Pertemuan 7 Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) Matakuliah : T0053/Web Programming
advertisement

Matakuliah
Tahun
Versi
: T0053/Web Programming
: 2006
:2
Pertemuan 7
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)
1
Learning Outcomes
Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa
akan mampu :
• Menjelaskan Teknik Akses Database
• Mengakes database menggunakan JDBC
• Membuat aplikasi Database menggunakan
Java
2
Outline Materi
•
•
•
•
RDBMS
JDBC
Transaksi menggunakan JDBC API
Aplikasi database
3
Relational Database Model
Database models
Hierarchal,
network, relational (most popular)
Focus on relational
Relational Database Model
Logical
representation of data
Consider relationships between data
Not concerned with implementation
4
Relational Database Model
Relational database
Composed
of tables
Rows called records
Columns are fields (attributes)
First
field usually primary key
Unique for each record
Primary key can be more than one field (column)
Primary key not required
5
Relational Database Model
Relational Database Structure
Table: Employee
A record
Number
Name
Department Salary
Location
23603
JONES, A.
413
1100
NEW JERSEY
24568
KERWIN, R.
413
2000
NEW JERSEY
34589
LARSON, P.
642
1800
LOS ANGELES
35761
MYERS, B.
611
1400
ORLANDO
47132
NEUMANN, C.
413
9000
NEW JERSEY
78321
STEPHENS, T.
611
8000
ORLANDO
Primary Key
A column
6
Relational Database Overview
Books.mdb database Structure:
Primary
key in bold
Rule of Entity Integrity
Every record has unique entry in primary key
field
7
Structured Query Language
Overview of SQL
Context of Books.mdb database
SQL keywords discussed in context
of complete
queries
Some keywords beyond scope of text
Used to
Query a database
Insert records into a database
Update existing records in a database
SQL keywords
SELECT,
FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING,
ORDER BY
INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, etc
8
Structured Query Language
Example SQL Query:
SELECT * FROM Titles
WHERE Title LIKE '*How to Program'
ORDER BY Title ASC
SQL Result:
ISBN
Title
0-13-118043-6
0-13-226119-7
0-13-528910-6
0-13-016143-8
C How to Program
C How to Program
C++ How to Program
Internet and World Wide Web How
to Program
Java How to Program
Java How to Program
Visual Basic 6 How to Program
0-13-012507-5
0-13-899394-7
0-13-456955-5
Edition Year
Publisher
Number Published ID
1
2
2
1
1992
1994
1997
1999
1
1
1
1
3
2
1
1999
1997
1998
1
1
1
9
JDBC – API Overview
JDBC API makes it possible to do three
things:
Establish
a connection with a database or
access any tabular data source
Send SQL statements
Process the results
10
JDBC Architecture for Java
Application
Type 1
Type 2
11
JDBC Architecture for Java Applet
Type 4
Type 3
12
JDBC Features
Leverage Existing Enterprise
Data
Simplified Enterprise
Development : Easy to use API
Zero Configuration for Network
Computers
Full Access to Metadata
No Installation
Database Connection
Identified by URL
Supported by many industry
13
JDBC Features
From java.sql.*: (standard)
Scrollable result set: MoveNext, MovePrev
Updatable result set
Supported BLOB and CLOB
Batch updates: performance improvement,
sending
multiple updated instead of single updated to DB
Savepoints: Ability to roll transactions back to where a
savepoint is set
From javax.sql.* (optional):
Connection pooling
Distributed transactions
JNDI support
14
Using JDBC API
Setup Database and JDBC Driver
Ex:
Books.mdb using JdbcOcbd bridge
Loading Driver
Class.forName(“sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver”);
Making Connection
Connection
con =
DriverManager.getConnection(“jdbc:odbc:books”,
“userName”, “password”);
Send/Execute Query
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(“SELECT
Authors”);
* from
15
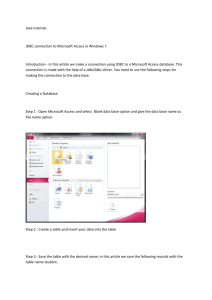
Setup Books.mdb Database
Setup dialog appears. Enter name used to reference database
and
description
(optional).
ODBC
Data Source
Administrator
now has Books. We
candata
nowsource
accessmust be registered with
The
Use Select... to choose
database
file.
This allows
to register
ourGo to
ODBC
data us
source
using
system.
JDBC
to Control Panel -> ODBC
Use
Advanced...
toData
create
a username
(anonymous) and
User
Data
Source
Name.
ODBC
driver.
Source
Administrator.
password (guest). When done, click OK
Go to the User DSN tab and
click Add...
