ANALISIS LINGKUNGAN INDUSTRI Pertemuan 11 Matakuliah : J0134/ Manajemen Strategik
advertisement

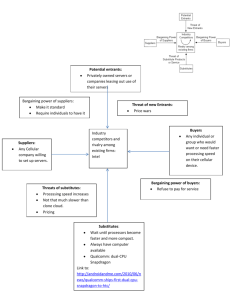
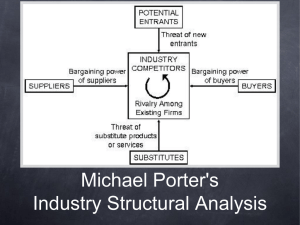
Matakuliah Tahun : J0134/ Manajemen Strategik : 2006 ANALISIS LINGKUNGAN INDUSTRI Pertemuan 11 1 Industrial Organization (I/O) View – Performing External Audit -- Industry factors more important than internal factors • Performance determined by industry forces 2 Competitive Forces Identifying Rival Firms Strengths •Weaknesses •Capabilities •Opportunities •Threats •Objectives •Strategies 3 Key Questions Concerning Competitors • Their strengths • Their weaknesses • Their objectives and strategiesTheir responses to external variables • Their vulnerability to our alternative strategies • Our vulnerability to strategic counterattack • Our product/service positioning • Should we keep our strategies secret from employees&stakeholders ? • Entry and exit of firms in the industry • Key factors for our current position in industry • Sales/profit rankings of competitors over time • Nature of supplier & distributor relationships • The threat of substitute products/services 4 Sources of Corporate Information •Asosiasi industri •Biro riset, exp: AC Nielson, SRI, SWA,dll •Moody’s Manuals •Standard Corporation Descriptions •Value Line Investment Surveys •Dun’s Business Rankings •Standard & Poor’s Industry Surveys •Industry Week •Forbes, Fortune, Business Week 5 7 Characteristics of most Competitive U.S. Firms: 1. Market share matters 2. Understand what business you are in 3. Broke or not, fix it 4. Innovate or evaporate 5. Acquisition is essential to growth 6. People make a difference 7. No substitute for quality 6 The Five-Forces Model of Competition Potential development of substitute products Bargaining power of suppliers Rivalry among competing firms Bargaining power of consumers Potential entry of new competitors 7 1.Rivalry Among Competing Firms • Most powerful of the five forces • Focus on competitive advantage of strategies Influences: • Number of competitors • Industry growth rate • Fixed costs, scale issues • Lack of differentiation • Low switching costs • High exit barriers (specialized assets, emotional commitment, restrictions) 8 2.Potential Entry of New Competitors • Barriers to entry are important: – – – – – – Economies of scale Differentiation/brand loyalty Capital requirements Switching costs Access to distribution channels Other cost disadvantages: • Location • Raw materials • Proprietary technology • Quality, pricing, and marketing can overcome barriers 9 3.Potential Development of Substitute Products • Pressures increase when consumer’s switching costs decrease • Firm’s plans for increased capacity & market penetration • Places an upper limit on prices • Consists of products with a similar function – – – – Electronic security/security guards DSL/Cable modem Coffee/tea/cola Fax/overnight delivery of documents 10 4.Bargaining Power of Suppliers • Large number of suppliers & few substitutes affects intensity of competition • Backward integration can gain control or ownership of suppliers • Influences: – Their size – Number – Ability to switch – Availability of substitutes – Criticality of product – Ability to vertically integrate: • Suppliers vertically integrate forward 11 5.Bargaining Power of Consumers • Customers concentrated or buy in volume affects intensity of competition • Consumer power is higher where products are standard or undifferentiated • Outcomes are a function of the relative bargaining power and dependencies of parties • Buyers vertically integrate backward • Bargaining power is evidenced through – Price – Quality – Service 12 Results of Industry Analysis To one in the industry --• Unattractive industry: intense rivalry, low entry barriers, strong suppliers and buyers, strong product substitutes • Attractive industry: little rivalry, high entry barriers, weak buyers and suppliers, weak product substitutes 13 The World Automobile Industry: Strategic Groups High Ferrari Lamborghini Porsche Mercedes* BMW Price Toyota Ford General Motors Chrysler* Honda Nissan Hyundai Kia High Low Low Breadth of Product Line 14