3.1/3.2 Review
advertisement

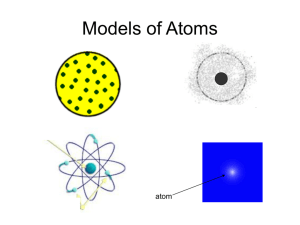
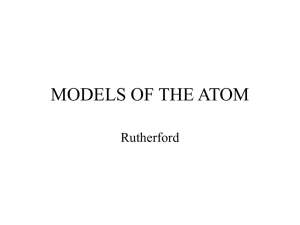
3.1/3.2 Review Name________________________________ Chemists & Models of the Atom Period_______Date_____________________ Part I: Chemists in History - Write the name of the chemist who proposed each of the ideas listed below. Some names may be used more than once. Democritus Franklin Rutherford Lavoisier Thomson Bohr Proust Becquerel Moseley Dalton Marie & Pierre Curie Modern Model _____________________ 1. Stated that matter is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. _____________________ _____________________ 2. Stated that a given compound always has the same relative number and kinds of atoms. _____________________ _____________________ 3. Discovered radioactivity while working with a sample of Uranium. _____________________ 4. Determined that a cathode ray is made of electrons. _____________________ 5. Isolated two new elements, radium and polonium. _____________________ 6. Understood the atom to have a central nucleus with electrons orbiting around in fixed paths like planets around the sun. _____________________ 7. Stated that all atoms of a given element are identical, but they differ from those of other elements. _____________________ 8. Stated that all matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. _____________________ _____________________ 9. Found that there are three types of natural radiation. _____________________ 10. First person to suggest that the atom is related to electricity. _____________________ 11. Uses Quantum Mechanics and states that the electron may be found in a probability region. _____________________ 12. Determined that each atom has it own atomic number (number of protons.) _____________________ 13. Used Gold Foil to determine that all the positive matter (protons) is concentrated into a very small, very dense nucleus and that most of the atom is empty space. Part II: Experiments about the Atom – Fill in the blanks with the appropriate word. Each word or number will only be used once. 0 +2 3 no anode electrons gamma negative beta empty space large positively cathode exposed mass proton (nucleus) 14. The negatively charged electrode of a cathode ray tube is the ___________________, the positively charged electrode is called the ______________________. 15. In Thomson’s experiment, the cathode ray is deflected by the magnet, this indicated that the ray had ____________________. When the electrically charged plates were turned on, the cathode ray was deflected toward the positive plate, this indicated that the beam had a ____________________ charge. 16. Therefore a cathode ray is made of a beam of ____________________. 17. Becquerel discovered radiation because a sample of uranium ore __________________ a piece of photographic film. 18. Rutherford used a radioactive sample and determined that natural radiation has ______ components: alpha particles which have a _______ charge and a relatively _______________ mass, ________________ particles which have a negative charge and a mass of ______ and ______________ rays which are neutral and have ________ mass. 19. Rutherford used alpha particles in his Gold Foil experiment. Because the alpha particles are relatively large and positive the fact that most of them proceeded straight through the foil proved that the atom is mostly _____________________________. Some of the positive alpha particles deflected directly back toward the source which indicated that the nucleus was _______________________ charged Thus, Rutherford is credited with discovering the ___________________. 20. Draw a simple sketch of each chemist’s model of the atom. Indicate charge where needed. Dalton Thomson Rutherford Bohr Modern Model