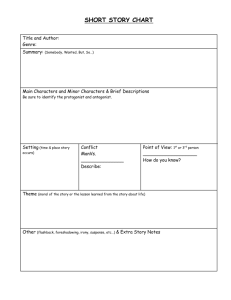
Literary Devices There are three different types of irony: Dramatic Irony
advertisement

Literary Devices IRONY: a contrast between what occurs and what is expected. There are three different types of irony: 1. Dramatic Irony: when the audience knows something that the characters on stage are not privileged to; the audience foresees an outcome of the character’s words and actions that is contrary to the character’s expectations; a device most often used in plays. 2. Structural Irony: Involves the use of a naïve hero whose view of the world differs widely from the true circumstances recognized by the author and readers. 3. Verbal Irony: Involves a discrepancy between what is said and what is really meant; sarcasm FORESHADOWING: The author provides hints or clues of future events. Purposes of foreshadowing are: To increase the reader’s curiosity By increasing interest, it will increase attention to detail Foreshadowing makes the story realistic because even surprising events can seem believable if some hints have been provided beforehand. PATHETIC FALLACY: When the weather matches the events that are occurring. SYMBOL: anything that stands for or represents something else; used to emphasize a conflict or issue within the literary work. PARODY: is a humorous imitation of a work, usually mocking the original by exaggerating or distorting some of its defining qualities. ALLEGORY: is a narrative where characters, setting, objects, or events represent ideas / qualities. (i.e., the Garden of Eden).