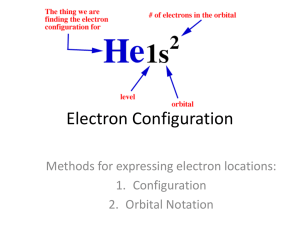
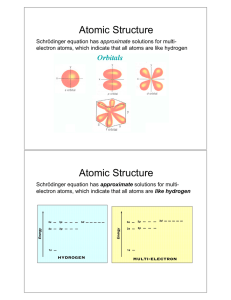
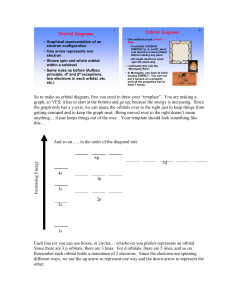
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Electron Configurations
advertisement

Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Electron Configurations Review of Sections 1 & 2 1. What is the equation that related speed, wavelength, and frequency? 2. Which theory of light, (wave or particle) best explains the following phenomena? a. The interference of light b. The photoelectric effect c. The emission of electromagnetic radiation by an excited atom. 3. Compare and contrast the Bohr model and quantummechanical model of the atom. 4. What is the principal quantum number? Review of Sections 1 & 2 5. How does “n” relate to the number of sublevels in each energy level? 6. For n = 4, how many sublevels are there and what are their designations? 7. How many possible orbital orientations are there for d and f sublevels? 8. What is the relationship between n and the total number of orbitals in each energy level? 9. How many electrons could be contained in the 3rd energy level? Electron Configurations • Orbital Notation for Carbon 1s _ _ __ 2s 2p • Electron Configuration for carbon 1s22s22p2 “Orbital Filling” Rules • Aufbau Principle Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals available • Pauli Exclusion Principle No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers; orbitals can hold a maximum of two electrons; two electrons in one orbital must have opposite spins. • Hund’s Rule Electrons fill equal energy orbitals one at a time until each is occupied by one electron; Electrons in singly occupied orbitals have the same spin. Write orbital diagrams and electron configurations for each of the following atoms. N Se F Te S Ar Cl Ne




![6) cobalt [Ar] 4s 2 3d 7](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009918562_1-1950b3428f2f6bf78209e86f923b4abf-300x300.png)