8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS
advertisement

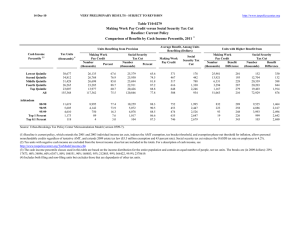
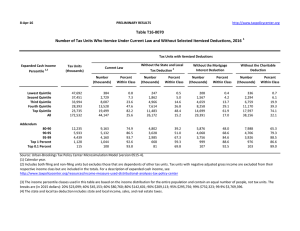
8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Click on PDF or Excel link above for additional tables containing more detail and breakdowns by filing status and demographic groups. Table T10-0035 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile, 2012 Summary Table 4 Percent of Tax Units 2,3 Cash Income Percentile With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax 5 Income Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change ($) Average Federal Tax Rate Change (% Points) 6 Under the Proposal 30.4 40.0 41.0 36.5 18.7 33.7 12.7 20.3 25.2 35.0 62.5 28.0 1.9 1.0 0.5 0.2 -2.1 -0.8 -10.7 -11.4 -9.1 -6.0 137.2 100.0 -210 -248 -216 -171 4,468 482 -1.8 -0.9 -0.4 -0.2 1.6 0.6 2.8 9.3 15.8 18.9 26.6 21.3 24.9 18.3 7.7 2.0 0.0 49.9 64.1 83.2 97.4 99.9 0.1 0.0 -1.0 -6.0 -7.7 -2.3 0.2 16.1 123.3 70.4 -151 23 2,621 78,620 445,271 -0.1 0.0 0.8 4.3 5.3 21.5 22.9 25.6 33.0 36.5 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4. Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 5.0 Proposal: 4.0 (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $19,356, 40% $37,493, 60% $65,656, 80% $111,659, 90% $161,739, 95% $226,402, 99% $599,181, 99.9% $2,727,123. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0035 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile, 2012 Detail Table Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate 6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 30.4 40.0 41.0 36.5 18.7 33.7 12.7 20.3 25.2 35.0 62.5 28.0 1.9 1.0 0.5 0.2 -2.1 -0.8 -10.7 -11.4 -9.1 -6.0 137.2 100.0 -210 -248 -216 -171 4,468 482 -39.6 -8.5 -2.6 -1.0 6.4 3.1 -0.3 -0.5 -0.6 -0.7 2.1 0.0 0.5 3.7 10.3 17.6 67.9 100.0 -1.8 -0.9 -0.4 -0.2 1.6 0.6 2.8 9.3 15.8 18.9 26.6 21.3 24.9 18.3 7.7 2.0 0.0 49.9 64.1 83.2 97.4 99.9 0.1 0.0 -1.0 -6.0 -7.7 -2.3 0.2 16.1 123.3 70.4 -151 23 2,621 78,620 445,271 -0.5 0.1 3.1 15.0 17.1 -0.5 -0.3 0.0 2.9 1.7 13.7 10.1 16.1 28.0 14.3 -0.1 0.0 0.8 4.3 5.3 21.5 22.9 25.6 33.0 36.5 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Number (thousands) Percent of Total Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of PreTax Income Share of PostTax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total 38,450 34,947 31,868 26,646 23,298 157,348 24.4 22.2 20.3 16.9 14.8 100.0 11,600 28,852 52,224 88,978 280,229 76,169 531 2,929 8,458 16,997 69,940 15,750 11,069 25,923 43,766 71,981 210,289 60,419 4.6 10.2 16.2 19.1 25.0 20.7 3.7 8.4 13.9 19.8 54.5 100.0 4.5 9.5 14.7 20.2 51.5 100.0 0.8 4.1 10.9 18.3 65.8 100.0 11,720 5,734 4,655 1,190 120 7.5 3.6 3.0 0.8 0.1 138,385 196,549 345,574 1,825,188 8,367,274 29,910 44,948 85,734 522,940 2,606,444 108,475 151,600 259,840 1,302,248 5,760,830 21.6 22.9 24.8 28.7 31.2 13.5 9.4 13.4 18.1 8.4 13.4 9.1 12.7 16.3 7.3 14.2 10.4 16.1 25.1 12.6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 5.0 Proposal: 4.0 (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $19,356, 40% $37,493, 60% $65,656, 80% $111,659, 90% $161,739, 95% $226,402, 99% $599,181, 99.9% $2,727,123. