The Cold War: East v. West, 1947-1980 Ch. 31 Pg. 732-760
advertisement

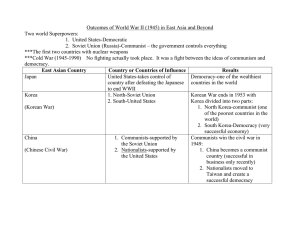
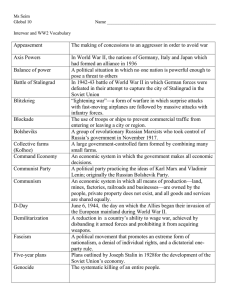
The Cold War: East v. West, 1947-1980 Ch. 31 Pg. 732-760 Post-WWII: the West • Forced to adjust – Food v. transportation – Refugees v. new boundaries – Decolonization v. nationalism Europe & Its Colonies • West’s weakness allowed peaceful decolonization – Exceptions: Algeria, Kenya, Vietnam The Cold War • Cold War built as USSR occupied Eastern Bloc – Installed communist regimes – Origin of Iron Curtain • U.S. responded with Marshall Plan loans to W. Europe – Germany as focal point: Berlin airlift • Cold War spread by rival defensive alliance: NATO v. Warsaw Pact Resurgence of W. Europe Spread of Liberal Democracy • Democracy became consensus political system – Opposition worked within democracy – New republics emerged Welfare State • W. Eur government commonly worked to cushion citizens against hardships New Challenges • Protests challenge democracy – 1960s: segregation, Vietnam War, materialism – 1970s: feminism, green movement • Thatcher & Reagan trim welfare state after recession Diplomatic Context • European identity over nationalism – Marshall Plan’s integration – Germany’s interdependence ↳Origins of European Union Economic Expansion • Western society became affluent – Post-rebuilding economic growth & technology – Shift to service sector • labor shortage spurred colonial immigration • Mass consumerism Cold War Allies (U.S. & white dominions) Former Dominions • Canada – Tension over integration w/ U.S. – Welfare state • Australia & New Zealand – Tension over integration w/ U.S. – Shift economy from Britain to Pacific Rim U.S. Century • Took over mantle of superpower • Communist threat yielded policy of containment & defense spending – Examples: • Korea • Vietnam • Latin America Western Culture & Society Social Structure • Increased prosperity & education blurred social lines & improved social mobility • Class distinction remained – Middle-class w/ clearly more consumer & leisure power than working-class – Crime, race riots, anti-immigrant violence remained Women’s Revolution • Women saw dramatic improvements in economic opportunities & rights – education, service economy, attractiveness of 2nd income – voting, divorce, sexual rights improve • But women were far from equal • Technology & new roles changed family relationships Western Culture • U.S. led scientific development – DNA, Space travel & satellites – Modern art – Social science turned to data collection Popular Culture • Superficial & pleasure-seeking – Internationalization of American blue jeans & tv; European music & fashion Post-WWII: the East Soviet Union as Superpower • As evidenced by: – Expansion – Heavy industry & military development – Strategic alliances & support of communist regimes Soviet Empire in E. Europe • Although technically independent, weakness of E.Europe & Soviet army allowed USSR to become dominant force in region – Limited church & opposition – Common economic plan w/ collectivization, industrialization, central planning ↳Warsaw Pact Evolution of Domestic Policies • Suspicion of U.S. & strong gov resulted in: – Industrial growth – Cultural & economic isolation – Extension of social services Soviet Culture • Explicitly fostered industrialization, loyalty of citizens, scientific thought – Valued science & education – Mass ceremonies – Classical ballet & literature – Secularism • Yet severely limited cultural freedom & expression Economy & Society • Urban & industrial w/ heavy state control – Lacked individual motivation & peasant success • Industrialization led to social similarities with West – Unique traits: • Long lines for consumer goods • Emphasis on authority • Greater female participation De-Stalinization • Khrushchev eventually replaced Stalin – Generally loosened policies • Central planning & communist control remained • Economy & science remained competitive • Diplomatically pushed for “peaceful coexistence” (usually) • Without Stalin’s harshness, worker motivation dropped Global Connections • Cold War dominated world history post-WWII • Both societies spread science, secularism, weapons, & female equality