ex5m4_1.doc
advertisement

Random Signals for Engineers using MATLAB and Mathcad
Copyright 1999 Springer Verlag NY
Example 4.1 Two Dimensional Discrete Distributions
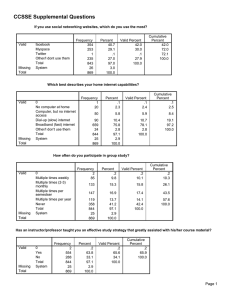
In this example we will show how we may plot the two dimensional cumulative distribution
functions. We define a set of discrete probabilities by a matrix and tabulate the random variables x i
and yj.
P=[1/8 0 0 0;0 3/8 0 0;0 1/8 2/8 0;0 0 0 1/8]
P =
0.1250
0
0
0
x0=0:3
y0=0:3;
x0 =
0
0
0.3750
0.1250
0
1
2
0
0
0.2500
0
0
0
0
0.1250
3
The cumulative distribution function is now plotted. This operation requires a lengthy computation
by Matlab because of the number of points involved and, if desired, the computation can be
suppressed until the final output is required.
xp= -.5:.2:4;
yp=-.5:.2:4;
r=F2D(xp,yp,x0,y0,P);
view([20 -20]); axis('ij');mesh(r)
The marginal functions can also be plotted and it may be verified that these correspond to the surface
plot at (x,3.5) for the x marginal and (3.5, y) for the y marginal distribution functions. The marginals
are plotted
plot(xp,FX(xp,x0,P),yp,FX(yp,y0,P'))
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
-1
0
1
2
3
4
The functions required by the plots are listed below.
function y=F2Ds(xp,yp,x0,y0,p)
% 2D cumulative probability function
n=length(x0);
y=0;
for j=1:n
for i=1:n
y=p(i,j)*stepfun(xp,x0(i))*stepfun(yp,y0(j)) + y;
end
end
function y=F2D(xp,yp,x0,y0,p)
% 2D cumulative probability function
np=length(xp);
y=zeros(np,np);
for i=1:np
for j=1:np
y(i,j)=F2Ds(xp(i),yp(j),x0,y0,p);
end
end
function y=FX(xp,x0,p)
% 2D cumulative probability function
n=length(x0);
np=length(xp);
y=zeros(1,np);
for j=1:n
for i=1:n
y=p(i,j)*stepfun(xp,x0(i)) + y;
end
end
function y=stepfun(t,t0)
%stepfun
for i=1:length(t)
y(i)=t(i)>t0;
end