Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms The Development of a New Atomic Model
advertisement

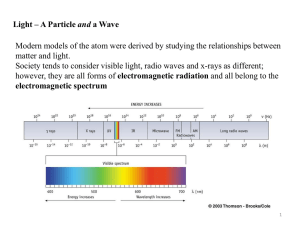
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms The Development of a New Atomic Model The Development of a New Atomic Model Objectives: 1. Identify the major regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. 2. Explain the mathematical relationship between wavelength, frequency and energy of light. 3. Distinguish between a continuous spectrum and line spectrum. 4. Explain how atoms emit light energy. Rutherford Model of the Atom The Wave Description of Light The Wave Description of Light Wavelength (λ) – the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves Frequency ()-the number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (waves/sec or Hz) Amplitude- the height of a wave measured from baseline to peak or baseline to trough. Speed (c)- distance time; 3.0 x 108 m/s for light traveling in a vacuum. (slightly slower through matter) The Wave Description of Light c •Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional The Development of a New Atomic Model Objectives: 1. Explain how line spectra demonstrate the quantized nature of light energy. 2. Describe the Bohr Model of the Hydrogen atom. The Photoelectric Effect • the emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal • The light must have a minimum frequency depending upon the metal The Photoelectric Effect Max Planck (1900) – suggested that objects emit energy is specific amounts called quanta Quantum- minimum amount of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom E h E = energy in Joules h = Planck’s constant (6.626 x 10-34 J*s) = frequency of radiation emitted The Photoelectric Effect Albert Einstein (1905) – proposed that light could exist as a stream of particles with each particle containing a quantum of energy photon- particle of electromagnetic energy carrying a quantum of energy E h The Hydrogen Atom Line Emission Spectrum • When substances absorb energy, they give of that energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. ground state – lowest energy state of an atom excited state – a state with higher potential energy Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom Niels Bohr (1913) – proposed a model for the H atom to account for the hydrogen line spectrum. Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom