Lecture - Population Geography
advertisement

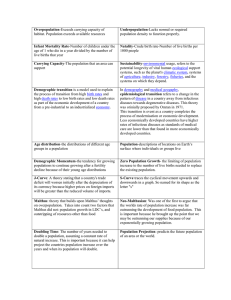
Population Geography Distribution of World Population Overpopulation (Malthus and NeoMalthusians Population Statistics Population Pyramids Demographic Transition Theory Population Control World and Country Population Totals Distribution and Structure: 3/4 of people live on 5% of earth's surface! Total: 6 billion on planet as of Oct. 12, 1999 Current Population Counter Five most populous regions and countries REGION POPULATION COUNTRY East Asia 1.5 billion South Asia1.2 billion Europe 750 million SE Asia 500 million East N. Am.120 million China India U.S. Indonesia Brazil POPULATION 1.254 billion 986 million 274 million 206 million 168 million Rates of Natural Increase Birth Control Programs One family/one child policies – Female infanticide – Social compensation fees Sterilization Loss of status Termination healthcare/food coupons Free birth control Increased literacy World Death Rates Infectious diseases – HIV/AIDS – SARS Degenerative diseases – Obesity – Tobacco use Epidemiology Epidemiological transition Doubling Times The doubling time is the number of years before a population will be twice as large as it is today. World = 50 U.S. = 34 MDC = 543 LDC = 40 Honduras = 22 Belize = 19 Denmark = 700 Russia = never? Fertility Rates 2.1 is generally regarded as a replacement rate (the rate at which a population neither grows nor shrinks) in the developed world. In less developed countries this rate should be higher (2.8?). Iran USA Italy 4.7 2.0 1.2 High infant mortality tends to result in higher fertility rates as families seek “insurance” for the loss of children. Infant Mortality Adults and Children Living with AIDS, 2004 U.S. Census Bureau Population Pyramid Animations CLICK HERE! Demographic Transition Model Demographic Transition Model Stage one – Crude birth/death rate high – Fragile population Stage two – Lower death rates – Infant mortality rate – Natural increase high Stage three – Indicative of richer developed countries – Higher standards of living/education Problems with the Demographic Transition Model • based on European experience, assumes all countries will progress to complete industrialization • many countries “stuck” in stage 2 or stage 3 • reflects logic of continuous economic growth, an impossibility Thomas Malthus (February, 1766 – December 23, 1834) • Malthus predicted population would outrun food supply, leading to a decrease in food per person. Population J-Curve Population Shift Population and Resource Consumption Population and the Environment I=PxAxT Impact = Population x Affluence x Technology Population influenced environmental problems: • Global Warming • Habitat Loss / Endangered Species • Resource Depletion • Food Shortages? Not globally, but regionally. Overpopulation? Malthusian theory – Pessimistic perspective – Thomas Malthus Preventive checks Positive checks Cornucopians – Optimistic perspectiv The End