12.1: The Circulatory System Supports other Systems
advertisement

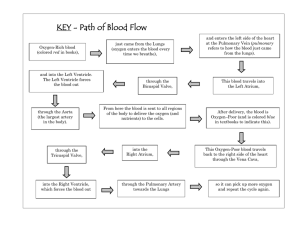
12.1: The Circulatory System Supports other Systems Circulatory has three main functions: 1. It supports the respiratory system by transporting oxygen to cells and carbon dioxide away from cells, and supports the digestive system by transporting nutrients to cells and waste materials away for elimination. 2. It keeps all systems healthy by transporting vital chemical substances and by regulating the body’s temperature. 3. It protects against blood loss and infection. Learning Check: 1. a) Where does oxygen enter the human circulatory system? [k/u] b) Describe oxygen’s path in the circulatory system. c) Where does carbon dioxide exit the circulatory system? 2. a) Where do nutrients enter the human circulatory system? [k/u] b) Describe the path of nutrients in the circulatory system. [k/u] 3. Page 450 of your textbook describes a dense network of capillaries in your nasal passage to warm the air before it enters your lungs. [t/i] a) How does this help to regulate the body’s temperature? b) How does it support the respiratory system? 4. a) What happens to a cut after it bleeds for a while? [t/i] b) This is an example of which main function of the circulatory system? The Human Heart A four chamber heart pumps blood around the human circulatory system following a specific path: 1. Blood coming from the body (with a high concentration of carbon dioxide and a low concentration of oxygen) is carried by veins called the vena cavae into the right atrium pf the heart. (notice the right atrium appears on the left side, when we look at the front of the heart) 2. From the right atrium, blood flows into the right ventricle and then is pumped to the lungs in the pulmonary arteries. 3. Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium of the heart. 4. The oxygenated blood flows into the left ventricle and is pumped onto the aorta to travel around the body. Definitions: Atrium: Ventricle: Pulmonary Arteries: Pulmonary Veins: Aorta: Vena Cavae: Atrioventricular Valves: Semilunar Valves: Sinoatrial (SA) Node: Atrioventricular (AV) Node: Purkinje Fibres: Electrocardiogram: Learning Check: 1. Label the diagram of the Human heart. [k/u] 2. a) What type of valve controls the flow of blood from the atria to the ventricle? [ k/u] b) Why is it important to keep blood moving forward in the heart? [app] 3. Name the four main blood vessels that connect to the heart. [k/u] a) The main artery leading to the body b) The main artery leading to the lungs c) The main veins coming from the body d) The main vein coming from the lungs 4. How does the SA node cause the heart to beat? [k/u] 5. What technologies can a doctor use to monitor the beating of a heart? [k/u] 6. What is the significance of each wave in the electrocardiogram? [t/i] a) P wave b) QRS wave c) T wave