Chapter 3 Section 2 Notes
advertisement

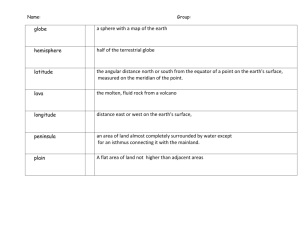
Chapter 3 Section 2 Notes Mapping Earth’s Surface - cartography – science of making maps - cartographer – scientists who make maps Data collected by field surveys and remote sensing are used to make maps - field survey – make measurements of the area o plot information on a map - remote sensing – the process of gathering and analyzing information about an object without physically being in touch with the object o satellite images o images from airplanes Map Projections - a flat map that represents a spherical surface Cylindrical Projection - a cylinder of paper is wrapped around a lighted globe - meridians appear as straight lines - outlines of continents, oceans and parallels are traced - parallels and meridians form a grid Azimuthal Projection - a sheet of paper is placed on a lighted globe so that only one point of the globe is being touched - little distortion occurs at the point of contact - unequal spacing between parallels causes a distortion in both direction and distance - great help to navigators in plotting routes used in air travel Conic Projections - placing a paper cone over a lighted globe so that the axis of the cone aligns with the axis of the earth - the cone touches the globe along one parallel of latitude - areas near the parallel are distorted least - polyconic projections – a series of conic projections used to increase the accuracy of mapping a number of neighboring areas Reading a Map Directions on a Map - maps are mostly drawn with the top of the map facing north - parallels run from side to side - meridians run from top to bottom - compass rose – a symbol that indicates the cardinal directions(north, south, east, west) Symbols - symbols are used for features on a map such as cities, roads and rivers - legend – a list of map symbols and their meanings Map Scales - a map must be drawn to scale to be accurate - scale – the relationship between the distance shown on a map and the actual distance - graphic scale – printed line that has markings on it that are similar to those on a ruler - fractional scale – a scale that uses a ratio Isograms - a line on a map that represents a constant or equal value of a given quantity - used to plot many types of data (i.e., atmospheric pressure on a map) - commonly used to show areas that similar measurements of precipitation, temperature, gravity, magnetism, density, elevation or chemical composition