Document 14343673
advertisement

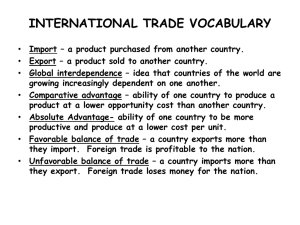
Capitalism: means of production are privately controlled Command: state-run, centrally planned economy; communism, socialism Differ based on who answers the 5 fundamental economic questions: What will be produced? How will goods and services be produced? Who will get the output? How will the system accommodate change? How will the system promote progress? There are no PURE command economies There are no PURE market economies Economic systems are MIXED Involve some Government ownership/control and some private ownership/control U.S. Mixed Government sets interest rates, collects taxes, controls money supply, sets minimum wage, has federal agencies (FDA, FAA, USDA, SEC, etc) Monetary Policy: Controlled by the Central Bank, the Federal Reserve Control of money sully & interest rates Fiscal Policy: Government spending and taxation Depression, Recession, Recovery, Peak Determined by economic factors such as: Unemployment levels Stock Market (Dow, S&P 500 index) GDP (Gross Domestic Product) CPI (level of inflation) Definition: The ability and willingness to buy specific quantities of a good at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus. Law of Demand: as the price of a good rises, the quantity demanded of the good falls, as the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded of the good rises, ceteris paribus. Definition: the ability and willingness to sell (produce) specific quantities of a good at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus. Law of Supply: as the prices of a good rises, the quantity supplied of the good rises, and as the price of a good falls, the quantity supplied of the good falls, ceteris paribus. Price of any given product at which supply equal demand. equilibrium Also known as Shortage Scarcity is the basic economic problem: our wants are unlimited but resources are limited. Occurs when demand is higher than supply Causes prices to rise Examples?? Scarcity occur because we have to make choices Economics is the study of why people make choices Every choice has an alternative, that’s opportunity cost. What do you give up? Example: You have $30 for your big date so it’s dinner OR a movie. If you choose the movie, opportunity cost is dinner, vice versa. Opportunity cost is only 1 thing, not many. Other examples? Occurs when supply is higher than demand Causes prices to fall Examples??? Goods that are related to each; that complement each other Examples CD’s and CD players PS2 and video games Others?? If the price of complementary goods increases then the demand for the original good decreases Example As gas prices rise, demand for SUV’s and cars in general have fallen Others??? If the price of complementary goods decreases then the demand for the original good will increase. Example If the price of DVD players decreases, it will likely cause an increase in the demand for DVD’s and thus increase DVD sales. Can be used instead of the original good Examples Choose PS2 over X box Choose Abercrombie over Am. Eagle Others??? If the price of substitute goods rises, the demand for the original good will increase If the price of substitute goods falls, the demand for the original good will decrease. The price of Gatorade increases from $1.00 to $1.50; the demand for PowerAde will increase. (PowerAde a substitute for Gatorade). The menu prices at Wendy’s decrease by 10%, the demand at McDonalds will decrease. (Wendy’s is a substitute for McDonalds). as a person increases consumption of a product, while keeping consumption of other products constant, there is a decline in the marginal utility. Examples: craving food at a buffet, the more you eat the less satisfaction, or utility you get. Roller coaster ride Sporting event Non-examples: Play chess, golf, boating, other sports/activities Selling products or services to buyers in another country is known as: _____________ ____________ refers to buying goods and services made in a foreign country. How is a product deemed an import or export if parts are made in several different countries? If _____% of the product is made in the U.S. it can be labeled “Made in the U.S.A.” 1. Boeing (U.S.) makes and sells planes to Qantas (Australia) Airlines Import for __________/_________; Export for __________/________ 2. CDW (U.S.) purchases Acer (Taiwan) laptops. Import for __________/_________; Export for __________/________ 3. Mitsubishi Endeavors sold to car dealerships in Tokyo. Import for __________/_________; Export for __________/________ 1. Tariffs: _____ placed on _______ goods Ex: U.S. places a 10% tariff on foreign jeans. $30 jeans now cost: $ _____ 2. Dumping: selling goods in a _______ market _______cost or below the cost in their home country to drive out competitors (like a retail store using a loss leader). 3. Quota: places ______ on the number of products that can enter 4._________no products allowed/accepted Example? Exchange rate: value of one country’s currency expressed in the currency of another country. $1US = ¥125 (Jap.Yen). A 12,500 ¥ camera in the U.S. would cost: If exchange rate changes to ¥ 100 camera in U.S. now costs: Yen ¥ Dollar Real Yuan Franc Pound £ Rand Rupee Peso Euro € Treaties: NAFTA: free trade among _____, ______ & ________ ______: enforces rules governing international trade. Stands for: U.S. signed it originally with just…. EU: _____ European countries __________ Why? Removes _______, encourages ____with the free movement of people, goods and ______. Bulgaria and Romania recent additions in ______. __ of 27 nations have adopted the Euro as their currency U.K.? Imports vs. Exports Imports exceed Exports = Trade ______ (negative) Exports exceed Imports = Trade _______ (positive) Top 5 U.S. Trading Partners? Absolute Advantage One country can produce an item more efficiently than anyone else Ex: crops in certain climates or specialized, cheaper labor or better technology Comparative Advantage ability to produce good or service at a lower marginal and opportunity cost over another Reason why it is beneficial for nations to trade Country A can produce 5 widgets per hour with 3 employees. Country B can produce 10 widgets per hour with 3 employees Who has an absolute advantage? Unit labor costs Cloth Wine Britain 100 110 Portugal 90 80 • It is most efficient for Britain to produce ____ and for Portugal to produce ______ • What is the opportunity cost for Britain to produce wine? For Portugal to produce wine? Lebron James has an absolute advantage in ________. Many say he could be a successful NFL Tight End or Defensive End, which should he focus on, basketball or football? If he tried to play in the NFL, what would the opportunity cost be of the time he spent practicing and training?