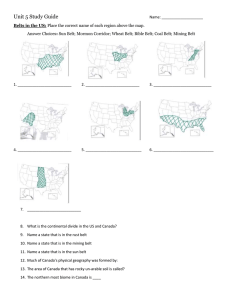
World Regions
advertisement

Regional Geography
and the United
States and Canada
WG.3b,4
Regions are used to simplify
the world for study and
understanding
Regional Landscapes
Regional landscapes reflect
the cultural characteristics of
their inhabitants. This can be
seen in the architectural
structures used in a region,
and in the statues and
monuments of local, national,
or global significance.
Architectural Structures
Mosques-Islam
Churches-Christianity
Synagogues (Judaism)
Temples (Buddhism)
Pagodas (Buddhism)
Dwellings (homes)
Tiles roofs in the Mediterranean
Chalets in Switzerland
Thatched Roofs
Tents and Yurts
Castles in Europe
Statutes, and Monuments
Many have
local,
national or
global
significance
Taj Mahal
Dome of the Rock and
Pyramids
Eiffel Tower and the White
House
Examples of other well know
monuments
Kaaba (Mecca), Western Wall
(Jerusalem), Church of the Holy
Sepulcher (Jerusalem),
Washington Monument,
Lincoln Memorial, Kremlin
(Moscow), Statute of Liberty,
Virginia State Capital building
Kaaba
Western Wall (Wailing Wall)
Examples of Physical and
Cultural Regions
Physical regions
Sahara, Taiga, Rainforest, Great
Plains, Low Countries
Cultural regions
Language (Latin America,
Francophone world)
Ethnic regions (Chinatown,
Kurdistan)
Religious regions (Islam, Buddhism)
Economic regions (Wheat Belt,
European Union)
Political regions (NATO, African
Union {AU})
Changes in perception regions
(Middle East, Sun Belt, Rust Belt)
United States and Canada
physical characteristics
Both nations have abundant
natural resources.
The Continental Divide sits at the
top of the Rocky Mountains and
acts as a divider for North America
Many important rivers (Mississippi,
St. Lawrence, Colorado,
Columbia, and Rio Grande)
US and Canada also have
other important water features.
(Gulf of Mexico, Great Lakes,
Arctic Ocean, Pacific Ocean,
Atlantic Ocean, and the
Hudson Bay)
Important landforms—Aleutian
Islands, Hawaiian archipelago,
Appalachian Mountains, Pacific
Coastal Ranges, Basin and
Range region, Rocky
Mountains, Great Plains,
Interior Lowlands, Atlantic and
Gulf coastal plains, Canadian
Shield, Grand Canyon
Both have varied climate
regions—they range from
the tundra in Alaska to a
tropical wet climate in
Hawaii
US and Canada economic
characteristics
Both countries are major
exporters of technology,
consumer goods, information
systems, and foodstuffs
Both have highly developed
infrastructures
Both have highly diversified
economies
Both have a rich supply of
mineral, energy, and forest
resources
Both are members of the North
American Free Trade
Agreement (NAFTA)
Both are home to many
multinational corporations
US is the center of the world
financial markets (New York
Stock Exchange)
Both have sustained economic
growth
Both have a widening gap
between the rich and the poor
The US exports our culture
via the global marketplace.
Examples—McDonald’s,
Coca-Cola, music, blue
jeans
Cultural characteristics of the
US and Canada
Both countries were originally
colonized by countries from
Europe
Both have multicultural
societies
Both have increasingly diverse
populations
Both have high literacy rates
Both have a high standard of
living
Both are highly urbanized
Canada struggles to maintain a
national identity
Both have highly mobile
populations
The world’s largest unfortified
border is between the US and
Canada
Both have a democratic form of
government
Both are members of NATO
Both have arts that reflect the
cultural heritage of their
multicultural societies
Important cities
(centers of culture and
trade)
Washington DC
Chicago
New York City
Los Angeles
Houston
Toronto
Montreal
Ottawa
Quebec
Vancouver,
British Columbia
Examples of the cultural
landscape
US Capital
building
Golden Gate
Bridge
Independence
Hall
St. Louis
Gateway Arch
Wheat fields
Skyscrapers
Shopping malls
Bilingual signs
Influence of
automobiles (ex.
Gas stations,
motels, interstate
highways, drive up
services)
Human interaction affects the
environment
Deforestation—examples are the
Amazon Basin, Nepal, and
Malaysia
Acid Rain—example is the Black
Forest in Europe
Decreased soil fertility—Example
is the Aswan High Dam in Egypt
Criteria for determining a
countries relative
importance
Gross Domestic Product
(GDP)
Land size
Population size
Resources
How do physical features
impact humans
Example—Water
Rio Grande River is a boundary
Ob River flows northward into
the Arctic Ocean
Zambezi River provides water
power
Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers
are flood hazards
Example—Mountains
Rocky Mountains create a rain
shadow on the leeward slopes
Himalayas block moisture and
create steppes and deserts in
Central Asia