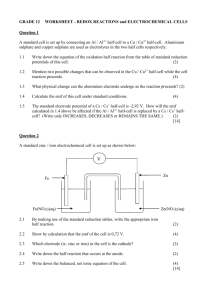
Zn CuSO
advertisement

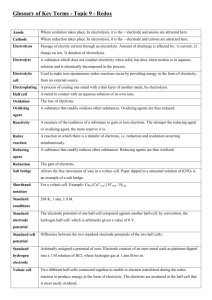
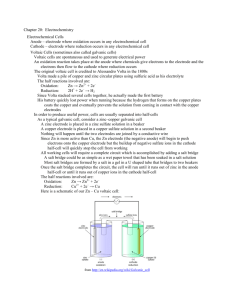
19.1 STANDARD ELECTRODE POTENTIALS [VOLTAIC (Spontaneous) Electrochemical Cells] *Voltaic cell animations: http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/essentialchemistry/flash/galvan5.swf *An arrangement of _____ half–cells that can produce electricity _______________________. *A complete _______can be split into two parts connected by a porous boundary or ______ bridge. Each part is called a half-cell. (*a group of two or more cells connected in series = a ___________) *Half-cell consists of an ____________ (___________ or ___________) and an __________________ *Ex. of VOLTAIC Cell: Ex. Shorthand Voltaic cell notation: *VOLTAIC Cells Connected in Series (i.e. a battery) Zn(s) ZnSO4(aq) CuSO4(aq) Cu(s) *Half-cell #1 = Electrode = _________ ; Electrolyte = ___________ *Half-cell #2 = Electrode = _________ ; Electrolyte = ___________ *In a Voltaic cell the anode is labeled ____________ and the cathode is the labeled ____________. EX. VOLTAIC Cell Activity: Draw and label a Silver-Copper Voltaic Cell after completing the following: Shorthand Notation: Net Notation: *Voltaic Pile *DETERMINING THE REACTIONS IN A VOLTAIC CELL (Memorize the Following Procedure/Theory): METHOD 1: *Using your Data booklet or p.____ of your text, determine the strongest oxidizing agent present in the cell. *SOA in previous example = ______ *The SOA always undergoes ________________at the ____________. (SOARC) *Remember: “REDuction CAThode”; Cathode = electron “_________” *Determine the strongest reducing agent present in the cell. *SRA = ______ *The SRA always undergoes _______________ at the ______________. *Remember: “ANode OXidation” ; Anode = electron “ ___________” *Electrons released by ________ travel through a wire to the ___________ where they are accepted by the _________. The energy produced by the electron flow can be harnessed and used to do work. *Electrons always move from the __________ towards the ___________. (a c) METHOD 2: Strongest Reducing Agent = MOST REACTIVE METAL = ANODE *FUNCTION OF THE SALT BRIDGE (…a hollow“U” shaped-tube) …or porous boundary The salt bridge contains a solution. (Solute = inert salt such as potassium nitrate, KNO 3) Without the salt bridge, current quickly _________________. enables electrolyte solution to maintain neutrality (i.e. prevents ___________________ ) anions migrate to the _____________ via the salt bridge (to offset the buildup of __________) cations migrate to the _____________(to offset the buildup of __________as more and more of the OA is reduced) *This process gives the impression that negative charges are attracted to the negatively labeled ________, and that positive charges are attracted to the positively labeled _____________. Standard Cells and Cell Potentials *What is meant by Standard Cell? Standard Cell = a cell where both the reactants and products are in their standard states i.e. – solutes at ______ mol dm-3 concentrations - gases at pressure of _____ kPa - solids and liquids in their pure form, all at a temperature of ______°C / _______ K(elvin) e.g. - E° for the reaction Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) metal electrodes and 1 mol dm-3 concentrations of Zn2+ and Cu2+. is the cell potential measured at 25°C for a cell that has pure Standard Reduction Potentials (Er˚) the Er˚ represents the ability of a standard half-cell to attract electrons in a reduction half reaction; these are the values found at the far left of the table next to each particular half-reaction Standard Cell Potentials (ΔE˚cell) the ____________ (i.e. the maximum potential difference) of a cell operating under standard conditions Memorize this formula!... ΔE˚cell = (i.e. Standard cell potential = the difference between the reduction potentials of the two standard half-cells…the voltage) *Simple translation: Voltage = Larger Er˚ – Smaller number Er˚ More Regarding Standard Electrode Potentials (E°r) HINTS: All reactions are written as reductions. The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE electrode) is defined as ___________ V (something had to be…see below). There are two important reactions with water – highlight them. They occur at -0.83 V and +1.23 V. (More on these later.) There are three different reactions of copper – make sure you pick the right one! A number of entities (H2O, Cu+, Sn2+, Cr2+, Fe2+) can behave as oxidizing agents or reducing agents. Obey significant figures when working out cell potentials – keep 2 decimal places. The STANDARD HYDROGEN HALF-CELL *Standard reduction electrode potentials are measured RELATIVE TO THE STANDARD HYDROGEN ELECTRODE HALF-CELL. NOTATED: Pt(s H2(g), H+(aq) 2H+(aq) + 2e- <===> H2(g) Er˚ = 0.00 V The inert electrode, _________________, in contact with 1 mol dm-3 hydrogen ion and hydrogen gas at 100 kPa and 298 K. SUMMARY (“SHE” ELECTRODE) - inert platinum electrode - [H+] = 1 mol dm-3 - H2(g) at 100 kPa and 298 K - E° = 0.00 V http://www.chem.iastate.edu/group/Greenbowe/sections/projectfolder/flashfiles/electroChem/voltaicCell20.html EXAMPLES: