Expense Dev. Hardware Total Year 0 2003 Year 1 Year 2 2004 2005 Year 3 2006 $ 150 $ 150 $ 240 $ 270 $ 60 $ 570 $ 440 $ 440 $ 580 $ 600 $ 100 $ 100 $ 1,120 $ 1,114 $ 360 $ 420 $ 80 $ 860 Year 4 2007 Annual recurring savings of $1,140 M beginning in year 4 Investment ($M) Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Imp. Labor Capital Support Total 2003 $ 800 $ 600 2004 $200 - 2005 - 2006 - 2007 - $ 200 $ 1,400 $ 400 $ 200 $ 200 $ 200 $ 200 $ 200 $ 200 Total Cost Total Incremental Savings ROI (3.2 years) $ 1,400M $ 1,140M 27.6% Project Scope Governance Rational Rose Requirements Microsoft .NET Design Develop Test Support Methodology / Process Standards / Guidelines Training / Mentoring Performance Measurement Use MSG’s .NET standardization effort as the base, purchase what we can, and build the rest How Will We Save - Measure $7.00 Productivity Cost per Defect $1,400 $6.00 $1,200 Cost/FP $5.00 $1,000 $4.00 $800 $3.00 $600 $2.00 $400 $1.00 $200 $0.00 $- Jan Feb Mar Apr May June July Aug S ept Oct Nov Dec 16% 14% 12% 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0% Reuse Efficiency Jan Feb Mar Apr May June July Aug S ept Oct Nov Dec Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 02 02 03 03 03 03 04 04 04 04 IT will apply metrics and measurement in the same way our plants do today Project Summary • This project will deliver a foundation for continuous improvement and establish on-going cost and quality improvements: – Quicker development life-cycle – Consistency in practice – Reuse – Less rework DCFROI Total Spending Average Yearly Savings NPV at 8% Years to attain Hurdle Rate 27.6 $ 1,400 M $ 1,140 M $ 780 M 3.2 Summary • IT is part of the business, it supports and enhances the business • IT doesn’t exist without the business • Learn the business of your company Questions?