Lab Exam 4 Study Guide
advertisement

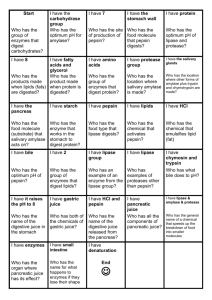
Physiology 31 Lab Exam #4 Study Recommendations Lab exam #4 will consist of questions to assess your understanding of information from Labs 37A & 37B (Respiratory Physiology), 41A & 41B (Urinary Physiology), and 39B (Digestion). The exam will be mainly fill-ins and short answer questions, with a few matching multiple choice questions. Be sure to refer to the lab manual explanations in each lab and the Review Sheets assigned for homework as you prepare for the exam. A review of the lecture notes that pertain to these exercises would be helpful. Also, be able to apply the information learned to real life situations. Labs 37A & 37B – Respiratory Physiology - Explain what is meant by tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, residual volume, vital capacity, total lung capacity, forced vital capacity, and forced expiratory volume, and know the normal values for each, as well as the formulas to calculate each. - What instrument is used to measure the above respiratory volumes? - What are bronchial sounds and vesicular breathing? At what regions of the chest can respiratory sounds be heard with a stethoscope? What are rales and wheezing, and what do they indicate? - Be able to calculate residual volume when given the vital capacity and age factor. - Calculate a predicted vital capacity when given the formula and a person’s height and age. Why is it useful to compare the predicted vital capacity with a person’s actual vital capacity? - Be able to read a spirogram and determine the TV, IRV, ERV, and VC. - Explain how the chemical reaction H2O + CO2 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3- in the blood is affected during hyperventilation and hypoventilation - What is a buffer? - What is the importance of the pleural membranes that surround the lungs? What is surfactant, and why is it necessary in the lungs? - What is the relationship between volume and pressure in lung inflation (inspiration) and deflation (expiration)? What muscles are involved in each? Labs 41A & 41B – Urinalysis & Renal Physiology - What are the parts of a nephron? What are the three main functions of the nephron, and in what part of the nephron does each occur? - What happens during glomerular filtration? What is the glomerular filtration rate, and what is a normal GFR value? What physiological factors maintain GFR homeostasis, despite changes in body conditions? - In what region of the nephron does the majority of reabsorption take place? What components of the plasma filtrate are normally reabsorbed? - What hormones are involved in urine formation? How do they affect urine formation? - What is secretion? In what part of the nephron does secretion occur? What substances are normally secreted? - What does the specific gravity of urine tell us about its solute concentration? - What is a normal pH for urine? - What are normal constituents of urine? What are abnormal components? Know what disorders are indicated by the abnormal components. Lab 39B – Chemical & Physical Processes of Digestion - Define enzyme and substrate. - What is amylase? What substrate does it digest? What is the optimal temperature and pH for amylase to function? What chemicals are used to test for amylase digestion products? What two organs produce amylase? - What is pepsin? What substrate does it digest? What is the optimal pH for pepsin to function? How was pepsin digestion determined in the experiment? In what organ is pepsin produced? - What is lipase? What substrate does it digest? What is the optimal pH for lipase to function? How was lipase digestion determined in the experiment? What is the main organ that produces lipase? - Is bile an enzyme? If not, what is it? What is bile’s digestive function? What organ produces bile? - What are peristalsis and segmentation? How does each affect the digestive process?