ABSTRACT: This paper presents the experimental and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)...
advertisement

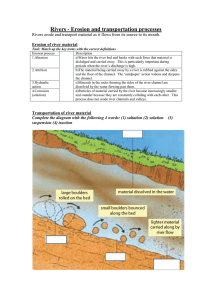
ABSTRACT: This paper presents the experimental and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) failure analysis of API 5L X42 NPS8 (NPS8) carbon steel pipe seriously eroded due to slurry erosion. The results of a previous study revealed that continuous impaction of water soil slurry causes rapid thinning of pipe wall led to its failure. In the current study, experimental and CFD methods were used to provide a greater understanding of the erosion behaviour. Appropriate modelling of jet flow patterns, velocity distributions and strain rates along the pipes have been successfully conducted. Photomicrographs of the impacted surfaces show that shallow ploughing and indentation were identified as the erosion mechanisms. CFD simulation results indicated that the highest strain rate region occurs above and below the impact point which closely corresponds to the failure region found from the experimental study.