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0035 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 Detail Table Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 38.0 37.9 43.7 34.2 15.3 33.7 9.6 18.2 22.2 32.6 60.9 28.0 2.9 1.0 0.5 0.3 -2.0 -0.8 -13.3 -9.8 -8.7 -6.9 138.7 100.0 -318 -229 -211 -174 3,514 482 -283.2 -10.5 -3.1 -1.2 6.0 3.1 -0.4 -0.4 -0.5 -0.7 2.0 0.0 -0.3 2.5 8.1 16.7 72.8 100.0 -2.9 -0.9 -0.5 -0.2 1.5 0.6 -1.9 7.5 14.4 18.4 26.4 21.3 20.9 13.3 6.9 1.7 0.1 48.0 63.2 81.6 97.3 99.9 0.1 -0.1 -0.9 -5.8 -7.6 -2.4 0.6 16.0 124.5 72.3 -121 60 2,042 65,753 384,868 -0.5 0.2 2.8 14.6 16.9 -0.5 -0.3 0.0 2.9 1.8 15.0 11.4 17.3 29.1 14.8 -0.1 0.0 0.7 4.2 5.2 21.7 23.1 25.3 32.6 36.1 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Number (thousands) Percent of Total Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 31,706 32,349 31,237 29,980 29,936 157,348 20.2 20.6 19.9 19.1 19.0 100.0 10,935 26,208 46,322 77,565 235,547 76,169 112 2,184 6,866 14,437 58,562 15,750 10,823 24,023 39,456 63,128 176,985 60,419 1.0 8.3 14.8 18.6 24.9 20.7 2.9 7.1 12.1 19.4 58.8 100.0 3.6 8.2 13.0 19.9 55.7 100.0 0.1 2.9 8.7 17.5 70.7 100.0 15,019 7,540 5,940 1,436 142 9.6 4.8 3.8 0.9 0.1 117,658 167,170 294,212 1,584,726 7,360,192 25,601 38,625 72,379 450,784 2,275,425 92,057 128,545 221,833 1,133,941 5,084,768 21.8 23.1 24.6 28.5 30.9 14.7 10.5 14.6 19.0 8.7 14.5 10.2 13.9 17.1 7.6 15.5 11.8 17.4 26.1 13.1 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 5.0 Proposal: 4.0 (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0035 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 Detail Table - Single Tax Units Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Share of Federal Taxes Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate 6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 20.7 20.9 33.0 19.0 10.3 21.3 10.6 22.7 24.9 34.8 56.9 26.7 1.5 0.5 0.4 0.2 -1.4 -0.4 -20.1 -14.9 -18.1 -8.4 162.3 100.0 -113 -91 -123 -70 1,610 138 -19.0 -4.3 -2.2 -0.6 4.1 1.5 -0.3 -0.3 -0.5 -0.4 1.5 0.0 1.3 4.9 12.3 20.7 60.8 100.0 -1.3 -0.5 -0.4 -0.1 1.1 0.3 5.7 10.1 16.4 20.5 26.6 21.1 13.7 7.8 5.7 2.0 0.0 45.3 59.8 78.0 96.5 99.9 0.1 -0.1 -0.5 -5.2 -7.7 -2.0 2.9 15.2 146.2 88.9 -37 118 803 38,533 267,282 -0.2 0.4 1.6 12.0 15.1 -0.3 -0.1 0.0 1.9 1.2 15.5 10.8 14.2 20.3 10.1 0.0 0.1 0.4 3.6 5.1 23.2 24.4 24.7 33.9 38.9 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 20121 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 16,972 15,474 14,005 11,543 9,596 68,932 24.6 22.5 20.3 16.8 13.9 100.0 8,380 19,970 34,261 55,833 151,979 43,878 591 2,115 5,725 11,507 38,836 9,128 7,789 17,855 28,536 44,326 113,142 34,749 5,066 2,373 1,795 361 32 7.4 3.4 2.6 0.5 0.1 84,037 119,032 204,548 1,060,631 5,243,107 19,525 28,942 49,619 321,259 1,771,848 64,512 90,090 154,929 739,373 3,471,259 Share of PreTax Income Share of PostTax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total 7.1 10.6 16.7 20.6 25.6 20.8 4.7 10.2 15.9 21.3 48.2 100.0 5.5 11.5 16.7 21.4 45.3 100.0 1.6 5.2 12.7 21.1 59.2 100.0 23.2 24.3 24.3 30.3 33.8 14.1 9.3 12.1 12.7 5.5 13.6 8.9 11.6 11.1 4.6 15.7 10.9 14.2 18.4 8.9 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0035 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 Detail Table - Married Tax Units Filing Jointly Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Share of Federal Taxes Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate 