Producing a Captioned Real Media Video
advertisement
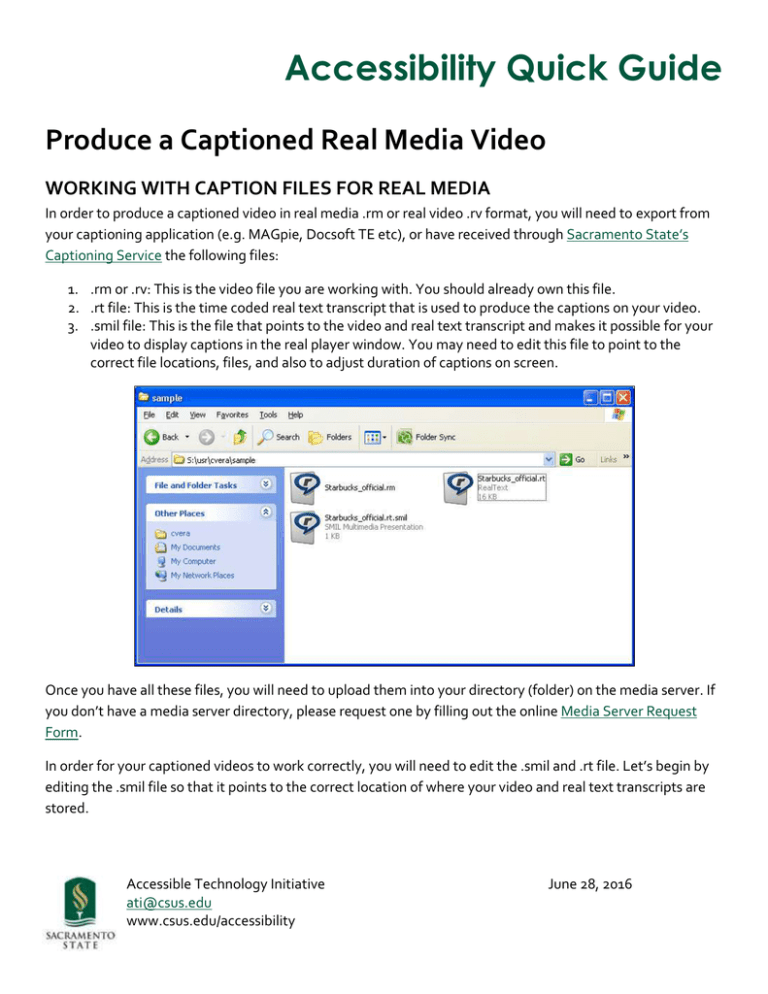
Accessibility Quick Guide Produce a Captioned Real Media Video WORKING WITH CAPTION FILES FOR REAL MEDIA In order to produce a captioned video in real media .rm or real video .rv format, you will need to export from your captioning application (e.g. MAGpie, Docsoft TE etc), or have received through Sacramento State’s Captioning Service the following files: 1. .rm or .rv: This is the video file you are working with. You should already own this file. 2. .rt file: This is the time coded real text transcript that is used to produce the captions on your video. 3. .smil file: This is the file that points to the video and real text transcript and makes it possible for your video to display captions in the real player window. You may need to edit this file to point to the correct file locations, files, and also to adjust duration of captions on screen. Once you have all these files, you will need to upload them into your directory (folder) on the media server. If you don’t have a media server directory, please request one by filling out the online Media Server Request Form. In order for your captioned videos to work correctly, you will need to edit the .smil and .rt file. Let’s begin by editing the .smil file so that it points to the correct location of where your video and real text transcripts are stored. Accessible Technology Initiative ati@csus.edu www.csus.edu/accessibility June 28, 2016 2 Editing the SMIL File with Correct file locations: To ensure that the transcript text is paired correctly to the location of the audio/video file, you will need to change the “video src” (video source) tag in the .smil file. To do this: 1. Navigate to the location of the SMIL file (it should be in your directory), 2. Right click on the .smil file name and select open with from the menu. Select WordPad or Notepad if you are working on a Windows computer or if working from a Mac ctrl click on the .smil file and select TextEdit from the options list. 3. The information for the .smil file will open in the text editor you selected. For this example, it will open in a WordPad document. The information we need to edit is located in the Video Source tag “ <video src = …” If you look at this tag, you will notice that the video source (video/audio file) indicates the current location of your video/audio file. Since you may have moved these files to your media directory on the media server, you will need to edit the location information so that the file can be found automatically regardless of location. To do this: 1. Select the content after the “<video src= “ tag up until before the name of the media file you are using. e.g. <video src="X:\prj\disted\archive\TEST\Captioning\02 Project Files\Spring 2011\Amy_Mickel\03Starbucks\Starbucks_official.rm" region="video" /><video 3 2. After you select that content, press the delete key, and replace that content with the following: ./ (period forward slash) 3. This “./” tells the media player to pull the source files (video and real text transcript) from their current location. 4. Do the same for the information after the tag: <textstream src =. Make sure the ./ (period forward slash) is before the name of the real text transcript file name. 5. Verify that the video src and textstream src file names match your video (.rm or .rv) and your real text (.rt) file names correctly. Please note: The <video src="./Starbucks_official.rm" region="video" /> tag indicates the video file that will be used and the <textstream src="./Starbucks_official.rt" region="text" /> indicates the real text transcript that will be used along with the video file to produce the captioned video you playback in real player. In this example, our video file name is “Starbucks_official.rm” and our real text file is “Starbucks_official.rt”. 6. After you are done editing the .smil file, go to file menu and click Save. Please note that the .smil file name will be used in the link you create that points to your captioned video. Make sure the file name has no spaces. Use underscore or dashes to separate words if needed in your file names. Indicating Caption Duration in Real Text File The Real Text .rt file is the time coded text transcript that is used to generate the captions in your video. You can edit the real text file directly to correct any transcript text and you can edit the caption duration which 4 tells the player how long captions should display on screen. Caption duration should match the end time of the last caption in the real text file. The beginning time of the last caption is displayed in the text file but there is no end time (this may vary across caption files) so you may have to playback the video to determine the end time of the last caption; end time is the point when all spoken content ends. When you work from certain captioning applications and export the .smil and .rt files, your Real Text file may not show the correct caption duration for which captions should display on screen. The issue with this is that captions may stop displaying on your video before the video is over because the correct time is not indicated. To address this issue do the following: 1. Locate the Real Text file in your media directory. Right click on the Real Text file and select open with Word Pad or Notepad if working on a Windows computer or if working from a Mac select TextEdit. 