Lesson 1 Geospatial Information Systems and Their Use in Nutrient Management
advertisement

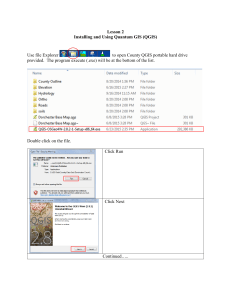
Lesson 1 Geospatial Information Systems and Their Use in Nutrient Management Quantum GIS (QGIS) GIS stands for Geospatial Information System. It is designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage and present all types of geographically referenced data. It is used in many applications for large and small municipalities, the military, commercial businesses and agriculture. The most well-known and used application is ArcGIS. In agriculture it is used to develop maps for NRCS and FSA offices throughout the country. It is used by conservation districts and NRCS to plan how water will be controlled. The Web Soil Survey is an online GIS based program. There are several applications used in commercial agriculture including Farm Works, SMS, and STS as well as many others. Precision agriculture requires the use of this type of software. Quantum GIS (QGIS) is an Open Source Program – it comes with the right to download, run, copy, alter, and redistribute the software. GRASS was developed at the US Army Corp of Engineers Construction Engineering Research Laboratory from 1980 to 1995. It was abandoned in 1995 and was saved because it was Open Sourced. A lot of closed-source software finds becomes open source. GIS programs use layers of data which when added together provide information for decision making. Below is a small example of six layers of data added one at a time. Aerial Photo (Ortho) Roads and Fields ( 2 Layers) “Blue Line” Streams Buffers (2 Layers: 10 ft. and 35 ft.) Only one additional layer is needed to provide all the information needed to measure, calculate and document distance to water, average length of slope and average percent slope - Contours: Smith Farm Field 1 Slope 1 Slope 2 Distance to Water: 143 Feet Slope 3 QGIS will also measure acres for fields that have not had acreage determinations completed by FSA or when FSA fields have been divided due to cropping or irrigation. Soils layer can also help provide the advisor with a quick overview of the soils in a field. Updated: 5/2/16