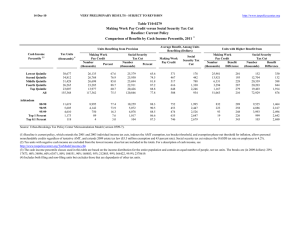
Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile, 2014
advertisement

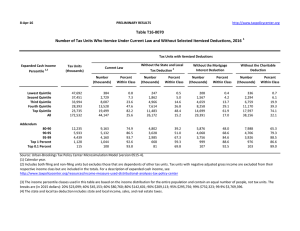
12-Oct-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Click on PDF or Excel link above for additional tables containing more detail and breakdowns by filing status and demographic groups. Table T10-0244 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile, 2014 1 Summary Table Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent of Tax Units With Tax Cut 4 With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax 5 Income Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change ($) Average Federal Tax Rate Change (% Points) 6 Under the Proposal 30.1 38.8 39.7 33.7 17.2 32.4 13.2 21.0 26.3 37.7 65.8 29.5 1.9 0.9 0.5 0.2 -2.3 -0.9 -9.2 -9.2 -7.7 -4.7 130.7 100.0 -217 -236 -219 -159 5,100 576 -1.8 -0.8 -0.4 -0.2 1.7 0.7 2.9 9.4 16.0 19.2 26.5 21.4 22.9 17.1 7.1 1.6 0.0 54.2 67.3 85.4 97.8 99.9 0.1 -0.1 -1.2 -6.2 -7.8 -2.1 0.6 16.9 115.3 64.8 -160 91 3,316 88,500 491,995 -0.1 0.0 0.9 4.5 5.4 21.8 23.2 25.8 32.4 35.6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 5.7 Proposal: 4.6 (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $19,925, 40% $38,371, 60% $67,991, 80% $116,859, 90% $169,290, 95% $237,098, 99% $632,966, 99.9% $2,923,051. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 12-Oct-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0244 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile, 2014 Detail Table Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent of Tax Units4 With Tax Cut With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 30.1 38.8 39.7 33.7 17.2 32.4 13.2 21.0 26.3 37.7 65.8 29.5 1.9 0.9 0.5 0.2 -2.3 -0.9 -9.2 -9.2 -7.7 -4.7 130.7 100.0 -217 -236 -219 -159 5,100 576 -37.7 -7.6 -2.4 -0.9 6.8 3.4 -0.3 -0.4 -0.6 -0.8 2.2 0.0 0.5 3.7 10.2 17.7 67.8 100.0 -1.8 -0.8 -0.4 -0.2 1.7 0.7 2.9 9.4 16.0 19.2 26.5 21.4 22.9 17.1 7.1 1.6 0.0 54.2 67.3 85.4 97.8 99.9 0.1 -0.1 -1.2 -6.2 -7.8 -2.1 0.6 16.9 115.3 64.8 -160 91 3,316 88,500 491,995 -0.5 0.2 3.6 15.9 18.1 -0.5 -0.3 0.0 3.0 1.7 13.8 10.2 16.1 27.7 14.0 -0.1 0.0 0.9 4.5 5.4 21.8 23.2 25.8 32.4 35.6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile, 2014 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Tax Units4 Number (thousands) Percent of Total Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 39,416 36,129 32,694 27,378 23,893 161,771 24.4 22.3 20.2 16.9 14.8 100.0 12,314 30,366 55,193 95,202 301,906 81,418 575 3,098 9,023 18,410 75,034 16,876 11,739 27,268 46,169 76,793 226,872 64,542 4.7 10.2 16.4 19.3 24.9 20.7 3.7 8.3 13.7 19.8 54.8 100.0 4.4 9.4 14.5 20.1 51.9 100.0 0.8 4.1 10.8 18.5 65.7 100.0 12,052 5,875 4,752 1,215 123 7.5 3.6 2.9 0.8 0.1 148,490 211,074 372,043 1,988,880 9,038,534 32,499 48,856 92,545 555,126 2,721,914 115,991 162,218 279,498 1,433,754 6,316,620 21.9 23.2 24.9 27.9 30.1 13.6 9.4 13.4 18.3 8.4 13.4 9.1 12.7 16.7 7.4 14.4 10.5 16.1 24.7 12.2 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 5.7 Proposal: 4.6 (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $19,925, 40% $38,371, 60% $67,991, 80% $116,859, 90% $169,290, 95% $237,098, 99% $632,966, 99.9% $2,923,051. