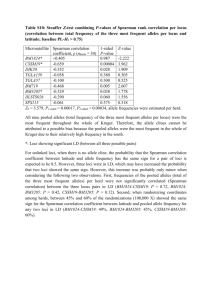
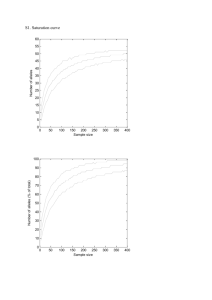
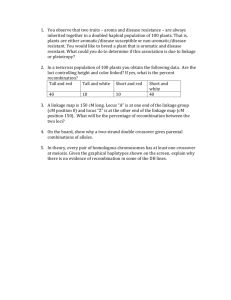
1) Linkage means
advertisement

1) Linkage means • A) Alleles at different loci are independent • B) Alleles at different loci are physically close to each other and on the same chromosome • C) Alternate alleles at the same locus are not independent • D) Alleles at different loci are not independent • E) Alternate alleles are fixed at alternate loci 2) independence, i.e. an absence of linkage disequilibrium • A) is caused by recombination over time • B) is likely for genes found within chromosome inversions • C) is a basic mendelian law that is not violated • D) means that traits do not evolve independently of each other • E) none of the above 3) If allele S at one locus has a frequency of 0.5 and allele t at a different locus has a frequency of 0.4, what is the expected frequency of the St haplotype if the loci are in equilibrium? • • • • • A) 0.54 B) 0.9 C) 0.2 D) 0.4 E) can not be determined from these data 4) What does sex do • A) recombines alleles at different loci thereby producing high levels of genotypic variation • B) decreases linkage disequilibrium • C) helps populations of organisms track changing environmental conditions • D) all of the above 5) Muller’s ratchet • A) is likely to be very important in large populations • B) is unlikely to be very important in large populations • C) reverses linkage • D) slows down evolution • E) eliminates deleterious alleles