We are using Access, so select
Microsoft Access Driver,
then Finish
16
Statement Class
Kelas ini biasa digunakan untuk query standar tanpa parameter:
Contoh:
String url=”jdbc:odbc:Kopi”;
String userID=”sa”;
String password=””;
Statement DataRequest;
ResultSet Results;
Connection Db;
try {
String query=”select * from customers”;
DataRequest =Db.createStatement();
Results=DataRequest.executeQuery(query);
DataRequest.close();
17
Statement for SELECT Query
For Forward Only and Read Only
ResultSet
Statement
stmf = con.createStatement();
For Updateable ResultSet (JDBC 2.0)
Statement
stmt = con.createStatement(
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE,
ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
18
ResultSet Record Navigation
Record Navigation
next();
MovePrev previous();
Last Record afterLast(); isAfterLast()
First Record beforeFirst(); isBeforeFirst()
Go to N position absolute(n), relative(n)
Record Count int recCount = rs.getRow();
MoveNext
19
Example
try {
//koneksi ke Ms.Access XP
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "", "");
//mengizinkan cursor maju mundur
//tidak sensitive terhadap perubahan oleh komponen J2EE lainnya
//mengizinkan resultset dapat diupdate
stmt = con.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,
ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
rs = stmt.executeQuery("Select * from mhs");
rs.first();
}
catch(SQLException ex){
System.err.println("SQLException : " + ex.getMessage());
}
20
Navigation
class Previous implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{ try{
if (!(rs.isBeforeFirst())) //jika belum di awal
{
rs.previous(); //ke data sebelumnya
isi();
}
if ((rs.isBeforeFirst()) && (rs != null))
{
rs.first();
//Menampilkan pesan di status bar
showStatus("Aduh udah mentok");
}
}
catch(SQLException ex)
{
System.err.println("SQLException : " + ex.getMessage());
}}}
21
Navigation
class Last implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
try {
rs.last(); //ke data terakhir
isi();
}
catch(SQLException ex)
{
System.err.println("SQLException : " + ex.getMessage());
}}} }
22
PreparedStatement Class
Sebuah query SQL dapat diprecompilasi dan dieksekusi
menggunakan objek PreparedStatement. Tanda Tanya
(?) dapat digunakan sebagai tempat untuk memasukkan
nilai.
try {
String query=”Select * from Customers where
CustNumber=?”;
PreparedStatement
pstatement=Db.preparedStatement(query);
pstatement.setString(1,”123”);
Results=pstatement.executeQuery();
pstatement.close();
23
CallableStatement Class
Objek CallableStatement digunakan untuk memanggil stored
prosedure dari objek java. Stored procedure ialah sekumpulan
sintaks sql yang mempunyai 1 buah nama dan dapat dipanggil oleh
program.
Contoh :
String ordernumber;
try {
String query=”{CALL StoredProcSaya (?)}”;
CallableStatement cstatement =Db.prepareCall(query);
sstatement.registerOutParameter(1,Types.VARCHAR();
sstatement.execute();
ordernumber=cstatement.getString(1);
cstatement.close();
24
Displaying database in Applet
At c:\j2se\jre\lib\security\java.policy, please add 2
lines:
grant{
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission
"accessClassInPackage.sun.jdbc.odbc";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "file.encoding",
"read";
};
25
First Sample
Perform query on Books.mdb database
Connect
to database
Query to Table “Authors”
Display results
26
First Sample
Authors table
Four
fields
AuthorID - ID number
FirstName
LastName
YearBorn
AuthorID
1
FirstName
Harvey
LastName
Deitel
YearBorn
1946
2
Paul
Deitel
1968
3
Tem
Nieto
1969
27
1 // Fig. 18.24: TableDisplay.java
2 // This program displays the contents of the Authors table
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// in the Books database.
import java.sql.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
Import the sql package.
10 public class TableDisplay extends JFrame {
Specify url, username, and
11
private Connection connection;
password. The database has
12
private JTable table;
password protection (next
13
section).
14
public TableDisplay()
15
{
16
// The URL specifying the Books database to which
17
18
19
20
21
22
// this program connects using JDBC to connect to a
// Microsoft ODBC database.
String url = "jdbc:odbc:Books";
Load class definition for database driver
String username = "anonymous";
(static method Class.forName).
String password = "guest";
23
24
25
26
27
28
// Load the driver to allow connection to the database
Attempt to connect to
try {
Use static method
Class.forName( "sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver" );
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(
url, username, password );
database.
getConnection, of class
DriverManager (java.sql).
28
29
}
30
31
catch ( ClassNotFoundException cnfex ) {
System.err.println(
32
"Failed to load JDBC/ODBC driver." );
33
cnfex.printStackTrace();
34
35
System.exit( 1 );
}
36
catch ( SQLException sqlex ) {
37
38
System.err.println( "Unable to connect" );
sqlex.printStackTrace();
39
}
40
41
getTable();
42
43
setSize( 450, 150 );
44
show();
45
46
}
47
private void getTable()
48
49
{
50
Statement statement;
ResultSet resultSet;
51
52
53
// terminate program
Create a Statement object that
will query the database.
try {
String query = "SELECT * FROM Authors";
54
55
56
statement = connection.createStatement();
resultSet = statement.executeQuery( query );
Returns a ResultSet object
containing results.
