Chemical Reactions Notes Evidence and Energy
advertisement

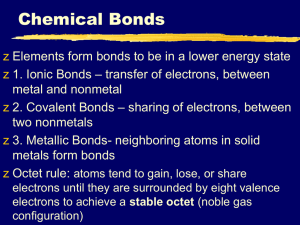
Chemical Reactions Notes Evidence and Energy Chemical vs. Physical Change • Physical change – anything that alters the form of a substance, but not the identity. • Ex:, molding clay, melting ice, mixing a milkshake, etc… • Chemical change – atoms rearrange and new substances are formed with new properties. • Ex:, cooking, digestion, rusting, burning candle Signs of a Chemical Change • 1. Color Change – leaves changing colors, bread browning in oven, copper tarnishing to green, eggs cooking and changing to white, etc… Other Signs of Chemical Change • 2. A precipitate forming – a solid that forms in a solution from 2 liquids. limewater + CO2 • 3. Gas Production Examples: Carbon dioxide produced from yeast in bread, baking soda and vinegar Other Changes • 4. Changes in temperature – Ex: hot pads, calcium chloride, sodium metal and water 5. Changes in properties • Baking a cake, texture, form and color changes. • Digestion – food changes from solids and is broken down into simplest forms. What’s Happening on the Atomic Scale: • Chemical reactions occur when chemical bonds are either formed or broken apart. • Chemical bonds are the glue which keep atoms together. • Some chemical bonds are easy to break, some are strong and difficult to change. • Ionic bonds are stronger than covalent bonds Subscript Chemical Equations Coefficient • 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O • Reactant – the materials you start with – located to the left of the arrow • Product – substances formed in a chem. Reaction • Subscripts - # of atoms of an element in a molecule. • Coefficients - # of molecules The Law of Conservation of mass • During a chem. Rxn, matter is neither created or destroyed. • Mass of atoms of the reactants always equals the mass of Atoms of the products Bonding NaCl = ionic bond, sodium gives valence e-, chlorine takes valence e- Water molecule – hydrogen atoms share its electrons with the 1 oxygen atom, and vice versa • When elements form compounds, they either take, give, or share electrons • Ionic bonds = give or take electrons • Covalent bonds = share electrons Example of Ionic Bond Example of Covalent Bond Energy and Chemical Reactions • Every Chemical reaction involves a change in energy. Some release energy, while others absorb energy Exothermic • A reaction that releases energy in the form of heat Endothermic Reaction • A reaction that absorbs energy and therefore feels cool to the touch. Rates of Reaction • Concentration – increase amount of reactant speeds up reaction • Surface area – increase surface area, increase speed of reaction • Temperature – increase temp, increase reaction Rates of Reaction • Catalyst- speeds up reactions by lowering activation energy It’s the match.com of chemicals! • Inhibitors – slows reaction down by raising activation energy. Ex: food preservatives. • Activation energy – energy required to get a reaction started.