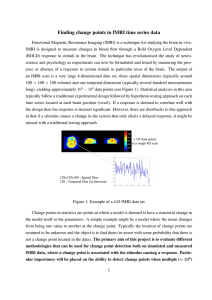
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is fast becoming the method... the field of neuroscience. The ability to interrogate the whole...
advertisement

Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is fast becoming the method of choice in the field of neuroscience. The ability to interrogate the whole brain with high spatial resolution with a number of different presentation types has been useful in understanding how the brain functions. Moreover, the non-invasive nature of MRI allows longitudinal studies to occur in normal and patient populations to understand the effects of development or the disease process. Recent advances in data analysis (voxel based morphometry) have also been developed to investigate volumetric changes in the same populations. In fMRI, the coupling between neural activity and blood flow has been exploited to produce activation maps. The neuronal activation signal is detected by the blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) signal changes that correlate with the paradigm presented to the subject. Issues related to the physiology of the BOLD signal and how it impacts the field of fMRI will be discussed. Furthermore, the details of the fMRI experiment will be reviewed as fMRI is moving from the research stage to clinical application. This lecture will provide an overview of the physiologic origins of the functional imaging signal, acquisition methods, paradigm design issues, and post-processing methods used to generate the activation maps. Educational Objectives: 1. Understand the origin of the MR based signal used for fMRI 2. Understand the issues related to an fMRI experiment including design, acquisition and processing 3. Understand the issues related to clinical application of fMRI