AFRICA Introduction
advertisement

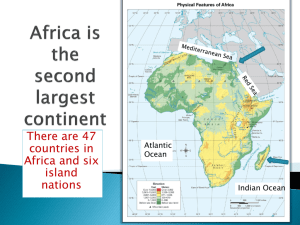
AFRICA Introduction The basic info • Africa is a continent, not a country. • It is made up of many countries (approximately fifty). • For centuries was known as the “Dark Continent.” • This nickname was a result of lack of knowledge about it. Why was there a lack of information? Why has Africa historically been behind the world in technology? Natural Barriers restricted the flow of information and limited contact with other peoples • The most important barrier of course was the… • SAHARA DESERT How did the Sahara affect Africa’s development? • Sahara Desert helped create an east-west flow of information. New ideas, inventions and technology did not spread south to reach sub-Saharan Africa. • Africans did not share in European and Asian advancements until much later. • Europe had limited contact with Africans to gain information about them. Other natural barriers • Mountains • Jungles • Rivers that were difficult to navigate • Coasts with few natural harbors • Tropical diseases Geographic disadvantages • Lack of quality farmland and resources have also plagued Africa throughout history. Africa’s Physical Features Sahara Sahel Tropical Rainforest Highlands Geographic Regions • Coastal – climate region along the Mediterranean and the oceans • Desert – in addition to the Sahara, there are also deserts in southern Africa • Sahel – area just south of the Sahara Desert that is semiarid and facing the problem of desertification (becoming desert) • Savanna – grasslands with few trees, abundant animal life • Rainforest – tropical regions, mostly around Congo Basin…Africa has far less tropical rainforest than desert • Highlands – Eastern Africa, comfortable climate despite being near equator We will be studying sub-Saharan Africa (below the Sahara) Savanna Desert Homes Cities of Africa • Capitals of Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Mozambique, and Eritrea Religion Religion • African religious beliefs vary. • Islam is the dominant religion of the northern part of the continent. • Christianity is the majority of many of the countries south of the Sahara, but Islam is still present in a significant amount. • Indigenous beliefs are still practiced – many Africans combine indigenous beliefs with Christianity. Ubuntu Africa Unit of Study • The slave trade. • Colonial period – European take over of Africa and movements for independence. • Post-independence and modern day situations. • Reading of novel.