This Credit By Exam Study Guide can help you prepare... what you need to study, review, and learn. To succeed,... Algebra 2B
advertisement

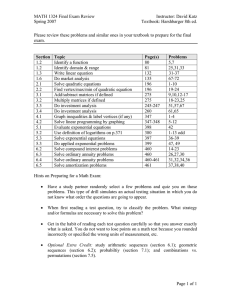
Algebra 2B Examination for Acceleration/Credit By Exam Study Guide This Credit By Exam Study Guide can help you prepare for the exam by giving you an idea of what you need to study, review, and learn. To succeed, you should be thoroughly familiar with the subject matter before you attempt to take the exam. Every question that appears on the Credit by Exam/Examination for Acceleration is grounded in the knowledge and skills statements and student expectations within the state-mandated standards, the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS). It should be noted that an exam will not test every student expectation. However, it is important that students study and know the entire scope of the TEKS so that they can develop a complete understanding of the content. The CBE/EAs are a global exam grounded in the TEKS and are not designed to be a final exam for the University of Texas high school courses. You can view the TEKS for this exam online at http://www.tea.state.tx.us/teks/. Since questions are not taken from any one source, you can prepare by reviewing any of the state-adopted textbooks. About the exam The Credit By Exam consists of 40 multiple-choice questions that are equally weighted. You will be allowed 3 hours to take the exam and you will be allowed to use a graphing calculator. Materials Provided The proctor will give you scratch paper to use during this exam. There is no formula sheet for this exam. Concepts and Objectives The bulleted list and sample questions below may not refer to all the material that will be in the exam. This list only provides additional information for some of the student expectations tested in the Algebra 2 Second Semester Credit by Exam. The use of problem-solving skills is important; all problem-solving activities require more than one step. In addition, you may be asked to use algebra and arithmetic skills from previous math courses. To prepare for this exam refer to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skill for Algebra 1, Geometry, and Algebra 2. Ultimately, you should use the TEKS to guide your exam preparation. In Algebra 2B, you learned about rational functions, exponential and logarithmic functions, and conic sections. On the exam, you should be able to: • use the area formula for rectangles to write quadratic function rules and to solve problem situations • determine a possible quadratic equation given the zeros • determine the characteristics of the discriminant given a quadratic function rule or graph • determine if a quadratic equation has one, two, or no solutions The University of Texas at Austin Continuing and Innovative Education K-16 Education Center 1 ALG 2B CBE/EA Review Sheet • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • identify a rational function given words that describe a problem situation, a table, a graph, or a function rule use words to a describe a rational function given a table, a graph, or a function rule make a table of values for a rational function rule given words that describe a problem situation, a graph, or a function rule graph a rational function rule given words that describe a problem situation, a table, or a function rule write a rational function rule given words that describe a problem situation, a table, or a graph interpret the meaning of specific points that make a rational function true describe the domain and range of a rational function identify the dependent and independent variables of a rational function find the x-intercepts and y-intercepts for a given rational function find the vertical and horizontal asymptotes for a rational function describe how changing a rational function rule shifts the graph to the left or right and up or down from the parent function solve rational equations and inequalities by using graphical and symbolic methods write an exponential function rule and solve for specific values given a problem situation (for example, solve problems involving carbon-14 dating, population, compounded interest, and continuous compounded interest) interpret the meaning of specific points that make an exponential function rule true graph exponential functions describe how changing an exponential function rule shifts the graph to the left or right and up or down from the parent function simplify exponential expressions, including problems with fractions as exponents solve exponential equations graphically and symbolically, including problems with fractions as exponents find the inverse of an exponential or logarithmic function provide a table of values that represents the inverse of a logarithmic or exponential function graph the inverse of a logarithmic or exponential function rewrite exponential equations in logarithmic form rewrite logarithmic equations in exponential form find the value of logarithmic expressions estimate the value of logarithmic expressions use properties of logarithms to solve exponential and logarithmic equations describe the behavior of the graph of a logarithmic function with restrictions placed on the value of the base of the logarithm describe how changing a logarithmic function rule shifts the graph to the left or right and up or down from the parent function state the domain and range, the asymptotes, the x-intercepts and y-intercepts, and graph logarithmic functions use properties of logarithms to write expressions in a condensed form use properties of logarithms to solve problem situations (for example, population growth problems) identify conic section equations for circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas find the axis of symmetry, vertex, directrix, and focus for a parabola The University of Texas at Austin Continuing and Innovative Education K-16 Education Center 2 ALG 2B CBE/EA Review Sheet • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • write an equation for a parabola given the focus and directrix find the center, foci, and vertices on the major axis for an ellipse write an equation for a ellipse given the vertex, center and focus find the center and radius of a circle write an equation for a circle given the center and radius find the center, foci, vertices, and asymptotes for a hyperbola write an equation for a hyperbola given the vertex and focus graph circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas write equations in standard form for circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas solve problem situations that are described as a parabola identify quadratic or square root functions given words that describe a problem situation, a table, a graph, or a function rule use words to describe quadratic or square root functions given a table, a graph, or a function rule make a table of values for quadratic or square root functions given words that describe a problem situation, a graph, or a function rule graph quadratic or square root functions given words that describe a problem situation, a table, or a function rule write quadratic or square root function rules given words that describe a problem situation, a table, or a graph describe the domain and range of quadratic and square root functions describe how changing a quadratic or square root function rule shifts the graph to the left or the right, shifts the graph up or down, and dilates or compresses the graph solve quadratic and square root equations and inequalities by using graphical and symbolic methods find and graph the inverse function for a quadratic function or a square root function solve quadratic equations by factoring, graphing, using a table, completing the square, and the quadratic formula The University of Texas at Austin Continuing and Innovative Education K-16 Education Center 3 ALG 2B CBE/EA Review Sheet Sample Questions These sample questions will give you a better idea of the types of questions you can expect on the Credit By Exam. These questions are provided to illustrate the format of the exam; they are not a duplicate of the actual exam. In order to be successful on the exam, you must study and review all of the concepts listed above. Multiple-Choice This part contains 5 multiple-choice questions. Circle the letter of the correct response to each of the following questions. 1. What is the value of log24? A 6 B 8 1 C 5 D 2 2. What does the following equation represent? (x − 4)2 (y − 7)2 + =1 4 9 A B C D Circle Parabola Ellipse Hyperbola 3. Which rule best matches the data in the table below? x 0 4 15 36 y 2 10 17.49 26 A y = 8x + 3 B y=4 x +2 1 C y= x−4 D y = x2 + 2x – 4 The University of Texas at Austin Continuing and Innovative Education K-16 Education Center 4 ALG 2B CBE/EA Review Sheet (x + 3)2 y2 4. Which graph represents the equation – = 1? 4 25 A C B D 5. Ricardo has a rectangular garden. The width of the garden is two feet shorter than the length. Which equation represents the area of the garden? A A = 2x2 + 3 B A = 2x + 3 3 C A= 5−x D A = x2 – 2x The University of Texas at Austin Continuing and Innovative Education K-16 Education Center 5 ALG 2B CBE/EA Review Sheet Answer Key Item Number 1 2 3 4 5 Correct Answer D C B D D TEKS (b)(2A.11)(D) (b)(2A.5)(D) (b)(2A.9)(B) (b)(2A.5)(B) (b)(2A.8)(A) The University of Texas at Austin Continuing and Innovative Education K-16 Education Center 6