CHAPTER 1 DEFINITIONS EARTH SCIENCE climate
advertisement

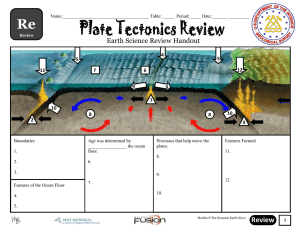
CHAPTER 1 DEFINITIONS EARTH SCIENCE climate – the patterns of weather that occur over long periods of time scientific method – organized and logical steps to solve a problem experiment – a procedure or series of steps that is carried out according to certain guidelines to test a hypothesis control group – a group that serves as a standard of comparison with another group that is identical except for one factor controlled experiment – an experiment that contains a control accuracy – the closeness of a measurement or a set of measurements to the accepted value precision – the exactness of a measurement or the closeness of a set of measurements error – an expression of the amount of imprecision or variation in a set of measurements confidence interval – describes the range of values for a set percentage of measurements model – a description, representation or imitation of an object, system, process or concept scientific law – a general statement that explains how the natural world behaves under certain conditions and for which no exceptions have been found Earth science – the scientific study of Earth and the universe around it geology – the scientific study of the origin, history and structure of Earth and the processes that shape Earth oceanography – the scientific study of the ocean, including the properties and movements of ocean water, the characteristics of ocean water and the organisms that live in the ocean meteorology – the scientific study of Earth’s atmosphere, especially in relation to weather and climate astronomy – the scientific study of the universe observation – the process of obtaining information by using the senses; the information obtained by using the senses hypothesis – an idea or explanation that is based on observations and that can be tested independent variable – in an experiment, the factor that is deliberately manipulated dependent variable – in an experiment, the factor that changes as a result of manipulation of one or more other factors peer review – the process in which experts in a given field examine the results and conclusion of a scientist’s study before that study is accepted for publication theory – the explanation for some phenomenon that is based on observation, experimentation and reasoning; that is supported by a large quantity of evidence; and that does not conflict with any existing experimental results or observations