Supplementary information , Bystrov et al. a) b)
advertisement
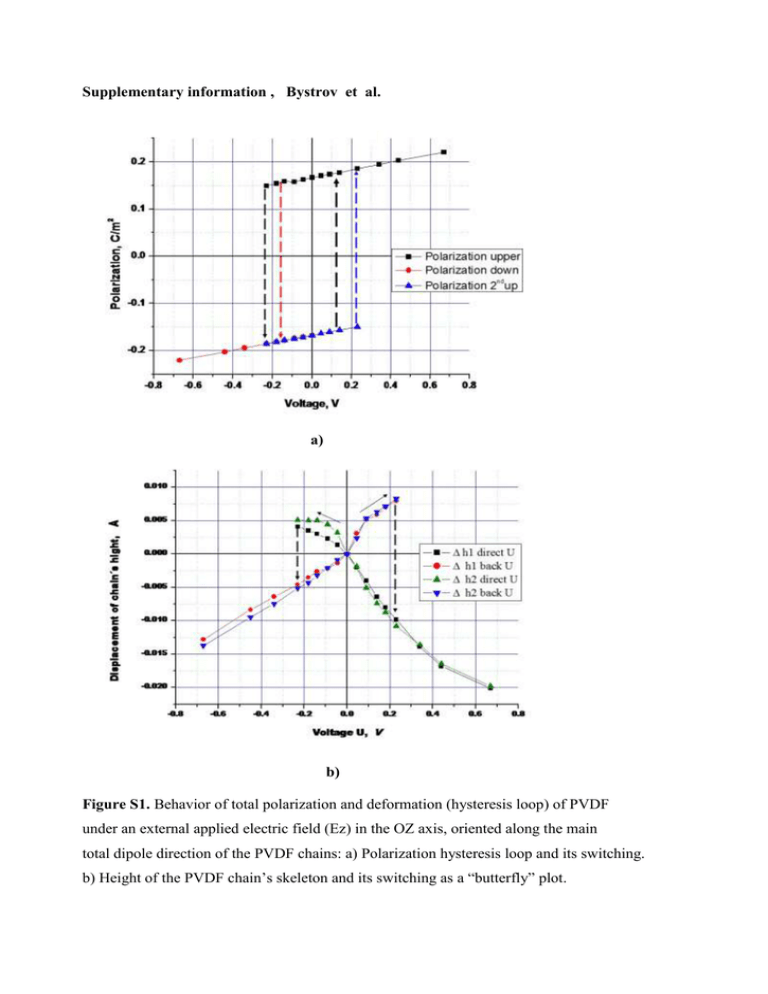
Supplementary information , Bystrov et al. a) b) Figure S1. Behavior of total polarization and deformation (hysteresis loop) of PVDF under an external applied electric field (Ez) in the OZ axis, oriented along the main total dipole direction of the PVDF chains: a) Polarization hysteresis loop and its switching. b) Height of the PVDF chain’s skeleton and its switching as a “butterfly” plot. Figure S2. Examples of total energy minimum variations of the PVDF unit cell (computed by BIO CHARM method, after PM3 for each chain), with changes of the distances of the b parameter of the unit cell (which is directed along the OZ axis, perpendicular to parameter c in the OX axis) under different values of the applied electrical field Ez: Ez = 0 and Ez = 0.005 a.u. = ~ 2.5 GV/m. PVDF film Udc (Uac) Bottom electrode a) b) PVDF (75/25)#3 18.01.2008 first loop second loop d33 eff, a.u. 400 200 0 -200 -400 -30 -20 -10 0 10 Voltage, V 20 30 c) d) Figure S3. Measured experimental data for a PVDF film, obtained by atomic force (AFM) and piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM): a) schematic of experimental setup; b) AFM image of topography, and PFM images before and after poling. After poling, the PFM image shows the opposite “light” and “dark” contrasting lines of two oppositely poled areas, corresponding to the opposite voltage directions (-30 V = “light” and +30V = dark”); c) and d) local piezoresponse hysteresis loop and butterfly-like plot of deformations.