6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 44.4 52.1 52.2 45.7 17.9 38.9 15.3 20.6 25.2 33.3 64.2 37.1 2.9 1.2 0.5 0.3 -2.1 -1.2 -3.9 -4.7 -4.4 -5.0 118.0 100.0 -423 -371 -275 -237 4,510 1,159 -362.3 -14.5 -3.5 -1.4 6.5 4.3 -0.2 -0.3 -0.4 -0.8 1.7 0.0 -0.1 1.1 5.1 14.3 79.5 100.0 -2.9 -1.1 -0.5 -0.3 1.6 0.9 -2.1 6.6 12.8 17.3 26.2 22.4 25.5 15.7 7.7 1.7 0.1 50.9 65.8 84.0 97.5 99.9 0.2 0.0 -1.0 -5.9 -7.5 -2.2 0.2 14.4 105.6 59.5 -178 34 2,634 73,956 413,532 -0.6 0.1 3.2 15.1 17.3 -0.7 -0.5 -0.2 3.1 1.8 14.9 12.2 19.4 33.1 16.6 -0.1 0.0 0.8 4.2 5.2 21.0 22.7 25.5 32.2 35.6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 20121 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 6,622 8,956 11,470 15,032 18,609 61,357 10.8 14.6 18.7 24.5 30.3 100.0 14,526 33,405 59,671 95,023 281,842 126,020 117 2,562 7,909 16,631 69,430 27,037 14,409 30,843 51,762 78,392 212,412 98,983 8,860 4,843 3,890 1,015 102 14.4 7.9 6.3 1.7 0.2 138,312 192,091 337,723 1,748,464 7,890,377 29,238 43,636 83,500 489,332 2,392,764 109,074 148,455 254,223 1,259,132 5,497,613 Share of PreTax Income Share of PostTax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total 0.8 7.7 13.3 17.5 24.6 21.5 1.2 3.9 8.9 18.5 67.8 100.0 1.6 4.6 9.8 19.4 65.1 100.0 0.1 1.4 5.5 15.1 77.9 100.0 21.1 22.7 24.7 28.0 30.3 15.9 12.0 17.0 23.0 10.5 15.9 11.8 16.3 21.1 9.3 15.6 12.7 19.6 30.0 14.8 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0035 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 Detail Table - Head of Household Tax Units Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Share of Federal Taxes Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate 6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 70.7 56.6 56.2 39.4 16.2 56.8 2.7 6.0 9.7 21.8 43.3 9.4 4.7 1.2 0.8 0.5 -1.2 1.0 63.4 31.3 20.0 9.8 -24.6 100.0 -681 -352 -331 -297 1,667 -344 70.6 -19.7 -4.4 -2.0 3.9 -6.0 -4.4 -1.4 0.5 1.3 4.0 0.0 -9.8 8.2 28.1 31.0 42.4 100.0 -5.1 -1.2 -0.7 -0.4 0.9 -0.8 -12.2 4.7 14.4 19.1 25.2 12.8 18.8 17.9 4.9 0.1 0.5 35.5 46.3 65.7 98.0 99.4 0.1 0.1 -0.6 -5.7 -7.5 0.7 0.2 -2.8 -22.7 -12.4 -73 -56 1,342 57,824 360,211 -0.3 -0.2 2.1 14.2 16.7 0.9 0.4 0.7 2.1 1.1 15.7 6.3 8.7 11.7 5.6 -0.1 0.0 0.5 4.1 5.2 22.7 23.2 23.8 32.8 36.2 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 20121 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 7,840 7,497 5,095 2,777 1,242 24,547 31.9 30.5 20.8 11.3 5.1 100.0 13,490 30,617 50,275 76,881 178,521 41,760 -965 1,792 7,575 14,983 43,239 5,698 14,455 28,825 42,700 61,898 135,282 36,062 805 232 173 33 3 3.3 0.9 0.7 0.1 0.0 112,763 154,893 278,418 1,423,600 6,950,503 25,684 36,005 64,856 408,525 2,156,597 87,079 118,888 213,562 1,015,074 4,793,906 Share of PreTax Income Share of PostTax Income Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total Percent of Total Percent of Total -7.2 5.9 15.1 19.5 24.2 13.6 10.3 22.4 25.0 20.8 21.6 100.0 12.8 24.4 24.6 19.4 19.0 100.0 -5.4 9.6 27.6 29.8 38.4 100.0 22.8 23.3 23.3 28.7 31.0 8.9 3.5 4.7 4.6 2.0 7.9 3.1 4.2 3.8 1.6 14.8 6.0 8.0 9.7 4.5 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0035 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 Detail Table - Tax Units with Children Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 78.3 71.9 66.1 50.1 24.0 59.3 2.0 4.4 9.8 22.9 56.9 17.7 5.0 