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 12-Oct-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0244 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Detail Table Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent of Tax Units4 With Tax Cut With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 37.7 36.5 42.5 31.5 14.3 32.4 10.3 18.6 23.5 35.2 63.8 29.5 2.8 0.9 0.5 0.3 -2.1 -0.9 -11.2 -8.0 -7.1 -5.9 132.2 100.0 -321 -221 -206 -180 4,030 576 -198.6 -9.3 -2.8 -1.2 6.4 3.4 -0.4 -0.4 -0.5 -0.8 2.0 0.0 -0.2 2.6 8.1 16.8 72.6 100.0 -2.8 -0.8 -0.4 -0.2 1.6 0.7 -1.4 7.8 14.5 18.7 26.4 21.4 19.7 12.1 6.6 1.3 0.0 51.3 66.6 83.6 97.9 99.9 0.1 -0.1 -1.1 -5.9 -7.6 -1.9 0.9 16.7 116.5 66.7 -117 111 2,572 74,327 426,172 -0.4 0.3 3.3 15.5 17.9 -0.6 -0.4 0.0 3.0 1.8 15.1 11.5 17.4 28.7 14.5 -0.1 0.1 0.8 4.3 5.4 22.0 23.4 25.5 32.0 35.3 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Tax Units4 Number (thousands) Percent of Total Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Rate6 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 32,445 33,595 32,248 30,634 30,589 161,771 20.1 20.8 19.9 18.9 18.9 100.0 11,625 27,586 48,898 83,092 254,362 81,418 162 2,363 7,274 15,682 62,991 16,876 11,463 25,223 41,623 67,410 191,371 64,542 1.4 8.6 14.9 18.9 24.8 20.7 2.9 7.0 12.0 19.3 59.1 100.0 3.6 8.1 12.9 19.8 56.1 100.0 0.2 2.9 8.6 17.6 70.6 100.0 15,343 7,725 6,061 1,461 146 9.5 4.8 3.8 0.9 0.1 126,648 179,728 316,716 1,731,056 7,958,455 27,959 41,885 78,230 479,127 2,379,965 98,688 137,842 238,486 1,251,929 5,578,490 22.1 23.3 24.7 27.7 29.9 14.8 10.5 14.6 19.2 8.8 14.5 10.2 13.8 17.5 7.8 15.7 11.9 17.4 25.7 12.7 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Number of AMT Taxpayers (millions). Baseline: 5.7 Proposal: 4.6 (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,694, 40% $25,631, 60% $43,537, 80% $71,347, 90% $102,829, 95% $145,557, 99% $382,124, 99.9% $1,787,588. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 12-Oct-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0244 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Detail Table - Single Tax Units Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent of Tax Units4 With Tax Cut With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 20.7 20.4 32.2 17.9 10.2 20.9 11.4 22.7 26.5 36.2 59.1 27.6 1.4 0.5 0.4 0.2 -1.5 -0.5 -17.2 -13.0 -14.4 -8.1 153.4 100.0 -118 -93 -117 -82 1,863 166 -18.5 -4.3 -2.0 -0.7 4.5 1.7 -0.3 -0.3 -0.5 -0.5 1.6 0.0 1.3 4.9 12.3 20.9 60.6 100.0 -1.3 -0.4 -0.3 -0.1 1.1 0.4 5.8 9.7 16.1 20.8 26.6 21.0 13.8 7.3 5.8 1.8 0.0 47.3 63.0 79.7 97.3 99.9 0.1 -0.2 -0.6 -5.4 -7.8 -1.5 3.2 15.7 135.9 81.4 -34 155 1,023 44,534 300,169 -0.2 0.5 1.9 13.0 16.0 -0.3 -0.1 0.0 2.0 1.2 15.5 11.0 14.2 20.0 10.0 0.0 0.1 0.5 3.8 5.3 23.5 24.4 24.8 33.2 38.2 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Tax Units4 Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 17,338 16,635 14,693 11,840 9,787 71,749 24.2 23.2 20.5 16.5 13.6 100.0 8,939 21,188 36,403 59,738 164,155 46,638 638 2,156 5,989 12,480 41,750 9,646 8,302 19,032 30,415 47,258 122,405 36,992 5,137 2,463 1,825 363 32 7.2 3.4 2.5 0.5 0.0 90,448 128,290 220,487 1,167,870 5,717,077 21,319 31,141 53,592 343,469 1,880,713 69,129 97,149 166,895 824,400 3,836,364 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 7.1 10.2 16.5 20.9 25.4 20.7 4.6 10.5 16.0 21.1 48.0 100.0 5.4 11.9 16.8 21.1 45.1 100.0 1.6 5.2 12.7 21.4 59.0 100.0 23.6 24.3 24.3 29.4 32.9 13.9 9.4 12.0 12.7 5.5 13.4 9.0 11.5 11.3 4.7 15.8 11.1 14.1 18.0 8.8 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,694, 40% $25,631, 60% $43,537, 80% $71,347, 90% $102,829, 95% $145,557, 99% $382,124, 99.9% $1,787,588. