CHEMICAL BONDING
advertisement

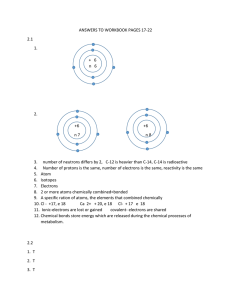
CHEMICAL BONDING Atoms are very active because of their high energy. They have tendency to be more stable and carry less energy through combination together to give molecules. Molecules are more stable and have less energy than atoms. Atoms join together through chemical bonding. Non-metal------------- Non-metal Chemical bonding may be formed between atoms of two nonmetals similar or different by sharing electrons to complete the outermost shell of each one to the electronic configuration of the nearest inert gas thus can acquire a stable, Nobel-gas structure (Lewis suggestion). Metal-------Non-metal Chemical bonding may also be formed between a metal and non-metal by transferring of one or more electron from the outermost shell of the metal to the outermost shell of the nonmetal to complete the outermost shell of each one to the electronic configuration of the nearest inert gas . Metal-------Metal Chemical bonding may also be formed between two metals via accumulation and rearrangement of these metals in a shape of metallic crystal. TYPES OF CHEMICAL BONDS: The covalent bond: It is formed between atoms of two non-metals similar or different by sharing electrons. Single covalent bond: A bond formed by sharing of one pair of electrons between two non-metallic atoms where each atom shares one electron . Double covalent bond: A bond formed by sharing of two pairs of electrons between two non-metallic atoms where each atom shares two electrons. Triple covalent bond: A bond formed by sharing of three pairs of electrons between two non-metallic atoms where each atom shares three electrons. The ionic bond: It is formed between a metal and non-metal by transferring of one electron or more from the outermost shell of the metal to the outermost shell of the non-metal. The outermost shell of an atom of a metal contains less than 4 electrons (1 ,2 or 3). Ions of metals are always positive because the metals tend to lose the electrons of the outermost shell, so the number of protons is greater than electrons. The outermost shell of non-metallic atom contains more than 4 electrons (5,6 or 7). Ions of non-metals are always negative because non-metals tend to gain electrons, so electron number is greater than proton number. Formation of ionic bond: An electrostatic force of attraction is developed between the positive ion and negative ion forming an ionic compound. Formation of NaCl: Atom of metal loses electrons and changes into positive ion. Sodium atom (atomic number = 11): Atoms of non-metal gains the electrons lost by the metal and changes into negative ion. Chlorine atom (atomic number = 17): Note: ionic bonds are strong while covalent bonds are weak. Polar and non-polar covalent bond (Electronegativity): Non-polar covalent bond has formed between two identical non-metals such as H-H, Br-Br,….. So there is no differences in the electronegativity value between them. Thus, the covalent bond in this case is considered non-polar covalent bond. Polar covalent bond has formed between atoms of two different non-metals such as H-Cl So the electronegativity between the two atoms is different where chlorine atom is more electronegative than hydrogen atom. Therefore, the pair of electrons will attract to the chlorine atom more than the hydrogen atom. So, chlorine atom will carries partially negative charge (-δ) while hydrogen atom will carries partially positive charge (+δ), H+δ – Cl-δ Thus, the covalent bond in this case is considered polar covalent bond. In CCl4 : the bond dipoles cancel and the molecule is non-polar. In CCl3 or in the bent H2O molecule: there is a net dipole, and the molecule is polar. Coordinate covalent bond: The coordinate covalent bond formed between two atoms, the donor atom and acceptor atom. The donor atom has non-bonding electrons and can sharing the covalent bond by its non-bonding electrons while the acceptor atom accepts these non-bonding electrons in its empty orbital. Coordinate covalent bond examples: The nitrogen atom in ammonia has one pair of non-bonding electrons and can make coordinate covalent bond. The oxygen atom in water has two pair of non-bonding electrons and can make coordinate covalent bond. Metallic bond: Atoms of the same metal are tend to be closed and rearranged in a crystal shape. Hydrogen bond: Hydrogen atom join with an electronegative atom through covalent bond, where the electronegative atom attracts the pair of sharing electrons and carries partially negative charge while hydrogen atom carries a partially positive charge. This bond formed between the molecules of water and ammonia to increase the cohesion force between molecules. Van der-Waals force: These are weak electrostatic forces appears due to the occurrence of a positive charge and negative charge at the terminals of the molecule causing attraction between these molecules with others of the same matter.