W-CDMA: Air Interface for 3G Systems
advertisement

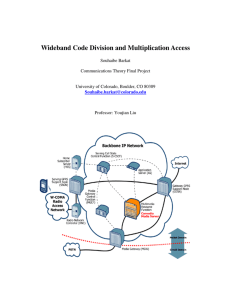
W-CDMA AIR INTERFACE FOR 3G SYSTEMS By Medapati, Sai Raghavendra Reddy Gadige, Raghunath INTRODUCTION What is W-CDMA? Stands for Wideband Code Division Multiple Access It is a type of 3G cellular network. It acts as an air interface for 3G systems. It is an ITU’s IMT-2000 standard. Uses CDMA technology Uses 5MHz wide frequency band. Evolution from 2G to 3G From 2G to 2.5G GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) data rates 56 kbps to 114 kbps From 2.5G to 2.75G GPRS to EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution) From 2.75G to 3G EDGE to UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service) Data rates 144kbps, 384kbps, 2 Mbps. Compare… Development GSM Successful, Plans 3G systems CoDiT (Code Division Testbed) started, first W-CDMA FRAMES ( Future Radio wideband Multiple Access Systems) started, to support European 3G standards 5 groups formed by ETSI (European Telecommunications Standard Institute) Contd… W-CDMA developed by NTT DoCoMo as air interface for 3G FOMA (Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access) ITU accepted W-CDMA as IMT-2000 standard. W-CDMA adopted in 55 countries Technical Features Data rates 384 kbps (wide coverage), 2 Mbps (local coverage) Operates in 2 modes FDD and TDD High service flexibility Efficient packet access Contd… Supports inter frequency handover, handover to other systems Uses 5 MHz wide frequency band. High speed. Built in support for future technologies and coverage enhancing technologies. Technologies Used Asynchronous Network Operation Cell Search As Asynchronous, no need to search for base stations Uses common base station code with unique base station time shifts Soft Handover Communicates same information through 2 or more base stations Per call synchronization Contd… Compressed mode Mobile devices dual mode Handover from WCDMA to GSM crucial Compressed mode, SF is changed and compress the transmitting and receiving information for a short time span. Remaining time for measuring other frequencies. Measures sent to network Contd… Uplink Power Control Due to near-far problem Power control for uplink needed Open loop and Closed loop Closed loop is used with update rate of 1500 Mhz. 2G systems use update rate of 800 Mhz Contd… Random access RACH( Random Access Channel), initial access. RACH codes transmitted through downlink Scrambling codes and a signature are randomly selected and sent with increasing power Sufficient power, acquisition indicator. Contd… Coherent Uplink Detection Used for data reception.“Pilot symbols” used in Uplink and Downlink. CDMA2000 adopted these Pilot symbols OVSF Codes higher flexible bearer system to send all kinds of data OVSF (Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor) codes, formed form code tree principle. Reduces interference, minimizes crosstalk Data Rate Indication TFCI (Transport Format Combination Indicator) Blind-rate detection Contd… Speech Codec Speech signal transmitted efficiently with high capacity, speech codec required 12. 2 kbps AMR codec used High-speed Packet Data HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access) an extension of W-CDMA Enhanced data rates up to 100 Mbps These are the 4 schemes used in HSPA shared channel with channel dependent scheduling, fast link adaption, hybrid ARQ with sort combining, a short TTI are used. Contd… Broadcast and Multi cast Services MBMS (Multimedia Broadcast and Multicast Service) The user residing at the cell edge, signal from adjacent base station is used. Downlink soft handover used. Increase in data rates and coverage W-CDMA uses same carrier for MBMS where CDMA2000 uses separate carrier and separate receiver Analysis Commercial WCDMA network Development WCDMA Subscribers base evolution WCDMA in Practice Uplink Capacity of satellite based WCDMA Systems Contd… The commercial and military operations now a days using satellite based WCDMA systems. The main factors to be considered are Uplink and Downlink Capacity. There are 2 types of WCDMA used in this system. Terrestrial WCDMA and GEOS( Geosynchronous) WCDMA. Contd… Equation to calculate pole capacity. Where, LF = Load Factor < 1 ful = Adjacent beam to within- beam MAI b = reduction in adjacent beam MAI due to beam forming G (lambda/μ) = 1+ (2.32/ sqrt( lambda μ) ) : Effect of dynamic traffic W = 3.84 MChips/sec Preq = Eb/(No+I0) required to meet QOS M = Channel fade margin needed to guarantee 99% availability ≥ 1 PC Gain = Reduction in fade margin due to power control ≥ 1 L = Losses (implementation losses) ≤ 1 Contd… Equation to calculate the capacity of the mixture of users Where, k = user type and channel combination Rcap( i) = Capacity of all users belonging to ith channel The above two equations are used to calculate the uplink capacity of satellite based WCDMA systems. Advantages W-CDMA provides faster data connection ( 384kbps and in future 10Mbps Can do all the activities that a normal phone does (SMS, MMS, INTERNET etc.) and supports fast video streaming. Simultaneous usage of all the activities even on call. We will only be billed for the data transferred but not for the time connected. Contd….. In W-CDMA , cells use single frequency with differentiated codes. Cell planning is easier. Uses asynchronous operation. Longer battery life. Limitations Uses wide frequency band. Mechanism for maximum usage. Cell planning is easier but it should be done carefully. Conclusion Drastic change in cellular technology HSPDA ( High Speed Downlink Packet Access). Extension of UMTS. W-CDMA used in almost every 3G mobile. Research on 4G started. Literature Cited http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-122199-153028/unrestricted/fakhrul_thesis.pdf http://www.comlab.hut.fi/opetus/238/lecture4_Intro_to_WCDMA.pdf( intro to wcdma) http://www.tech-faq.com/wcdma.shtml http://0el70beril.blogspot.com/2007/06/technical-features.html http://www.ericsson.com/technology/whitepapers/innovations_in_wcdma.pdf http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2G http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3G http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/W-CDMA http://www.umtsworld.com/technology/wcdma.htm http://www.researchinchina.com/report/Telecommunications/470.html http://delivery.acm.org/10.1145/1300000/1292336/a4shanmugan.pdf?key1=1292336&key2=1523038221&coll=GUIDE&dl=GUIDE&CFID=13694613&CFTO KEN=23668837 Thank You…