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 12-Oct-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0244 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Detail Table - Married Tax Units Filing Jointly Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent of Tax Units4 With Tax Cut With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 43.7 50.4 50.5 41.6 16.6 36.7 16.0 21.8 26.4 37.0 67.5 39.7 2.7 1.1 0.5 0.3 -2.3 -1.3 -3.2 -3.7 -3.6 -4.2 114.6 100.0 -415 -357 -266 -236 5,167 1,384 -200.4 -12.5 -3.2 -1.3 6.9 4.7 -0.2 -0.2 -0.4 -0.9 1.7 0.0 -0.1 1.2 4.9 14.2 79.6 100.0 -2.7 -1.0 -0.4 -0.2 1.7 1.0 -1.4 7.1 13.0 17.5 26.3 22.6 23.8 14.1 7.2 1.3 0.1 54.9 69.3 86.0 98.0 99.9 0.2 -0.1 -1.2 -6.0 -7.6 -1.8 0.5 15.4 100.6 55.9 -174 93 3,314 83,187 455,802 -0.6 0.2 3.7 16.0 18.3 -0.8 -0.6 -0.2 3.2 1.9 15.1 12.3 19.5 32.7 16.2 -0.1 0.1 0.9 4.4 5.4 21.3 23.0 25.8 31.6 34.7 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Tax Units4 Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 6,636 8,855 11,532 15,214 19,015 61,925 10.7 14.3 18.6 24.6 30.7 100.0 15,449 35,411 63,113 102,030 304,240 136,599 207 2,856 8,442 18,069 74,681 29,414 15,242 32,555 54,671 83,961 229,558 107,185 9,075 4,934 3,970 1,036 105 14.7 8.0 6.4 1.7 0.2 148,661 206,766 363,199 1,904,848 8,500,613 31,899 47,507 90,240 519,102 2,489,680 116,762 159,259 272,959 1,385,746 6,010,932 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 1.3 8.1 13.4 17.7 24.6 21.5 1.2 3.7 8.6 18.4 68.4 100.0 1.5 4.3 9.5 19.2 65.8 100.0 0.1 1.4 5.3 15.1 78.0 100.0 21.5 23.0 24.9 27.3 29.3 16.0 12.1 17.1 23.3 10.6 16.0 11.8 16.3 21.6 9.5 15.9 12.9 19.7 29.5 14.4 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,694, 40% $25,631, 60% $43,537, 80% $71,347, 90% $102,829, 95% $145,557, 99% $382,124, 99.9% $1,787,588. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 12-Oct-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0244 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Detail Table - Head of Household Tax Units Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent of Tax Units4 With Tax Cut With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 69.4 55.7 55.6 37.3 13.2 55.6 3.2 6.2 10.5 24.0 48.0 10.3 4.5 1.2 0.8 0.5 -1.3 0.9 65.3 31.3 21.3 11.1 -29.1 100.0 -682 -349 -341 -325 1,934 -335 74.9 -16.1 -4.2 -2.0 4.1 -5.3 -3.9 -1.2 0.3 1.1 3.7 0.0 -8.5 9.1 27.4 30.9 41.0 100.0 -4.8 -1.1 -0.6 -0.4 1.0 -0.8 -11.2 5.6 14.7 19.5 25.3 13.4 14.5 17.2 5.1 0.0 0.1 40.3 51.8 68.7 98.3 99.3 0.1 0.0 -0.7 -5.8 -7.6 0.6 0.1 -3.7 -26.1 -13.8 -65 -20 1,700 63,664 403,713 -0.2 -0.1 2.4 15.0 17.7 0.8 0.3 0.7 2.0 1.0 15.2 6.1 8.6 11.2 5.1 -0.1 0.0 0.6 4.2 5.3 23.0 23.6 23.9 32.2 35.4 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Tax Units4 Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 8,213 7,711 5,352 2,936 1,291 25,605 32.1 30.1 20.9 11.5 5.0 100.0 14,265 32,535 53,424 82,768 193,413 44,717 -911 2,160 8,207 16,491 46,893 6,333 15,176 30,375 45,217 66,277 146,520 38,385 836 234 185 35 3 3.3 0.9 0.7 0.1 0.0 121,470 168,242 298,680 1,516,552 7,596,169 27,974 39,746 69,726 423,877 2,283,498 93,497 128,496 228,954 1,092,675 5,312,671 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total -6.4 6.6 15.4 19.9 24.3 14.2 10.2 21.9 25.0 21.2 21.8 100.0 12.7 23.8 24.6 19.8 19.2 100.0 -4.6 10.3 27.1 29.9 37.3 100.0 23.0 23.6 23.3 28.0 30.1 8.9 3.4 4.8 4.7 2.0 8.0 3.1 4.3 3.9 1.6 14.4 5.7 8.0 9.2 4.1 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,694, 40% $25,631, 60% $43,537, 80% $71,347, 90% $102,829, 95% $145,557, 99% $382,124, 99.9% $1,787,588. