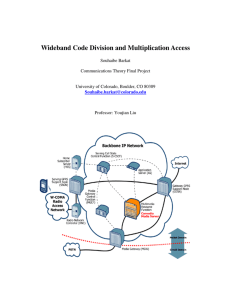
Wideband Code Division and Multiplication Access Souhaibe Barkat December 11
advertisement
University of Colorado at Boulder Wideband Code Division and Multiplication Access December 11th , 2006 presented by: Souhaibe Barkat 1. WCDMA Use • 3rd generation cellular network • Sprint, AT&T, Nokia, and Ericsson • More bandwidth means more capabilities 2. Frequency Band Allocation In The United States WCDMA Uplink Downlink Total 1710-1770 2110-2170 2x60 MHz In Europe and Japan Uplink Downlink Total UMTS-FDD 1920-1980 2110-2170 2x60 MHz UMTS-TDD 1900-1920 2110-2025 20+15 MHz 3. Standard Body • Concept formed by FRAMES research project with Panasonic, Fujitsu, and NEC + many other • (FRAMES) Future Radio Wideband Multiple Access System • Uplink physical layer adopted by FRAMES • Downlink was modified by several companies 4. Information Bits and Modulation Baseband Transmitter 4. Information Bits and Modulation Baseband Receiver 5. Error Control Coding • Convolutional encoding for MPEG4 >> BER of 10^-3 • Turbo encoding for data application >> BER of 10^-6 6. Constellations Used • QPSK for downlink transmission • 16QAM is used for HS-DSCH to provide higher speed data HS-DSCH: High Speed Dedicated Physical Control Channel WCDMA Receiver RAKE Receiver 7. IQ Modulator I-Q Uplink Modulator 7. IQ Modulator I-Q Downlink Modulator 8. Pulse Shape Used • Root Raised Cosine with roll-off = 0.22 Root Raised Cosine for WCDMA, FB=100, RRCF with alfa=0.22, k=9 1.5 1 0.5 0 -0.5 -1 -1.5 -0.05 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 9. Broadcast Technology Used • WCDMA does both FDD and TDD • Uplink: Multiple users send signals to the base station • Downlink: Base station sends different signals to different users 10. Multi-Antenna Technology Transmitter Receiver 11. Major Players 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Alcatel Ericsson Lucent Motorola Nokia Nortel Siemens/NEC Questions?