5.6 Ionic compounds
advertisement

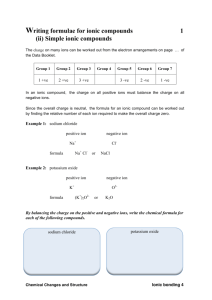
5.6 Ionic compounds Making ionic compounds Metal + Non-metal Made up of positive and negative ions Cations and anions attract each other to form ionic compounds The non-metal atom takes electrons from the metal atom To form a compound, the correct ratio of positive and negative ions is required that makes the overall compound neutral Example: Sodium chloride (table salt) is an ionic compound made up of sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl -) Na Cl [Na]+ [ Cl ]- Ionic bond Attraction that holds oppositely charged ions together in a compound Ionic compounds are those held together by ionic bonds When ionic compounds are placed in water they dissolve Solutions that contain dissolved ions are good conductors of electricity Practice: Ionic bonding 1. Mg and Cl 2. Al and O 3. Na and P 5.7 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Naming ionic compounds 1. Write the name of the metal first, then the name of the non-metal 2. Change the ending of the second element to ‘–ide’ “-ide’ indicates a binary compound (only 2 different types of elements form the compound) Example: NaCl is named sodium chloride Practice: 1. AlCl3 ______________ 2. Na2O ______________ 3. K2S ______________ 4. CaBr2 ______________ 5. KCl ______________ Writing chemical formulas for ionic compounds 1. Write the symbols for each element in the correct order (metal first, non-metal second) 2. Add the ionic charge of each ion above the symbol 3. Cross-over the ionic charge – this balances the charge 4. Simplify if necessary Example: magnesium oxide is MgO Practice: 1. lithium fluoride ______________ 2. sodium oxide ______________ 3. calcium sulfide ______________ 4. aluminum oxide ______________ 5. calcium chloride ______________ Elements with multiple ionic charges Some metals have more than one ionic charge so they need a ROMAN NUMERAL in their name to differentiate which ionic charge is used. For example Copper forms ions with a + and 2+ charge Cu+ + Cl- CuCl Cu2+ + Cl- CuCl2 These ions are named like other cations, except that Roman numerals in rounded brackets are used to indicate ionic charge of the metal. Example: Cu+ ion is called copper(I) ion Cu2+ ion is called copper(II) ion Examples of Elements with multiple ionic charges Metal Chemical Symbols of Ions Names of ions Copper Cu+ Cu2+ copper(I) copper(II) Iron Fe2+ Fe3+ iron(II) Iron(III) Lead Pb2+ Pb4+ lead(II) lead(IV) Manganese Mn2+ Mn4+ manganese(II) manganese(IV) Tin Sn2+ Sn4+ tin(II) tin(IV) Practice: Write the formulas for the following compounds: 1. copper(I) chloride ______________ 2. copper(II) chloride ______________ 3. iron(II) oxide ______________ 4. tin(IV) sulfide ______________ 5. tin(II) bromide ______________ Practice: Name the following compounds: 1. CuO ______________ 2. SnBr4 ______________ 3. FeO ______________ 4. PbCl2 ______________ 5. MnO2 ______________