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 12-Oct-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0244 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Detail Table - Tax Units with Children Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent of Tax Units4 With Tax Cut With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 78.3 70.4 64.3 46.9 22.1 57.6 2.1 4.7 10.8 25.7 60.8 19.2 4.8 1.5 0.7 0.4 -2.4 -0.7 -31.0 -20.1 -15.7 -14.4 181.2 100.0 -819 -523 -411 -389 5,805 544 64.9 -21.1 -4.0 -1.8 6.8 2.6 -0.7 -0.6 -0.7 -0.9 2.8 0.0 -2.0 1.9 9.4 19.5 71.1 100.0 -5.2 -1.4 -0.6 -0.4 1.8 0.5 -13.3 5.3 14.8 19.1 27.6 21.2 31.1 18.8 5.9 0.9 0.0 46.6 64.1 87.6 98.4 100.0 0.3 0.0 -1.7 -6.9 -8.1 -6.4 -0.3 32.8 155.1 79.3 -389 -34 5,547 109,678 594,754 -1.0 -0.1 4.9 16.9 18.5 -0.6 -0.3 0.4 3.3 1.7 15.8 10.8 17.6 27.0 12.7 -0.2 0.0 1.3 4.9 5.6 22.6 24.1 27.5 33.9 35.9 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Tax Units4 Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 10,239 10,393 10,382 10,009 8,454 49,780 20.6 20.9 20.9 20.1 17.0 100.0 15,665 36,734 65,963 110,334 330,139 102,631 -1,263 2,474 10,194 21,430 85,133 21,174 16,927 34,260 55,769 88,904 245,006 81,457 4,468 2,003 1,599 383 36 9.0 4.0 3.2 0.8 0.1 169,045 241,711 432,254 2,245,797 10,608,037 38,552 58,220 113,488 650,973 3,216,198 130,493 183,491 318,767 1,594,824 7,391,838 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total -8.1 6.7 15.5 19.4 25.8 20.6 3.1 7.5 13.4 21.6 54.6 100.0 4.3 8.8 14.3 22.0 51.1 100.0 -1.2 2.4 10.0 20.4 68.3 100.0 22.8 24.1 26.3 29.0 30.3 14.8 9.5 13.5 16.8 7.5 14.4 9.1 12.6 15.1 6.6 16.3 11.1 17.2 23.7 11.0 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Note: Tax units with children are those claiming an exemption for children at home or away from home. (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,694, 40% $25,631, 60% $43,537, 80% $71,347, 90% $102,829, 95% $145,557, 99% $382,124, 99.9% $1,787,588. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income. 12-Oct-10 PRELIMINARY RESULTS http://www.taxpolicycenter.org Table T10-0244 Administration's FY2011 Budget Proposals Major Individual Income and Corporate Tax Provisions Baseline: Current Policy 1 Distribution of Federal Tax Change by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Detail Table - Elderly Tax Units Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Percent of Tax Units4 With Tax Cut With Tax Increase Percent Change in After-Tax Income5 Share of Total Federal Tax Change Average Federal Tax Change Dollars Percent Share of Federal Taxes Change (% Points) Under the Proposal Average Federal Tax Rate6 Change (% Points) Under the Proposal 5.7 5.7 8.6 11.9 4.4 7.1 25.1 39.6 60.9 71.0 87.8 55.3 0.1 0.0 -0.1 -0.1 -2.6 -1.5 -0.2 0.2 0.8 1.3 97.9 100.0 -14 5 41 76 5,476 996 -5.3 0.6 1.7 0.9 8.8 7.5 0.0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.7 1.0 0.0 0.3 1.7 3.4 10.1 84.4 100.0 -0.1 0.0 0.1 0.1 2.0 1.3 2.2 3.7 5.7 10.9 24.5 17.9 5.5 4.6 3.2 1.0 0.0 82.8 87.7 93.9 98.0 99.8 -0.3 -0.4 -1.0 -5.6 -7.5 2.1 2.6 9.8 83.4 51.7 270 586 2,270 64,493 369,321 1.5 2.0 3.7 14.5 17.2 -0.6 -0.5 -0.7 2.8 2.0 9.9 9.3 19.1 46.1 24.7 0.2 0.4 0.8 4.0 5.2 15.8 18.4 22.1 31.7 35.5 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Baseline Distribution of Income and Federal Taxes 1 by Cash Income Percentile Adjusted for Family Size, 2014 Cash Income Percentile2,3 Lowest Quintile Second Quintile Middle Quintile Fourth Quintile Top Quintile All Tax Units4 Average Income (Dollars) Average Federal Tax Burden (Dollars) Average AfterTax Income5 (Dollars) Number (thousands) Percent of Total 5,217 8,927 6,483 5,566 5,729 32,167 16.2 27.8 20.2 17.3 17.8 100.0 11,689 23,861 42,973 75,950 276,230 79,440 271 866 2,389 8,232 62,078 13,258 11,418 22,995 40,584 67,718 214,151 66,182 2,522 1,413 1,379 