Slide 1 - Images
advertisement

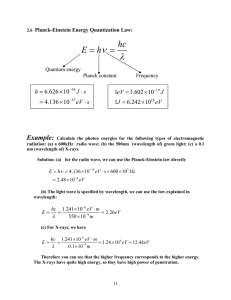
Warm-up: To be turned in • Use your periodic table to determine which of the following would have a larger atomic radius: • • • • Phosphorous or Silicon Sodium or Lithium Chlorine or Fluorine Neon or Krypton Ch. 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms 4.1 The Development of a New Atomic Model Light • Before 1900, scientists thought that light behaved only as wave • discovered that also has particle-like characteristics Light as a Wave • electromagnetic radiation: – form of energy that acts as a wave as it travels • All forms are combined to form electromagnetic spectrum Electromagnetic spectrum High Frequency Gamma Rays Short Wavelength X-Rays Ultraviolet Rays Visible Light Infrared Rays Microwaves Low Frequency Radio Waves Long Wavelength Light as a Wave • all form of EM radiation travel at a speed of 3.0 x 108 m/s in a vacuum • it has a repetitive motion • wavelength: (λ) distance between points on adjacent waves; in nm (1nm= 10-9m) • frequency: (ν) number of waves that passes a point in a second, in waves/second c Inversely proportional! What is the wavelength of X-rays having a frequency of 4.80 x 1017 Hz? Photoelectric Effect • when light is shone on a piece of metal, electrons can be emitted – Didn’t happen if the light’s frequency was below a certain value • scientists could not explain this with their classical theories of light Photoelectric Effect • Max Planck- 1877 • suggested that an object emits energy in the form of small packets of energy called quanta • quantum- the minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom E h Planck’s constant (h): 6.626 x 10-34 J*s Calculate the energy of a photon of radiation with a frequency of 4.3 x 1015 Hz. Photoelectric Effect • Einstein added on to Planck’s theory in 1905 • suggested that light can be viewed as stream of particles called photons – no mass and carry one quantum of energy – Energy depends on frequency Bohr Model • created by Niels Bohr (Danish physicist) in 1913 • linked atom’s electron with emission spectrum • electron can circle nucleus in certain paths, in which it has a certain amount of energy Bohr Model • Electron gains energy by moving to a higher rung on ladder • Loses energy by moving to lower rung on ladder Bohr Model a photon is released that has an energy equal to the difference between the initial and final energy orbits Bohr Model • problems: – True only for hydrogen atom – did not explain chemical behavior of atoms