Cell Review Power Point
advertisement

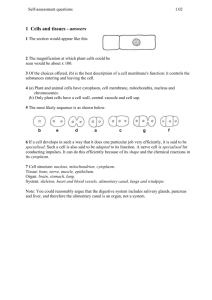
Which instrument is best for viewing cells and cell parts? A. B. C. D. glasses microscope telescope magnifying glass What is the best description of a cell? They are A. the smallest thing that scientists know about. B. free-swimming animals that have cilia. C. box shaped units that cork is made from. D. the small units that all living things are made of. How are all cells similar? A. They perform the functions of life. B. They make food from sunshine, air and water. C. They have the same parts as one another. D. They can swim in water and find their own food. Using the following diagram of a cell to answer the next two questions: Organelle X controls cell functions. What have scientists named this organelle? A. nucleus B. cytoplasm C. cell membrane D. cell wall What substance is found at Y? A. B. C. D. DNA cytoplasm membrane cell wall Which part of the cell contains genetic materials? A. B. C. D. cell membrane nucleus cytoplasm cell wall What are the food-making structures in plant cells? A. B. C. D. cell membrane nucleus cytoplasm chloroplasts Which cell organelle do all cells have that controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell? A. B. C. D. Cell wall Nuclear membrane Nucleus Cell membrane Which organelles would you expect a plant cell to have but not an animal cell? A. cell wall, chloroplast B. nucleus, cell membrane C. cytoplasm, diffusion D. osmosis, cell membrane Which diagram best represents a plant cell? A. B. C. D. A B both neither What is the function of the green circles in “B”? A. B. C. D. get rid of cell waste products control the entry of food into the cell use sunlight to make sugar control the activities of the cell What is the difference between the outer covering of “A” and “B”? A. A has a shell like an egg, B is a soft membrane. B. A has a cell membrane, B has a cell wall C. A and B both have cell walls that support the organism D. A is covering a plant cell, B is covering an animal cell What is the process by which water moves across a cell membrane called? A. B. C. D. osmosis active transport diffusion resolution A cell is placed in pure water. What will happen to the cell size? A. B. C. D. it will shrink it will expand in size it will not change it is impossible to predict The cells are separated by a membrane that allows water to pass through. How will water move in this example? The dots represent sugar atoms. The rest of each cell is filled with water. A A. B. C. D. B more will move from A to B move will move from B to A it will move equally back and forth it will not move Why does the sugar stay in the cell? A. B. C. D. A B it is dissolved in the water it is connected to the nucleus it cannot pass through the membrane it is a solid made of crystals. Why does osmosis occur? It happens because A. gravity pulls all matter toward the center of Earth. B. water moves from high concentrations to low. C. cells are alive and only living things have osmosis. D. cells are the smallest parts of living things. How do cells get energy from food? A. Cells break food into smaller parts, releasing energy. B. Cells have electricity in the nucleus that travels to the rest of the cell. C. Cells create energy because they are able to move. D. The sun sends food through space that turns into energy. What do cells do with waste products? A. They store wastes in the cell membrane. B. Wastes are passed out through the cell membrane. C. Wastes are broken down into helpful substances. D. The cells store the wastes, which allows them to grow. Why are only plant cells able to produce food from sunlight? Plant cells A. have cell walls that tell the cell how to produce food. B. have cytoplasm which creates and stores food. C. have chloroplasts which is where food is produced. D. have a cell wall to give the plant support and strength. Which is a plant cell, A or B? A. Cell A because plant cells are not round. B. Cell A because plant cells have a cell wall that helps hold their shape. C. Cell B because the oblong structures in cell B look like chloroplasts. D. Neither is a plant cell. Plant cells do not have that maze-looking structure. What guides all cell processes? A. genetic material in the nucleus B. energy from the mitochondria C. movement through the cell membrane Which answer correctly identifies the 5 levels of cell organization from simplest to most complex? A. tissue, organs, organ systems, cell, organism B. organism, organ system, organ, tissue, cell C. organ system, cell, tissue, organ, organism D. cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism Which answer correctly identifies the 5 levels of cell organization in a dogs body from simple to most complex? A. bone cell, bone tissue, femur (thigh bone), skeleton, dog B. dog, skeleton, femur, bone tissue, bone cell C. skeleton, bone tissue, bone cell, dog, femur D. bone tissue, bone cell, femur, skeleton, dog Overlapping circles can be used to show relationships. In this diagram, levels of organization within living things are shown. If each circle is made from the smaller circles inside it, what does circle “W” stand for? A. B. C. D. organs cells tissues organ systems What would circle “Y” be? A. B. C. D. organs cells tissues organ systems The brain is an example of which level of organization in a body? A. B. C. D. E. cell tissue organ organ system organism A nerve is an example of which level of organization in a body? A. B. C. D. E. cell tissue organ organ system organism The lining of the stomach is an example of which level of organization in a body? A. B. C. D. E. cell tissue organ organ system organism A cow is an example of which level of organization in a body? A. B. C. D. E. cell tissue organ organ system organism Which organ system transfers gasses into and out of the blood? A. B. C. D. nervous system respiratory system skeletal system lymphatic system Which organs collect and excrete cell wastes? A. B. C. D. skin and heart stomach and pancreas bladder and kidneys lungs and heart Which organs breakdown food for cells? A. B. C. D. heart, arteries, blood stomach, intestine, pancreas nerve, brain, spinal cord skin, pancreas, skeletal THANK YOU