414 45 7.8 4.4 4.3 1.3 0.1 114,468 163,898 286,923 1,607,917 7,094,632 17,794 29,530 61,111 445,728 2,150,675 96,674 134,368 225,812 1,162,188 4,943,956 Share of PreTax Income Percent of Total Share of PostTax Income Percent of Total Share of Federal Taxes Percent of Total 2.3 3.6 5.6 10.8 22.5 16.7 2.4 8.3 10.9 16.5 61.9 100.0 2.8 9.6 12.4 17.7 57.6 100.0 0.3 1.8 3.6 10.7 83.4 100.0 15.5 18.0 21.3 27.7 30.3 11.3 9.1 15.5 26.1 12.5 11.5 8.9 14.6 22.6 10.4 10.5 9.8 19.8 43.3 22.6 Average Federal Tax Rate6 Addendum 80-90 90-95 95-99 Top 1 Percent Top 0.1 Percent Source: Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center Microsimulation Model (version 0509-4). Note: Elderly tax units are those with either head or spouse (if filing jointly) age 65 or older. (1) Calendar year. Current policy extends the 2009 AMT patch and indexes the AMT exemption, rate bracket threshold, and phaseout exemption threshold for inflation; makes the 2001 and 2003 individual income tax cuts permanent and makes 2009 estate tax law permanent. The proposal would: (a) extend the higher EITC credit value for families with 3 children and higher phase-out thresholds for married couples; (b) modify the saver's credit making it equal to 50% of the first $500 of retirement savings ($1,000 for couples) and fully refundable; (c) create automatic 401(k)s and IRAs; (d) extend the American Opportunity Tax Credit; (e) extend the $3,000 child tax credit refundability threshold; (f) raise the child and dependent care tax credit phase-out threshold to $85,000; (g) change the threshold for the 36-percent tax bracket to $250,000 less the standard deduction and two personal exemptions for married couples filing jointly and $200,000 less the standard deduction and one personal exemption for single filers, indexed for inflation after 2009; (h) set the thresholds for the personal exemption phase-out and limitation on itemized deductions to $250,000 of AGI (married) and $200,000 (single), indexed for inflation after 2009; (i) impose a 20 percent rate on capital gains and qualified dividends for taxpayers in the top two tax brackets; (j) limit value of itemized deductions to 28 percent. Business provisions included were making the research and experimentation tax credit permanent, taxing carried interest as ordinary income, repealing LIFO, international corporate tax reforms, and reforms affecting the tax treatment of financial institutions. (2) Tax units with negative cash income are excluded from the lowest income class but are included in the totals. For a description of cash income, see http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/TaxModel/income.cfm (3) The cash income percentile classes used in this table are based on the income distribution for the entire population and contain an equal number of people, not tax units. The incomes used are adjusted for family size by dividing by the square root of the number of people in the tax unit. The resulting percentile breaks are (in 2009 dollars): 20% $13,694, 40% $25,631, 60% $43,537, 80% $71,347, 90% $102,829, 95% $145,557, 99% $382,124, 99.9% $1,787,588. (4) Includes both filing and non-filing units but excludes those that are dependents of other tax units. (5) After-tax income is cash income less: individual income tax net of refundable credits; corporate income tax; payroll taxes (Social Security and Medicare); and estate tax. (6) Average federal tax (includes individual and corporate income tax, payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, and the estate tax) as a percentage of average cash income.