NUTRIENTS AND LIVING SYSTEMS
advertisement
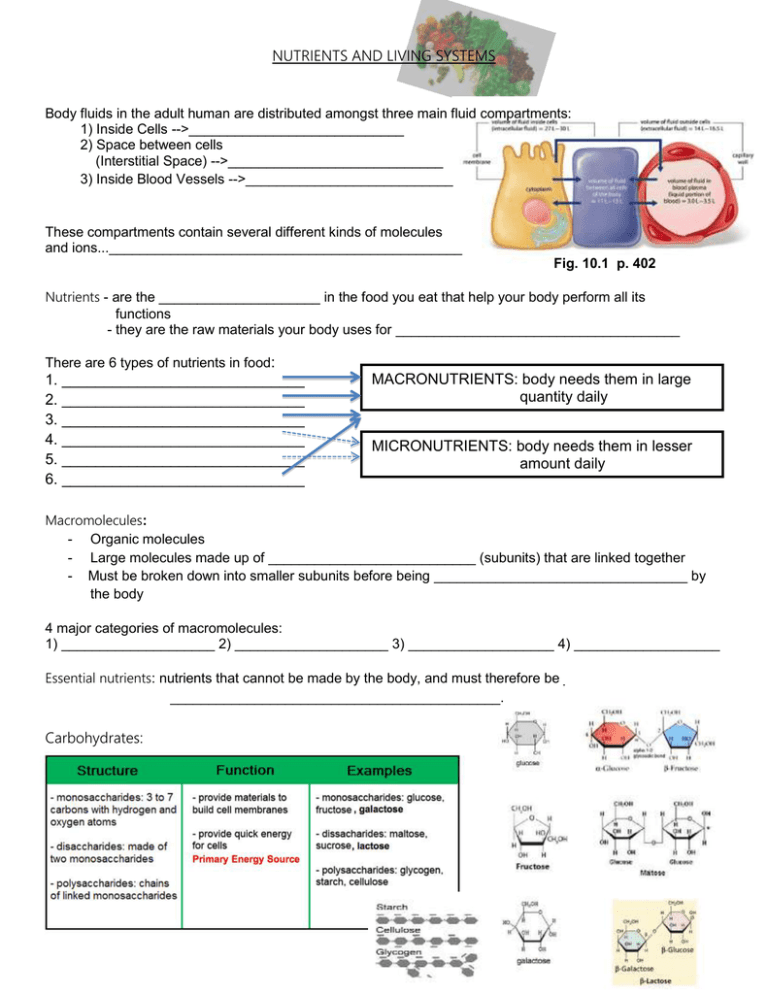
NUTRIENTS AND LIVING SYSTEMS Body fluids in the adult human are distributed amongst three main fluid compartments: 1) Inside Cells -->____________________________ 2) Space between cells (Interstitial Space) -->____________________________ 3) Inside Blood Vessels -->___________________________ These compartments contain several different kinds of molecules and ions...______________________________________________ Fig. 10.1 p. 402 Nutrients - are the _____________________ in the food you eat that help your body perform all its functions - they are the raw materials your body uses for _____________________________________ There are 6 types of nutrients in food: 1. _____________________________ 2. _____________________________ 3. _____________________________ 4. _____________________________ 5. _____________________________ 6. _____________________________ MACRONUTRIENTS: body needs them in large quantity daily MICRONUTRIENTS: body needs them in lesser amount daily Macromolecules: - Organic molecules - Large molecules made up of ___________________________ (subunits) that are linked together - Must be broken down into smaller subunits before being _________________________________ by the body 4 major categories of macromolecules: 1) ____________________ 2) ____________________ 3) ___________________ 4) ___________________ Essential nutrients: nutrients that cannot be made by the body, and must therefore be ___________ ___________________________________________. Carbohydrates: Proteins: Lipids: Nucleic Acid: BREAKING DOWN MACROMOLECULES: ENZYMES Hydrolysis: Chemical reaction in which _______________ breaks macromolecules into smaller molecules (into their subunits). Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids all need to be broken down by hydrolysis _______________________________________________. Enzymes: Proteins that ___________________________________________ chemical reactions such as hydrolysis. Large macromolecules must be broken down to into their smallest subunits in order to pass through ___________________________ in the body (eg. small intestines), and be ______________________into the blood so that they can be used by the entire body. VITAMINS - Organic nutrients that regulate your body processes (such as ___________________________, _________________ and ________________________) and enable chemical reactions to occur. - They are found naturally in _____________________________________. Two types of vitamins: __________________________ and ______________________________. - Water-soluble (eg. Vits _____ and _____) cannot be stored in your body and thus, should be included in your diet. - Fat-soluble (eg. vits _____, ______, ______, and _____) can be stored in the fatty tissue of your body for future use. MINERALS Vitamin Key Functions in the Body - Inorganic nutrients that perform many different tasks (eg. ________________ and ______________) and enable _________________________________ to occur. They are found naturally in many foods. Mineral Key Functions in the Body WATER - One, if not the, most important nutrient - An average adult produces ______________ of urine per day and loses 1 litre of water through normal cellular and body activities (eg.________________, _______________, ____________ and _________________________). - In the human body, water: · transports dissolved nutrients into the intestinal cells · flushes toxins from cells · lubricates tissues and joints · makes up the bulk of essential body fluids (eg. blood) · · · regulates body temperature (sweat) eliminates waste materials (urine and sweat) it makes up the bulk of blood