2. Scroll to the bottom of the transcript and note the time indicated for the last time code. Play back the video in real player and forward to the time indicated for the last time code. Look at the lower right hand corner on the play bar and note the time for which the last spoken content ends. Time is usually indicated in minutes and seconds e.g. 9:46 is 9 minutes and 46 seconds. 3. On the WordPad file locate the first tag on the transcript: <window version="1.5" bgcolor="#000000"> And replace it with: <window type="generic" extraspaces="use" wordwrap="true" width="300" duration="00:00:00.00" bgcolor="#000000"> 5 4. In the Duration area you will be replacing the 00:00:00.0 with the actual time of the file. In this example the end time for the last caption in the video is 9 min and 30 seconds so we will insert that information as: “00:09:30.00” 5. In order to have captions appear in the bottom center of the video, change the information in the “<font color” tag as follows: <font color="#FFFFFF" face="Verdana" size="3"><center> 6. You may also have to change the font size of the subtitles depending on how they look on the video. The font size is usually “3.” Insert the appropriate size next to “size = “#” 7. Click the Save button when all changes have been made. Test Captioned Video/Audio File You can now test to see whether the captions appear correctly on the media file by double clicking on the SMIL file in your directory. The .smil file will open in real player and should playback the video with captions. You may need to enable captions from the video player menus if these do not show at first. If video plays back correctly, the next step will be to create a link to your captioned video to be used in a SacCT course or webpage. Create Links to Captioned Real Media Video Depending on your needs, you may have students or the general public open access your captioned video(s) from a website or a SacCT course. In order to do this you will need to create a link or URL that points to the video on the media server and opens the captioned video in real player. 1. The format to follow when creating URL’s are as follows: http://media1.csus.edu:8080/ramgen/usr/directorynamehere/foldername /videosample.rt.smil http://media1.csus.edu:8080/ramgen : Your URL must include this information which deals with the Real Time Streaming Protocol that controls the streaming media server such as the Media 1 6 server on our campus. In other words, this information is necessary to control the playback of your media files from the server. /usr/directory namehere/: this information indicates the location of your user directory/folder on the media server. The name of the folder is usually your saclink ID. Your media server directory name will be emailed to you upon requesting a Media Server account. /test/ videosample.rt.smil: this information indicates the location of the .rm video, real text transcript, and smil file. If you have organized your files into folders, folder names will appear before the smil file name. In this example our caption files and video are located in a folder called “test” . The last part of the URL should be the complete .smil file name. In this example, the smil file name is “videosample.rt.smil”. 2. I have created a captioned video stored in my directory “cvera” on the media server. The URL that opens that captioned video is as follows: http://media1.csus.edu:8080/ramgen/usr/cvera/sample/Starbucks_official.rt.smil 3. Finally test your link by opening a browser window such as Internet Explorer or Firefox and copying and pasting the URL into the address bar. Depending on the browser you use or browser settings, you may be prompted to open or save the video. Choose Open video. Real Player will open your captioned video. If you do not have real player installed on your computer, you can download the player for free at: http://www.real.com 7 CAPTIONING RESOURCES For more information about how to work with .smil files, .rt real text files and real media video, visit WebAIM’s Captioning for Real Player (http://webaim.org/techniques/captions/real/) webpage. To request Captioning Service for videos to be used in a course or event at Sac State, visit our Captioning Services (http://www.csus.edu/accessibility/captioning.html) website.