29
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
displayResultSet( resultSet );
statement.close();
}
catch ( SQLException sqlex ) {
sqlex.printStackTrace();
}
statement closed when
not needed.
}
private void displayResultSet( ResultSet rs )
throws SQLException
{
Positions to first record in ResultSet
// position to first record
(initially before first record).
boolean moreRecords = rs.next();
// If there are no records, display a message
if ( ! moreRecords ) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( this,
"ResultSet contained no records" );
setTitle( "No records to display" );
return;
}
Create new Vectors, similar to
dynamic arrays.
setTitle( "Authors table from Books" );
Vector columnHeads = new Vector();
Vector rows = new Vector();
try {
// get column heads
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
Get meta data, which
describes contents of
ResultSet.
30
87
88
for ( int i = 1; i <= rsmd.getColumnCount(); ++i )
89
columnHeads.addElement( rsmd.getColumnName( i ) );
90
91
// get row data
92
do {
93
Get names of column heads,
add to Vector.
rows.addElement( getNextRow( rs, rsmd ) );
94
} while ( rs.next() );
95
96
// display table with ResultSet contents
97
table = new JTable( rows, columnHeads );
98
JScrollPane scroller = new JScrollPane( table );
99
getContentPane().add(
100
scroller, BorderLayout.CENTER );
101
validate();
102
}
103
catch ( SQLException sqlex ) {
104
sqlex.printStackTrace();
105
106
Utility method getNextRow
returns a Vector with row
data. Creates a Vector of
Vectors (like double scripted
array).
Create a JTable, takes
Vector of Vectors and
Vector of column heads.
}
}
107
108
private Vector getNextRow( ResultSet rs,
109
ResultSetMetaData rsmd )
110
111
112
113
throws SQLException
{
Create Vector to hold one row of data.
Vector currentRow = new Vector();
31
114
115
for ( int i = 1; i <= rsmd.getColumnCount(); ++i )
switch( rsmd.getColumnType( i ) ) {
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
case Types.VARCHAR:
currentRow.addElement( rs.getString( i ) );
break;
case Types.INTEGER:
currentRow.addElement(
Test for column type, add appropriate
new Long( rs.getLong( i ) ) );
type of element to Vector.
break;
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
default:
System.out.println( "Type was: " +
rsmd.getColumnTypeName( i ) );
}
130
131
132
133
134
135
public void shutDown()
{
try {
connection.close();
}
136
137
138
139
140
141
}
return currentRow;
catch ( SQLException sqlex ) {
System.err.println( "Unable to disconnect" );
sqlex.printStackTrace();
}
}
32
142
public static void main( String args[] )
143
{
144
final TableDisplay app = new TableDisplay();
145
146
app.addWindowListener(
147
new WindowAdapter() {
148
public void windowClosing( WindowEvent e )
149
{
150
app.shutDown();
151
System.exit( 0 );
152
}
153
}
154
155
);
}
156 }
33
Update Query
For INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE use:
stmt.executeUpdate(“DELETE
YearBorn=1946”);
from Authors where
Bacth Update (JDBC 2.0):
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
con.setAutoCommit(false);
stmt.addBatch("INSERT INTO employees VALUES
(1000, 'Joe Jones')");
stmt.addBatch("INSERT INTO departments VALUES
(260, 'Shoe')");
int [] updateCounts = stmt.executeBatch();
34
Using Transaction
Transaction processing
Changes
can be undone
Interface Connection
Method setAutoCommit
true
- each SQL statements performed individually
false - several statements grouped as a transaction
Terminating Statement that executes SQL statements
Method commit - commit changes to database
Method rollback - return database to previous state
Method getAutoCommit
Returns auto commit state
35
Using Transaction
con.setAutoCommit(false);
PreparedStatement updateSales = con.prepareStatement(
"UPDATE COFFEES SET SALES = ? WHERE COF_NAME LIKE
?");
updateSales.setInt(1, 50);
updateSales.setString(2, "Colombian");
updateSales.executeUpdate();
PreparedStatement updateTotal = con.prepareStatement(
"UPDATE COFFEES SET TOTAL = TOTAL + ? WHERE
COF_NAME LIKE ?");
updateTotal.setInt(1, 50);
updateTotal.setString(2, "Colombian");
updateTotal.executeUpdate();
con.commit();
con.setAutoCommit(true);
36
Database Error Processing
catch (SQLException se)
{
do {
System.out.println (“SQL Error:” +
se.getMessage() + “Code:” + se.getErrorCode()
+ “ SQL State::” + se.getSQLState());
se.getNextException();
} while (se!null);
}
37
References
www.java.sun.com/jdbc
Deithel, “Java How To Program”, 5th ed,
2006
Widodo Budiharto, “Panduan Lengkap
Pemrograman J2EE”, Andi Offset
Yogyakarta, 2006
www.apache.org
www.struts.org
www.netbeans.org
38