1.7 0.8 0.4 -2.2 -0.6 -39.6 -26.9 -20.3 -17.1 204.0 100.0 -808 -538 -409 -362 5,076 421 62.1 -26.4 -4.4 -1.9 6.5 2.2 -0.8 -0.6 -0.7 -0.8 2.9 0.0 -2.2 1.6 9.5 19.4 71.7 100.0 -5.5 -1.6 -0.7 -0.4 1.7 0.4 -14.3 4.3 14.4 18.6 27.4 20.7 33.3 21.1 7.1 1.1 0.0 42.2 59.4 85.3 98.6 99.9 0.3 0.1 -1.5 -6.8 -8.0 -8.2 -1.1 33.4 179.8 93.9 -385 -114 4,416 99,478 539,330 -1.1 -0.2 4.2 16.1 17.5 -0.5 -0.3 0.4 3.3 1.8 15.8 10.8 17.5 27.6 13.4 -0.2 -0.1 1.1 4.8 5.5 22.1 23.7 27.1 34.4 36.8 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 10,133 10,359 10,251 9,800 8,315 49,155 20.6 21.1 20.9 19.9 16.9 100.0 14,723 34,672 62,298 103,142 306,063 95,419 -1,302 2,038 9,395 19,572 78,732 19,366 16,025 32,634 52,903 83,570 227,331 76,053 4,398 1,976 1,567 374 36 9.0 4.0 3.2 0.8 0.1 157,496 224,546 400,356 2,088,455 9,839,694 35,216 53,216 104,147 618,704 3,077,034 122,280 171,329 296,208 1,469,751 6,762,660 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total -8.8 5.9 15.1 19.0 25.7 20.3 3.2 7.7 13.6 21.6 54.3 100.0 4.3 9.0 14.5 21.9 50.6 100.0 -1.4 2.2 10.1 20.2 68.8 100.0 22.4 23.7 26.0 29.6 31.3 14.8 9.5 13.4 16.7 7.6 14.4 9.1 12.4 14.7 6.5 16.3 11.1 17.2 24.3 11.7 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Note: Tax units with children are those claiming an exemption for children at home or away from home. (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 8-Feb-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0035 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 Detail Table - Elderly Tax Units Percent of Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 With Tax Cut Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 5.8 5.6 9.4 13.5 4.6 7.6 24.2 40.8 59.9 69.2 87.5 55.3 0.2 0.0 -0.1 -0.1 -2.4 -1.4 -0.3 0.2 0.6 1.1 98.3 100.0 -17 5 29 55 4,727 884 -6.5 0.6 1.2 0.7 8.0 6.8 0.0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.6 0.9 0.0 0.3 1.7 3.4 10.1 84.6 100.0 -0.2 0.0 0.1 0.1 1.8 1.2 2.3 3.8 5.8 11.1 24.8 18.3 6.1 4.9 2.8 1.5 0.0 81.9 88.1 93.6 97.2 99.8 -0.3 -0.4 -0.9 -5.2 -7.4 2.1 2.5 9.6 84.1 51.8 230 498 1,863 52,378 329,614 1.4 1.8 3.2 13.2 16.1 -0.5 -0.5 -0.7 2.6 1.9 9.5 9.2 19.8 46.1 23.8 0.2 0.3 0.7 3.8 5.1 15.7 18.6 22.5 32.2 36.6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2012 1 Tax Units4 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 5,016 8,213 5,981 5,495 5,617 30,543 16.4 26.9 19.6 18.0 18.4 100.0 10,899 22,528 41,094 70,238 257,048 75,737 262 845 2,350 7,708 59,067 12,990 10,637 21,683 38,744 62,530 197,981 62,747 2,427 1,362 1,394 434 42 8.0 4.5 4.6 1.4 0.1 105,444 153,103 267,882 1,396,961 6,520,091 16,363 27,984 58,445 397,639 2,053,637 89,081 125,118 209,437 999,322 4,466,454 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 2.4 3.8 5.7 11.0 23.0 17.2 2.4 8.0 10.6 16.7 62.4 100.0 2.8 9.3 12.1 17.9 58.0 100.0 0.3 1.8 3.5 10.7 83.6 100.0 15.5 18.3 21.8 28.5 31.5 11.1 9.0 16.1 26.2 12.0 11.3 8.9 15.2 22.6 9.9 10.0 9.6 20.5 43.5 21.9 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Note: Elderly tax units are those with either head or spouse (if filing jointly) age 65 or older. (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,219, 40% $24,782, 60% $41,864, 80% $68,188, 90% $97,830, 95% $138,709, 99% $361,983, 99.9% $1,670,467. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income.