16 Investment and Personal Financial Planning Chapter
advertisement

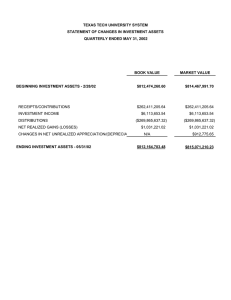
Chapter 16 Investment and Personal Financial Planning Business versus Investment Activity Business activity Time and talent on regular basis Profit partially attributable to personal involvement Income is considered earned income Losses are fully deductible “above the line” Hobby losses only deductible to extent of hobby income – personal enjoyment vs. plausible profit motive Investment activity Investment of capital rather than time and talent Income is considered unearned income Losses are generally deductible only to extent of gains from sale of other investment assets, plus $3,000 Investments in Financial Assets Common investments in financial securities: Common and Preferred stock (equity securities) Savings accounts, CDs, bonds (debt securities) How do you distinguish between debt vs. equity securities? Return on / Income from investment includes Interest (ordinary income) Dividends Gains (Losses) on sale of assets. Gains/Losses on Securities Realization requires a sale or exchange Gain/loss = Proceeds - adjusted basis Character is capital—time period matters < 1 year holding period → short term capital gain or loss > 1 year holding period → long-term capital gain or loss Preferential rates apply to net long-term capital gains Securities/investment assets: 0-20% Unrecaptured Section 1250 Recapture: 25% Collectibles: 28% Net short-term capital gains taxed as ordinary income Preferential rates do not apply