Demographic Vocabulary: Key Terms & Definitions
advertisement

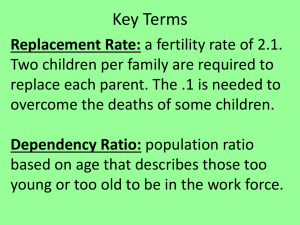
Demographic Vocabulary Note: Canada stats are of 2007 Birth Rate (BR) – the number of births in a country for every thousand people in the population. - example: if 150 000 children are born in a given year in a country with a population of 5 000 000, the BR would be 150 000/5 000 000 x 1000 = 30/1000 - A BR over 30 is high, a BR below 15 is low - Canada’s BR is 11/1000 Death Rate (DR) - number of deaths in a country for every thousand people in the population. - example: if 100 000 children die in a given year in a country with a population of 5 000 000, the DR would be 100 000/5 000 000 x 1000 = 20/1000 - A DR over 30 is high, a DR below 15 is low - Canada’s DR is 08/1000 Natural Increase (NI) – is the difference between a countries BR and DR. - example – a countries BR is 30 and DR is 20 (30-20=10). The NI = 10/1000 or 1% - A NI over 2% is typical of a developing country, under 1% is typical of a developed country - Canada’s NI is 11-8=3/1000 or .3% Immigration Rate (IR) – measures the number of people who move to a country. - example: if 15 000 people move to a country of 5 000 000, the IR would be 15 000/5 000 000 x 1000 = 3/1000 - Canada’s IR is 7.2/1000 Emigration Rate (ER) – measures the number of people who move out of a country. - example: if 10 000 people move to a country of 5 000 000, the ER would be 10 000/5 000 000 x 1000 = 2/1000 - Canada’s ER is 1.3/1000 Net Migration Rate (NMR) – is the difference between a countries IR and ER. - example – a countries IR is 3 and ER is 2 (3-2=1). The NMR = 1/1000 or .1% - Most countries have small or negative NMR, exceptions are Canada, USA, & Australia. - Canada’s NI is 7.2-1.3=5.9/1000 or about .6% Population Growth Rate – combines NI and NMR to calculate the rate at which a country’s population is changing (usually measured in %). - A pop. GR of over 2% is considered high. - Canada’s Pop. GR is 3/1000 + 5.9/1000 = 8.9/100 or about .9% Population Pyramid –a type of bar graph that shows the age & gender structure of a population. Dependency Load – the percentage of a country’s population that is under 14 and over 65. - These people are dependent upon the working class who pay taxes. - Canada’s dependency load is 31% Working Class – the percentage of a country’s population that is between 15-64 years old. - These people support the dependency load with the taxes they pay. - Canada’s working class is 69% Life Expectancy – is the average life span, at birth, of a human being. - A lifespan less than 50 is short and one over 75 is long. - Canada’s lifespan is about 80 years old Infant Mortality Rate – is the number of children in a country who die in the first year of life for each 1000 births. -An infant mortality rate over 80 is high, less than 15 is low. -Canada’s infant mortality rate is 5.3/1000 Total Fertility Rate – is the average number of children that each woman will have (15-45) -A high fertility rate is greater than 5 and low is less than 2.1 -Canada’s total fertility rate is 1.61 Replacement Rate – is the total fertility rate that produces a NI rate of zero. - 2.1 is the replacement rate (the extra .1 is to account for women who cannot have or choose not to have kids or die before child bearing age) Rule of 70 – a simple way to estimate how long it would take for a country’s population to double. Calculated by taking 70 and dividing it by the population growth rate in % form - Canada: 70/1% = 70 years