Double Displacement Reactions Study Guide
advertisement

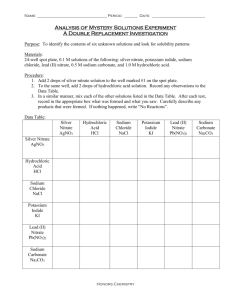
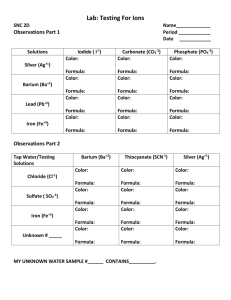
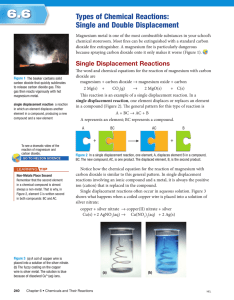
Name:__________________________________________________Hour:_________ Date:__________ Double Displacement Reactions Study Guide Complete the following study guide as you watch the Double Displacement Reactions Video OR read page 184 in your textbook. A double displacement reaction occurs when two ionic compounds in aqueous solution exchange ion partners: AC + BD AD + BC Usually one of the products becomes _______________(forms a solid precipitate). The other product stays _______________(dissolved in water). If both products are soluble, then essentially there is no reaction and all ions stay dissolved. Use the _____________________ to help you! This only applies to the products in a double displacement reaction… Notice that the positive ions always combine with the negative ions! A+ combines with Dand B+ combines with C-. Don’t forget to check ion charges when you write new formulas! Examples: Silver nitrate reacts with sodium chloride to form silver chloride and sodium nitrate: Lead (II) nitrate reacts with sodium iodide to form: Predict the products: CaCl2 + NaOH Are the products soluble in water? How do you know? Solubility Rules: Using your solubility reference sheet, label the following 10 compounds as soluble (aq) or insoluble (s): 1. 2. 3. 4. PbCl2 CaSO4 LiCl LiOH 5. 6. 7. 8. Na2SO4 NH4Br K2S Mg3(PO4)2 9. NaNO3 10. BaSO4 Name:__________________________________________________Hour:_________ Date:__________ Writing Reactions Practice: Write the complete balanced equation for the following chemical reactions, including the states of matter. 1. Aluminum iodide + mercury (II) chloride 2. Silver nitrate + potassium phosphate 3. Copper (II) bromide + aluminum chloride 4. Calcium acetate + sodium carbonate 5. Copper (II) sulfate + silver nitrate 6. Silver fluoride + nickel (II) chloride 7. Magnesium nitrate + ammonium chloride 8. Lead (II) nitrate + potassium chloride 9. Lead (II) nitrate + magnesium fluoride 10. Silver nitrate + sodium bromide 11. Barium nitrate + potassium sulfate 12. Iron (III) chloride + ammonium hydroxide 13. Potassium chromate + barium nitrate