Programmed Cell Death A genetically controlled cell suicide pathway
advertisement

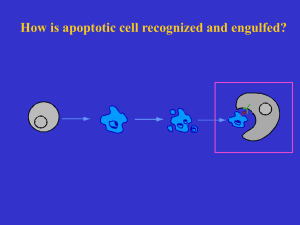
Programmed Cell Death A genetically controlled cell suicide pathway video The Morphology of Apoptosis Cytoplasm shrinks Chromosomes condense and fragment Nuclear membrane breaks down Apoptotic body formation Engulfment of the cell corpse Difference Between Apoptosis and Necrosis • Necrosis (pathological cell death): dying cells swell and lyse; toxic contents leak out and result in inflammatory response. • Apoptosis (physiological or programmed cell death): dying cells shrink, are engulfed and degraded by other cells, leave no trace, and don’t result in harmful outcomes Functions of apoptosis Sculpt body structures, e.g. hand digit Serve some function but no longer needed e.g. tadpole tail of frog. Needed in one sex but not another e.g. Mullerian duct important for female is eliminated in males by apoptosis. Produced in excess, e.g. extra neurons are removed by apoptosis during neurogenesis. Serve in immune system as a defense mechanism to get rid of harmful or damaged cells. The Nematode C. elegans As a Model Organism in the Study of PCD • A great genetic system • Completely defined cell lineage • Study of cell death at a single cell resolution in living animals The C. elegans Cell Lineage z yg ote B A S M E C D P 4 Cell Death Can Be Studied at a Single Cell Resolution P11 P11aap X X Adapted from Sulston and Horvitz, Dev. Bology 56, 110-150, 1977 The First Cell Death Mutants Identified in C. elegans In 1976, J. Sulston first described programmed cell death in nematodes and reported the first cell death mutant (nuc-1), in which DNA in the death cells fail to be degraded. Wild-type nuc-1 In 1980, E. Hedgecock isolated two cell death mutants (ced-1 and ced-2) which are pivotal for identification of the other cell death genes. Wild-type ced-1 What went wrong with the ced-1 mutant? What could go wrong with the ced-1 mutant? a) Apoptotic cells fail to die b) Normal cells die ectopically c) Apoptotic cells fail to be engulfed d) Normal cells are ectopically engulfed e) Cells undergo necrosis Wild-type A)a and b B) b and c C)c and d D)d and e E) e and a ced-1 Phenotypic analysis of ced-1 and ced-2 mutants 1) More cell deaths? 2) Dying cells cannot be removed or engulfed How to distinguish these two possibilities? Follow the cell lineage in the mutant animals What is next? Suppressor screens: ced-3 and ced-4 What are the functions of ced-3 and ced-4? H. Ellis and R.H. Horvitz What could be the functions of ced-3 and ced-4? 1) ced-3 and ced-4 promote cell corpse engulfment 2) Inhibitors of cell corpse engulfment 3) ced-3 and ced-4 could promote cell deaths 4) ced-3 and ced-4 could inhibit cell death 5) ced-3 and ced-4 could promote necrosis A) B) C) D) E) 1 and 2 2 and 3 3 and 4 4 and 5 5 and 1 What are the functions of ced-3 and ced-4? 1) ced-3 and ced-4 promote cell corpse engulfment? Then the mutations must be increase-of-function 2) Inhibitors of cell corpse engulfment? Then the mutations should be loss-of-function 3) ced-3 and ced-4 could promote cell deaths Then the mutations should be loss-of-function How to distinguish 2) and 3)? Lineage analysis suggest: Many cells that normally die now survive ced-3 and ced-4 are involved in cell killing How do ced-3 and ced-4 kill the cells? 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Cells die by murder? Cells die by suicide? cells die by aging? Cells die because of injuries? Cells die by sickness? Cells Die by Suicide Rather Than Murder • Yuan and Horvitz demonstrated by mosaic analysis that ced-3 and ced-4 function in the dying cells to kill. • ced-3 encodes a protein with homology with IL-1b converting enzyme (ICE), a cysteine protease. • ced-4 encodes a protein similar to apoptotic protease-activating factor (Apaf-1). THE GENETIC PATHWAY FOR PROGRAMMED CELL DEATH IN C. elegans All dying cells Specific cells engulfing cell healthy cell committed to die dead cell healthy cell DECISION TO DIE NSM sister cells: ces-2 CEM cells ces-1 egl-1 EXECUTION OF DEATH ced-9 ced-3 ced-4 ced-11 ced-8 ceh-30 DEGRADATION ENGULFMENT ces-1: zinc-finger transcription factor ces-2: bZip transcription factor egl-1: Bid-like protein ced-9: Bcl-2-like protein ced-1 ced-6 ced-7 ced-2 psr-1 ced-5 ced-10 ced-12 nuc-1 cps-6 wah-1 ced-2: Crk II ced-5: DOCK 180 ced-6: PTB protein ced-7: ABC transporter ced-10: Rac 1 ced-3: ICE-like protease ced-4: Apaf-1-like protein