Chapter Nineteen: Managing Workforce Diversity and Wellness Organization Development and Change
advertisement

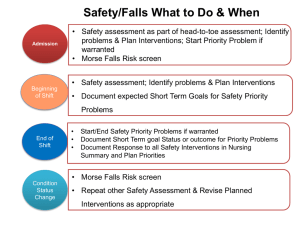
Organization Development and Change Chapter Nineteen: Managing Workforce Diversity and Wellness Thomas G. Cummings Christopher G. Worley Learning Objectives for Chapter Nineteen To examine human resources management interventions that address increasing workforce diversity and employee wellness. To understand how OD efforts can enhance traditional human resource approaches to these issues. 19-2 A Framework for Managing Diversity External Pressures For & Against Diversity Management’s Perspectives & Priorities Strategic Responses Implementation Internal Pressures For & Against Diversity 19-3 Age Diversity Trends Median age up Distribution of ages changing Implications Health care Mobility Security Interventions Wellness programs Job design Career development and planning Reward systems 19-4 Gender Diversity Trends Percentage of women in work force increasing Dual-income families increasing Implications Child care Maternity/paternity leaves Single parents Interventions Job design Fringe benefit rewards 19-5 Disability Diversity Trends The number of people with disabilities entering the work force is increasing Implications Job skills and challenge issues Physical space design Respect and dignity Interventions Performance management Job design Career planning and development 19-6 Culture and Values Diversity Trends Rising proportion of immigrant and minority-group workers Shift in rewards Implications Flexible organizational policies Autonomy Affirmation and respect Interventions Career planning and development Employee involvement Reward systems 19-7 Race/Ethnicity Diversity Trends Minorities represent large segments of workforce and a small segment of top management/senior executives Qualifications and experience of minority employees is often overlooked Implications Discrimination Interventions Equal employment opportunities Mentoring programs Education and training 19-8 Sexual Orientation Diversity Trends Number of single-sex households up More liberal attitudes toward sexual orientation Implications Discrimination Interventions Equal employment opportunities Fringe benefits Education and training 19-9 A Model of Stress and Work Occupational Stressors Stress • How the • Physical Environment • Individual: role conflict and ambiguity, lack of control • Group: poor peer, subordinate or boss, relationships individual perceives the occupational stressors • Organizational: poor design, HR policies, politics Individual Differences Cognitive/Affective: Biologic/Demographic: Type A or B, hardiness, social support, negative affectivity Age, gender, occupation, race Consequences • Subjective: anxiety, apathy • Behavioral: drug and alcohol abuse • Cognitive: poor focus, burnout • Physiological: high blood pressure and pulse • Organizational: low productivity, absenteeism, legal action 19-10 Stress and Wellness Workplace Interventions Role Clarification A systematic process for determining expectations and understanding work roles Supportive relationships Establish trust and positive relationships Work Leaves Health Facilities Employee Assistance Programs 19-11 2-12