Chapter 2 – Nature of Matter

Chapter 2 – Nature of Matter
Chapter 2 – Nature of Matter
Section 1 – Describing Matter, p. 58 - 67
Guide for Reading
What kinds of properties are used to describe matter?
What are elements, and how do they relate to compounds?
What are the properties of a mixture?
Standards
8.3.b – Students know that compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and that compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements.
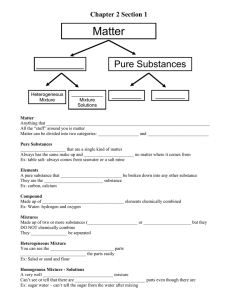
Matter
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
All the “stuff ” around you is matter
Matter can be divided into two categories: mixtures and pure substances
Pure Substances
Substances that are a single kind of matter
Always has the same make up and properties no matter where it comes from
Ex: table salt- always comes from seawater or a salt mine
Elements
A pure substance that CANNOT be broken down into any other substance
They are the simplest substance
Ex: carbon, calcium
Compound
Made up of two or more elements chemically combined
Ex: Water- hydrogen and oxygen
Mixtures
Made up of two or more substances
(elements or compounds) but they DO
NOT chemically combine
They CAN be separated
Granite Rock
Heterogeneous Mixture
You can see the different parts
Separate the parts easily
Ex: Salad or sand and flour
Homogenous Mix - Solutions
A very well mixed mixture
Can’t see or tell that there are different parts even though there are
Ex: sugar water – can’t tell the sugar from the water after mixing
Question 1: c.
d.
a.
b.
What would salt water be considered?
An element
A compound
A solution or homogenous mixture
A heterogeneous mixture
Question 2:
Which is an example of a heterogeneous mixture?
a.
b.
Fruit punch
Sand and rocks c.
d.
Sugar water
Kool-Aid
Question 3:
Matter can be divided into two categories, what are they?
Mixtures and Pure Substances
Properties of Matter
Every form of matter has 2 kinds of properties:
Physical Properties
Chemical Properties
Physical Property
A characteristic of a substance that can be observed without changing it into another substance.
Used to classify matter
Examples include: color, texture, melting point, density, etc.
Chemical Property
A characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into different substances.
To observe chemical properties, you must try to change it to another substance.
Cannot be observed by just looking at the substance