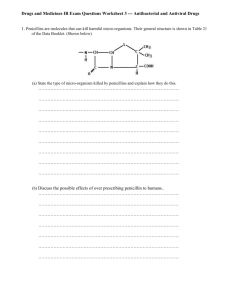
D.2 (PART 2): PENICILLIN
advertisement

D.2 (PART 2): PENICILLIN INTRO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CQG5B27euPo (PENICILLIN – PERIODIC TABLE OF VIDEOS) UNDERSTANDINGS - Penicillins are _______________ produced by ____________. - A _________-___________ ring is a part of the core structure of penicillins. - Some antibiotics work by preventing cross-linking of the bacterial cell ___________. - Modifying the __________-chain results in penicillins that are more resistant to the penicillinase ____________. APPLICATION AND SKILLS - Discussion of the effects of chemically modifying the side-chain of penicillins - Discussion of the importance of patient compliance and the effects of the over-prescription of penicillin. - Explanation of the importance of the beta-lactam ring on the action of penicillin. INTRO: Q. What are antibacterials called in many countries? ____________________ Q. What do antibacterials do? A. Antibacterials are drugs that ________________ the growth of, or kill, ___________________ that cause _______________________ diseases; they are used to control predominantly ___________________ infections (*they are effective in combating a few ________________). Q. Antibacterials are referred to as being selective drugs. What does this mean? A. Antibacterials act against infecting _______________ much more than they act against _________ cells. 1. DISCOVERY AND GENERAL STRUCTURE YEAR 1890s EVENT / DISCOVERY -scientists discovered that certain ______________ killed bacteria -experiments on mice bacterial infection prevented when exposed to these fungi; initial successes largely _______________ 1928 -discovery of penicillin -Alexander Fleming, a bacteriologist working in England, made similar observations to those made some 30 years earlier while working with an infectious _____________ called staphylococcus aureus. He found, rather serendipitously, that a ___________ (penicillium notatum) growing in a petri dish containing this bacterium _______________ the growth of the bacterium. He called the compound in the mold that was responsible for this inhibition ______________________. - Fleming gave up the project after being unable to ________________ and _____________ the penicillin. 1940 1941 - more mice experiments – mice infected with deadly bacteria given penicillin – mice __________ - Penicillin first used on a _________________ in an attempt to combat serious __________poisoning – effect was immediately ___________________. - penicillin mold produced on a _______________ scale in the _____________ (labouriously grown in large tanks containing corn-steep liquor) 1943 - penicillin available ______________________ 1945 - supply of penicillin large enough to meet the demand (i.e. everyone suffering from an infectious disease / thousands of lives saved during ______________) - Fleming, Florey and Chain receive Nobel Prize for ________________ 1950s - _________________ of penicillin determined - enabled synthesis of different types of penicillin and other antibiotics in the _______ without recourse to moulds e.g. PENICILLIN G - the ____________ penicillin - broken down by stomach __________ so had to be __________ - _____________ able to deactivate by synthesizing an enzyme (penicillinase) or *Identify on the above diagrams: (i) basic structure of all penicillins (ii) the “R” group (iii) the beta-lactam ring SIDE-CHAIN MODIFICATIONS -alters properties of the penicillin e.g. PENICILLIN V AMOXICILLIN - acid resistant - basic penicillin structure maintained; side-chains modified 2. MODE OF ACTION -THE BETA LACTAM RING -All penicillins contain a ____________-membered beta-lactam ring. -The high reactivity of the ____________ group within this ring structure is a result of ring _____________. The ring opens so that the penicillin becomes ________________ bonded to the enzyme that synthesizes bacterial cell _________, thus blocking its action. Thus, penicillins work by preventing bacteria from making normal cell ______. Ultimately, the cell swells, and the _____________ pressure causes the wall to disintegrate and the bacterium dies. - Identify the four membered beta-lactam ring on the adjacent penicillin. Label each member, 1 to 4, starting in the upper left and moving clockwise. Carbon (#1) = ______ hybridized ; normal bond angle = ________ Carbon (#2) = ______ hybridized ; normal bond angle = ________ Nitrogen(#3) =______hybridized ; normal bond angle =_________ Carbon(#4) = _______hybridized ; normal bond angle = _________ - These normal bond angles are unable to be obtained. This makes the ______________ group in the ring highly reactive as the ring can readily break due to _____________angles. When the ring opens these parts of the penicillin become _____________ bonded to the enzyme that synthesizes bacterial cell walls, thus blocking its action. -THE DETAILS: The beta-lactam structure is very similar to the combined structure of two amino acids - _____________ + __________. These amino acids are used to synthesize bacteria cell walls. The __________ that synthesizes these cell walls “thinks” it is bonding to these amino acids when, in fact, it is bonding to the structurally similar penicillin. 3. RESISTANCE TO PENICILLINS -Penicillin has been often overprescribed in the past…especially when it became readily available in the 1950s. -Resistant penicillin possess the enzyme penicillinase. *DISADVANTAGES OF OVER-PRESCRIBING PENICILLINS 1. REACTIONS - about _______% of the population is allergic to penicillin - __________________ use can sometimes lead to allergic reaction 2. DESTROYING OF BACTERIA - repeated use can eliminate _____________ and ___________ bacteria in the ___________________tract 3. RESISTANCE PROBLEMS (a) Resistance some bacteria develop resistance to a particular antibiotic and pass on this immunity to succeeding generations (e.g. malaria, typhoid, gonorrhea, TB all have strains that are resistant to many antibiotics) (b) Resistance due to random, favourable alterations to a bacteria’s ________ that result in resistance (c) Use of Penicillin in Feedstock ________________ and ___________ are given the _______________ antibiotics that humans are in order to increase ________________. Therefore, more bacteria are able to develop ________________ within animal feedstock as a result of this increased exposure to the antibiotic. **As a result of all these potential resistance problems, antibiotics are in constant need of ____________ and should only be prescribed as a _________ resort. *YOUTUBE: GENERAL INTEREST VIDS: 1. ‘What Causes Antibiotic Resistance?’ (Kevin Wu) 2. Tuberculosis Documentary: ‘The Deadliest Killer in Human History –The Forgotten Plague’ 3. ‘The Black Death National Geographic Documentary”