STATISTICS (MID-CHAPTER REVIEW) PART I: SAMPLING TECHNIQUES
advertisement

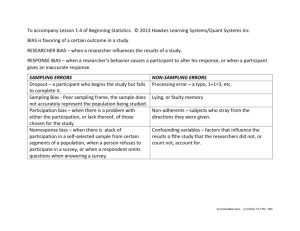
STATISTICS (MID-CHAPTER REVIEW) PART I: SAMPLING TECHNIQUES population: all individuals or items that belong to a group being studied (the target group) sample: a group of individuals or items that are representative of the population from which they are taken Ex 1: Each student in the MBF class is surveyed as to their favourite snack so the cafeteria knows which snacks they should sell. population: sample: Match each definition to the type of sampling technique. Ex 2: ____ simple random sample A. the population is divided into clusters and every member of certain clusters respond ____ stratified random sample B. every nth member of the population is selected ____ voluntary–response sample C. each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected ____ cluster sample D. the sample contains members of the population who have chosen to respond ____ convenience sample E. the population is divided into subgroups and a random sample is selected from each subgroup in proportion to its size in the population ____ systematic sample F. the sample contains those members of the population from which data is easily collected Ex 3: Choose the best sampling technique for each survey. a) b) c) Unit 8 A bolt manufacturer wants to determine the average length of bolt being made by a machine. ________________ The president of a company wants to know which of two potential vice-presidents the employees prefer. ________________ A music store wants to know what type of music they should stock for an upcoming sale. ________________ Page 1 of 5 PART II: COLLECTING AND ANALYZING DATA primary source of data: a person collects data for their own use by surveying a sample secondary source of data: a data base or research collected by someone else is used ex. Internet, Statistics Canada Ex 1: Identify each as a primary or a secondary source of data. a) b) bias: Ex 2: Ex 3: Rachel has her friend Siobhan survey students at her school about their musical preference. ________________ Monique asks students in her science class to suggest the most important scientific discovery over the past 100 years. ________________ an intentional or unintentional distortion of the data collected in a survey Match each description with the type of bias. ____ response bias A. small sample size due to lack of response ____ measurement bias B. a leading question affects the response ____ non-response bias C. exaggerated or underestimated results Identify the bias in each sample and suggest a way to remove it. a) A phone-in radio show asks callers their opinion about the city's baseball team not making the playoffs the day after they are eliminated. b) To learn which team Canadians feel will win the Stanley Cup, researchers call 100 people from Ottawa. c) A radio talk show host asks listeners to phone in and express their opinions on a rock band’s latest CD. Unit 8 Page 2 of 5 PART III: DISPLAYING DATA Ex 1: continuous data: data that can have any numerical value within a finite or infinite interval (a histogram or line graph may be used) discrete data: data that are distinct and can be counted (a bar graph or circle graph may be used) Classify each set of data as continuous or discrete. a) temperature measured throughout the day ________________ b) the number of students in mathematics classes in every high school in Ontario ________________ the volume of air in an average breath taken by students in your science class ________________ c) Ex 2: Ex 3: What type of graph would best represent the data in each case? a) how a school's art budget is spent ________________ b) the time students take to eat lunch ________________ c) the number of students in each grade ________________ d) the change in gas price over time ________________ The histogram shows the distribution of shoe sizes of the grade 9 boys. a) How many boys were surveyed? b) How many boys have a shoe size of 10 or larger? c) What percent of these boys have a shoe size of 10 or larger? Unit 8 Page 3 of 5 PART IV: HOMEWORK QUESTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. Identify the population and the sample in each situation. a) All the dentists in the GTA are asked if they would recommend a new toothpaste, so the manufacturer can indicate the percent of dentists who recommend the product on the box. b) A new sandwich shop will open soon. The owners offer samples to people passing by on a busy Saturday afternoon to help them decide on their final menu. Choose the best sampling technique for each survey. a) Steve wants to know at which festivals his dance company would like to perform. b) Sherry wants to find out which Canadian actress is most popular with Ontario teens. c) Bruno wants to know which search engine is used most often by high school students. Renee works as a quality control officer at a lumber yard. She selects every 200th two-by-four that is cut and measures its dimensions. a) What type of sampling technique is she using? b) Why is it not practical to measure every two-by-four? Identify each as a primary or a secondary source of data. a) b) Ruis checks Statistics Canada to find out which Ontario provincial park is the largest. Travis' survey indicated that almost 40% of his friends eat the same lunch every Monday. 5. A popular television sports show asked people to phone in their pick for the NBA Most Valuable Player. With 30 min left in the show, they announce the results to that point. How might this announcement affect the outcome of the survey? 6. Melissa asks five of her friends about their favourite type of movie. Four say their favourite is comedy. She reports that 80% of teenagers prefer comedies over all other movie types. Explain two flaws in her survey. 7. Barney wants to know what the best-selling lunch item is in the cafeteria. He records what he sees on the students’ trays as they leave the cafeteria during his lunch period. He asks the cafeteria staff to keep track of the items they sell during the other lunch periods. Which data are primary data? Which data are secondary data? Unit 8 Page 4 of 5 8. 9. 10. Identify the bias in each survey. Suggest how it might be removed. a) The student council surveys the students in the bleachers at a football game to determine whether they feel the ticket proceeds should go to purchasing a new score board or new calculators for the math club. b) A market research company mails surveys to 1000 households and 200 are returned. c) Shoppers at a mall are asked, “Are you against the poor decision made to close this mall in order to build a subdivision, making the traffic in the area even more congested?” Classify each set of data as either discrete or continuous. a) the number of blue cars in a parking lot b) the temperature outside at noon measured each day for a week c) the number of students taking math at OLMC The results of a mathematics test are shown. Create a frequency table and histogram to represent the data. 83, 54, 66, 27, 93, 91, 24, 63, 68, 71, 81, 75, 88, 54, 73, 70, 62, 48, 41, 73, 54, 77, 86, 81, 92, 67, 61, 58, 31, 89 ANSWERS: 1. a) population: all dentists in Ontario b) population: all potential customers sample: the dentists in the greater Toronto area sample: people walking past the shop on Saturday afternoon 2. a) voluntary-response sampling b) stratified random sampling c) convenience sampling or voluntary-response sampling 3. a) systematic sampling b) too time consuming 4. a) secondary source b) primary source 5. More people might call in than would have called before. 6. Her sample is too small and is made up of her friends who likely have similar tastes is movies. 7. Barney’s observations are primary data; the cafeteria staff’s observations are secondary data. 8. a) measurement bias b) non-response bias c) response bias 9. a) discrete b) continuous c) discrete Unit 8 Page 5 of 5