Different Kinds of Cells Notes
advertisement

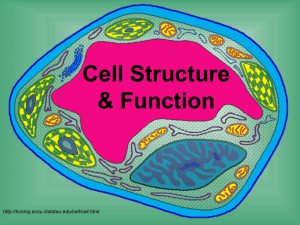
Welcome to the Wonderful World of the Cell! The way the world works: atoms-cells-tissues-organs-organ systems-organisms-populations-ecosystem Cell Theory: 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Variety makes the world go round… Red blood cell: 8 m Nerve cell: 1m Largest single cell is an egg: average diameter of 8cm Most cells: 2-200 m 3 Types of Cells: viruses, prokaryotic, eukaryotic 1. Virus: a. Examples: small pox, HIV, rabies b. Virus-from the Greek word meaning “poison” c. Constructed of compounds associated with living organisms BUT ARE NOT living organisms i. WHY??? 1. NO nucleus 2. NO cytoplasm 3. NO organelles 4. NO cell membrane d. not able to replicate themselves-they need a host to use their enzymes and organelles VIRAL STRUCTURE o ALL viruses have: Nucleic acid (DNA/RNA-can be helical, loop, varied shapes) Protein coat surrounding the nucleic acid (capsid) o Some viruses have an envelope outside the capsid taken from the host’s cell membrane during replication o On the surface of the envelope are glycoproteins (projections that the virus uses to attach to the host cell) 2. Prokaryotic: a. Examples: bacteria b. Pro-before c. Karyo-kernel (nucleus) d. ALL PROKARYOTES HAVE i. Cell wall ii. Cell membrane iii. Cytoplasm iv. Ribosomes (to make proteins) v. DNA/RNA e. NONE HAVE i. Membrane-bound organelles (mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, etc.) ii. Membrane-bound nucleus 3. Eukaryotic: a. Examples: plants, animals, fungi (amoeba, kelp), protists (mushrooms, mildew, mold) b. Eu-true c. Karyo-kernel (nucleus) d. ALL EUKARYOTES HAVE i. Membrane-bound organelles ii. Membrane-bound nucleus