Adding Depth and Complexity to Your Lessons-Grade Level 8 Social Studies- US History to 1877
advertisement

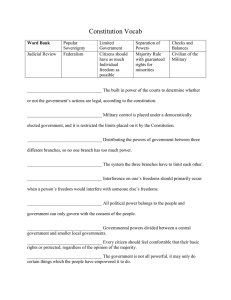
Adding Depth and Complexity to Your Lessons Grade Level(s): 8th Grade Content Area : Social Studies – US History to 1877 TEKS Objective: SS.8.4C, SS.8.30B, SS.8.16D Language of the Discipline Questions/Discussion Opportunities: Define the following terms and concepts: Constitution, structure and function of government, power, Federalism, checks and balances, separation of powers, division of power, Republicanism, popular sovereignty, individual rights, consent of the governed, acquisition of power, limited government, (G/T extension terms) democracy, absolutism, anarchy, oligarchy, mercantilism, providence, colonialism, post-colonialism. Student Activities/Products: Use cooperative grouping strategy: Have students break up into 7 small groups and create a poster of the following 7 Constitutional principles: Federalism, Checks & Balances, Separation of Powers, Republicanism, Popular Sovereignty, Consent of the Governed, Limited Government in the following structure: Unanswered Questions Questions/Discussion Opportunities: 1. How do principles of federalism, checks and balances, and separation of powers affect the division of power in a limited government? 2. How do the principles of republicanism, popular sovereignty, and individual rights affect who gets and keeps powers in a limited government? G/T Extension Questions: 3. Justify the Founder’s use of limited government during a period of history that focused on Absolutism. 4. Justify the use of terminology such as “divine providence” and the principle of the First Amendment’s “Congress shall make no law respecting … the establishment of religion or the free exercise thereof…” 5. Explain what is meant by the phrase: “The United States is NOT a ‘pure’ democracy.” Student Activities/Products: Have students use the above questions to focus their reading and research to accomplish a Socratic Seminar. See G/T Curriculum Framework, Differentiated Instructional Strategies MS section. Adding Depth and Complexity to Your Lessons Grade Level(s): 8th Grade Content Area : Social Studies – US History to 1877 TEKS Objective: SS.8.4C, SS.8.30B, SS.8.16D Multiple Perspectives/ Big Ideas Questions/Discussion Opportunities: Explain the dichotomy of the principle of individual liberty and the continuance of slavery in the United States after ratification of the Constitution. Student Activities/Products: Additional questions that may be used in the Socratic Seminar or other discussions. See G/T Curriculum Framework, Differentiated Instructional Strategies MS section. Ethics Questions/Discussion Opportunities: 1. Defend the Anti-Federalist position that only educated people should vote. 2. Defend the Anti-Federalist position that individual rights should not be included in the body of the Constitution. 3. Defend the Federalist position that the national government should have more power than the states. 4. Defend the Federalist position that created oligarchy structures in the Constitution such as the appointment of Senators and the Electoral College. Student Activities/Products: Use the above statements in a debate format to look at the final debates of the Constitutional Convention. See G/T Curriculum Framework, Differentiated Instructional Strategies MS section.