ch3-withPineValley.ppt
3-1
Modern Systems Analysis and Design
Third Edition
Jeffrey A. Hoffer
Joey F. George
Joseph S. Valacich
Chapter 3
Managing the Information
Systems Project
Copyright 2002 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Learning Objectives
3.2
Explain the process of managing an information systems project
Discuss skills required to be an effective project manager
Describe skills and activities of a project manager during project initiation, planning, execution and closedown
Explain Gantt and Pert charts
Review commercial project management software packages
3.3
Managing the Information
Systems Project
Focus of project management
To ensure that information system projects meet customer expectations
Delivered in a timely manner
Meet time constraints and requirements
3.4
3-4
Technological
Change
Customer and
Management
Expectations
Documentation
And
Communication
Systems
Development
Life cycle
The Art
Of
Project
Management
Organizational
Change and
Complexity
Contractors
And Vendors
Managing
People
Time and
Resource constraints
Methodologies
And Tools
3.5
3.6
3-5
3.7
Figure 3-1
Three computer applications at Pine Valley Furniture: Order
Filling, Invoicing, and Payroll
(Source: Hoffer, Prescott, and McFadden, 2002)
3.8
Managing the Information
Systems Project
Project Manager
Systems Analyst responsible for:
Project initiation
Planning
Execution
Closing down
Managing the Information
Systems Project
Project Manager
Activities include:
Management
Leadership
Technical
Problem solving
Conflict management
Customer relations
Team management
Risk and change management
3.10
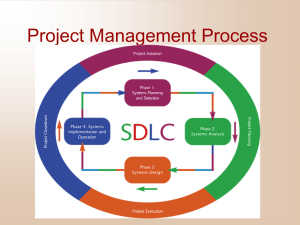
Project Management Process
Project
Planned undertaking of related activities to reach an objective that has a beginning and an end
Four Phases
Initiation
Planning
Execution
Closing down
3.11
3-6
3.12
Initiating the Project
Establish project initiation team
Establish relationship with customer
Establish project initiation plan
Establish management procedures
Establish project management environment and workbook
TABLE 3-2
Elements of Project Initiation
•
Establishing the project Initiation Team
•
Establishing a Relationship with the customer
•
Establishing the project Initiation Plan
•
Establishing Management Procedures
•
Establishing the Project Management
Environment and Project Workbook
3.13
3.14
Planning the Project
Describe project scope, alternatives and feasibility
Scope and Feasibility
Understand the project
What problem is addressed
What results are to be achieved
Measures of success
Completion criteria
3.15
Planning the Project
Divide the project into manageable tasks
Work breakdown structure
Gantt chart
Estimate resources and create a resource plan
Develop a preliminary schedule
Utilize Gantt and PERT charts
3.16
3-7
3.17
Planning the Project
Develop a communication plan
Outline communication processes among customers, team members and management
Determine project standards and procedures
Specify how deliverables are tested and produced
3.18
Planning the Project
Identify and assess risk
Identify sources of risk
Estimate consequences of risk
Create a preliminary budget
Develop a statement of work
Describe what the project will deliver and duration
Set a Baseline Project Plan
Estimate of project’s tasks and resources
3.19
3-9
3.20
3.21
Executing the Project
Execute Baseline Project Plan
Acquire and assign resources
Train new team members
Keep project on schedule
Monitor project progress
Adjust resources, budget and/or activities
3.22
3.23
Executing the Project
Manage changes to Baseline Project
Plan
Slipped completion dates
Changes in personnel
New activities
Bungled activities
Maintain project workbook
Communicate project status
3.24
3.25
Closing Down the Project
Termination
Types of termination
Natural
Requirements have been met
Unnatural
Project stopped
Documentation
Personnel Appraisal
3.26
Closing Down the Project
Conduct post-project reviews
Determine strengths and weaknesses of:
Project deliverables
Project management process
Development process
Close customer contract
3.27
3.28
Representing and Scheduling
Project Plans
Gantt Charts
Useful for depicting simple projects or parts of large projects
Show start and completion dates for individual tasks
PERT Charts
Show order of activities
Figure 3-16
Graphical diagrams that depict project plans
(a) A Gantt Chart
(b) A PERT chart
3-10a
3.29
3-10b
3.30
Comparison of Gantt and
PERT Charts
Gantt
Visually shows duration of tasks
Visually shows time overlap between tasks
Visually shows slack time
PERT
Visually shows dependencies between tasks
Visually shows which tasks can be done in parallel
Shows slack time by data in rectangles
3.31
3-11
3.32
3-12
3.33
3-13
3.34
3-14
3.35
3-15
3.36
3-17
3.37
3-18
3.38
Gantt and PERT Charts for
Pine Valley Furniture
Steps
Identify each activity
Requirements Collection
Screen Design
Report Design
Database Design
User Documentation
Software Programming
Installation and Testing
3.39
Gantt and PERT Charts for
Pine Valley Furniture
Determine time estimates and expected completion times for each activity
Determine sequence of activities
Determine critical path
Sequence of events that will affect the final project delivery date
3.40
Project Management Software
Many systems are available
Three activities required to use:
Establish project start or end date
Enter tasks and assign task relationships
Select scheduling method to review project reports
3.41
Summary
Skills of an effective project manager
Activities of project manager
Initiation
Planning
Execution
Closedown
Gantt and PERT Charts
Commercial Project Management Software