Chapter 2 Section 2 Notes
advertisement

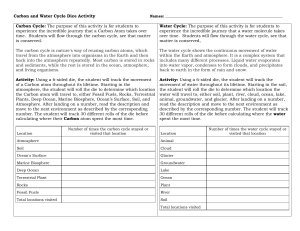
Section 2 Energy in the Earth System System - an organized group of related objects or components that interact to create a whole - vary in size (subatomic to universe) - all have boundaries - Earth system is an interaction between matter and energy o Matter – anything that has mass and volume o Energy – the ability to do work Heat Light Vibrations Electromagnetic waves Closed system – energy is exchanged, not matter Open system – both energy and matter are exchanged Earth system is almost closed because matter exchange is very limited Earth’s Four Spheres Atmosphere - blanket of gases that surrounds Earth’s surface - provides the air that you breath - shields Earth from sun’s harmful radiation - 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 1% a mixture of gases Hydrosphere - all of Earth’s water except the water that is in gaseous form in the atmosphere - 71% of Earth’s surface is covered - 97% of water is in salty oceans Geosphere - mostly solid part of the Earth - all of the rock and soil on the surface and on the ocean floor - includes the solid and molten interior of the Earth Biosphere - composed of all of the forms of life in the geosphere, in the hydrosphere, and in the atmosphere - any organic matter that has not decomposed - extends from the deepest parts of the ocean to the atmosphere a few kilometers above Earth’s surface Earth’s Energy Budget First law of Thermodynamics Energy Budget Second law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy Sources - decay of radioactive atoms - convection – movement of hot materials toward the surface o cooler, denser materials sink o this process drives plate tectonics External Energy Sources - sun o movement of air masses o generates wind and ocean currents o allows plants to produce food - the pull of the sun and the moon on the oceans, combined with Earth’s rotation, generates tides that cause currents and drive the mixing of ocean water Cycles in the Earth System Reservoir – a place where matter and energy is stored Cycle – a group of processes in which matter and energy repeatedly move through a series of reservoirs - Nitrogen Cycle – nitrogen moves from air to soil, soil to plants and animals and back to air again - Carbon Cycle - Phosphorous Cycle – moves through every sphere except the atmosphere - Water Cycle – water to gas to precipitation to water