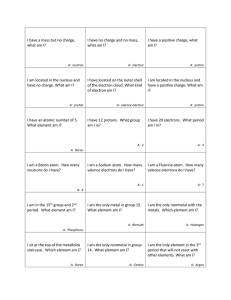
Key to Final 2015 1. Water cycle 2. Nucleus
advertisement

Key to Final 2015 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. Water cycle Nucleus Having a nucleus DNA, chromatin, nucleolus Lysosome Ribosomes Mitochondria Regulates what materials enter and exit the cell Burst due to water moving into cell Made up of phospholipids Lack a nucleus Stores DNA, controls processes, and contains info needed to make protein Chloroplast Movement of particles from an area of high to low concentration Osmosis During the M phase S phase Cell division Series of events that cells go through as they go and divide A. centromere B. sister chromatids Tall is dominant gene The allele for shortness and the allele for shortness segregated when the F1 plants produced gametes. Principle of probability can be used to predict traits used by the offspring for genetic crosses All possible results of a genetic cross, the genotypes of the offspring, and alleles in the gamete of each parent 3;6 When genetic material is exchanged between chromosomes Prophase of meiosis 1 4 genetically different haploid cells They would have the same phenotype. They both have dominant and recessive traits. Homozygous Law of segregation Meiosis Haploid cells Burning paper Crystalline Solid Ability to react with oxygen Energy Evaporation Baking soda in water 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. Physical Density= Mass/volume Chemical Ability to be crushed Density Protons and neutrons Located in energy levels Number of protons 2 in 1st level and 8 in 2nd level Mass number- atomic number 12 protons, 2 electrons in first energy level, 2 valence electrons Same element with different atomic masses Valence Electron Fluoride will form an ionic bond by taking on a -1 charge Group 2 Selenium It has one valence electron 4 energy levels 9 protons, 9 electrons, and 10 neutrons Same number of valence electrons Increases adding energy levels Hydrogen, lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium 2-8-4 Similar Lithium loses an electron Predicted outcome that is testable Line graph Describes the graph Design experiments that test only one variable Group as comparison Group being tested Variable being measured Variable being tested